Why in News?
- A proposal in this regard was recently sent to the state government by the deputy conservator of forest (wildlife) of the National Chambal Sanctuary project.
About National Chambal Sanctuary:
- National Chambal Sanctuary, also called the National Chambal Gharial Wildlife Sanctuary, is a 5,400 sq . km tri-state protected riverine sanctuary along 425 km length of the Chambal River and ravines.
- Location: It lies at the tri-junction of three states Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan.
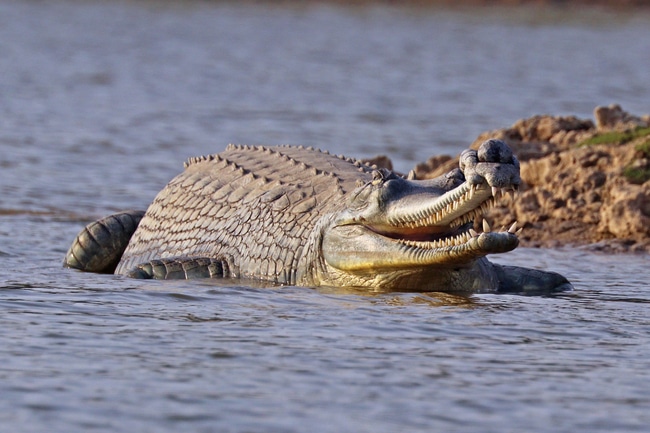
- The main focus of the sanctuary is to protect the critically endangered Gharial, Red-crowned roof turtle & endangered Ganges dolphin.
- Chambal supports the largest population of Gharials in the wild.
- It is listed as an important bird area (IBA).
- Topography: The topography is full of ravines, hills & sandy beaches.
- Vegetation: It is part of the Kathiar-Gir dry deciduous forest ecoregion.
- Other Fauna:
- Other animals which are also in the Threatened category like mugger crocodile, smooth-coated otters, Striped Hyena & Indian wolfs are also found here.
- Chambal River support 8 out of 26 rare species of turtle family like Indian narrow-headed soft shell turtle, three- striped roof turtle & crowned river turtle.
- Mammals are also seen, which include Sambhar deer, Neel Gai (blue bull), Indian gazelle, Rhesus Monkey, Hanuman Langur, Indian grey & small Asian mongoose, Bengal Fox etc.
Key facts about the Chambal River:
- It is one of the tributaries of the Yamuna River and the most pollution-free river in India.
- It originates at the Singar Chouri peak on the northern slopes of the Vindhya mountains.
- On its south, east and west, the basin is bounded by the Vindhyan mountain ranges and on the northwest by the Aravallis.
- The Hadauti plateau in Rajasthan occurs in the upper catchment of the Chambal River to the southeast of the Mewar Plains.
- Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Sipra, Parbati, etc.
- Major Dams on the River: Gandhi Sagar Dam, Rana Pratap Sagar Dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam.
Q1) What are Gharials?
They are fresh-water crocodiles. They live in deep fast-flowing rivers. Compared to alligators and crocodiles, a gharial has a very long and narrow snout (instead of a broad snout). Globally Gharial is found only in India and Nepal. In India too, the major ‘breeding’ populations are confined to two rivers only:
- Girwa : The Girwa River originates in Nepal and runs through Katarniaghat Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Chambal : Chambal supports the largest population of Gharials in the wild.
Source: Uttar Pradesh: Chambal river to have dolphin sanctuary soon
Last updated on December, 2025
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is scheduled to be released on January 14, 2026.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Mains Question Paper 2025 is out for Essay, GS 1, 2, 3 & GS 4.
→ UPSC Mains Indian Language Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Mains Optional Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi