About Ahom Dynasty:
- The Ahom Dynasty (1228–1826, called Kingdom of Assam in medieval times) was a medieval kingdom in the Brahmaputra valley in Assam that maintained its sovereignty for nearly 600 years and successfully resisted Mughal expansion in North-East India.
- It was able to establish its suzerainty over the Brahmaputra valley and had a profound effect on the political and social life in the region.
- The Ahom dynasty was established by Sukaphaa, a Shan prince of Mong Mao who came to Assam after crossing the Patkai Mountains.
- Though it came to be called the Ahom kingdom in the colonial and subsequent times, it was largely multi-ethnic, with the ethnic Ahom people constituting less than 10% of the population toward the end.
- The people of the kingdom used to call them ‘Chaopha’ or ‘Swargadeo’.
- The kingdom came under repeated Mughal attacks in the 17th century, and on one occasion in 1662,the Mughals under Mir Jumla occupied the capital, Garhgaon.
- The Mughals were unable to keep it, and finally, during the battle of Saraighatin 1671, the Ahomsled by Lachit Borphukan successfully defeated the Mughals.
- Borphukan is mainly known for his leadership in this battle.
- By 1682, the Mughal influence in the region was completely eradicated.
- Following a period of confusion, the kingdom got itself the last set of kings, the Tungkhungia kings,established by Gadadhar Singha.
- The kingdom became weaker with the rise of the Moamoria rebellion, and subsequently fell to a succession of Burmese invasions.
- With the defeat of the Burmeseafter the First Anglo-Burmese War and the Treaty of Yandabo in 1826,control of the kingdompassed into British (East India Company) hands.
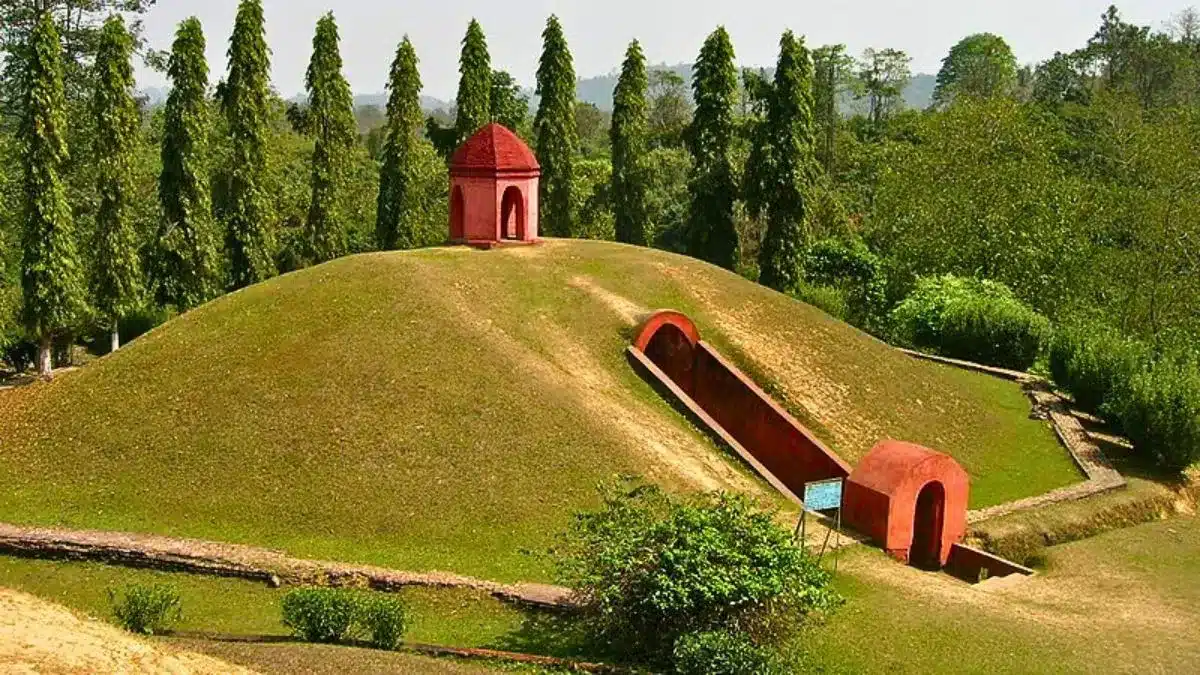
What are Moidams of Ahom dynasty?
- The Moidams (also spelt as Maidam) are burial mounds of Ahom kings, queens, and noblesin Assam.
- The name “Moidam” comes from the Tai words “Phrang-Mai-Dam” or “Mai-Tam,” meaning to bury and the spirit of the dead.
- These mounds are distinct for their architecture and reflect the Ahom’s foreign influences.
- They are found throughout upper Assam, with Charaideo, the first Ahom capital, being the main necropolis.
- Each Moidam has three main parts:
- A vault or chamber where the body is placed.
- A hemispherical earthen mound covering the chamber.
- A brick structure (Chaw-chali) on top for annual offerings and an octagonal boundary wall with an arched gateway.
- Originally, vaults were made of wooden poles and beams but were replaced with stone and brick during the reign of King Rudra Singha (CE 1696-1714).
Inside the vault, the dead were buried with their belongings, including clothes, ornaments, and weapons.
Q1: What is the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)?
It is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It was founded with the mission of contributing to peace and security by promoting international collaboration through education, science and culture.UNESCO cultural conventions and projects provide platforms for international cooperation and establish a holistic cultural governance system based on human rights and shared values. UNESCO has 193 member States and 11 associate members.
Source: UNESCO adds Assam’s Ahom Dynasty Moidams to World Heritage list
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi