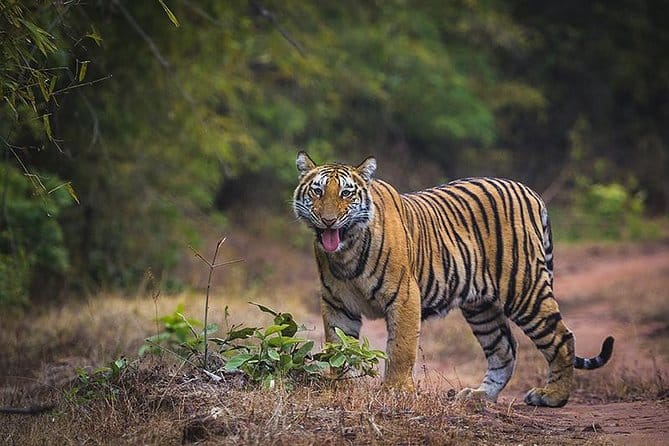
About Bandhavgarh National Park:
- Location:
- It is located in the Umaria district of Madhya Pradesh.
- It is spread over the Vindhya hills.
- It was declared a national park in 1968 and then became Tiger Reserve in 1993.
- It is known for the Royal Bengal Tigers. The density of the tiger population at Bandhavgarh is the highest known in India as well as in the world.
- The park derives its name from the most prominent hillock in the area, which was said to be given by Hindu Lord Rama to his brother Lakshmana to keep a watch on Lanka. Hence the name Bandhavgarh (Sanskrit: Brother’s Fort).
- The national park was the former hunting preserve of the Maharaja of Rewa.
- Topography: Varies between steep ridges, undulating forests and open meadows.
- Vegetation: It is mostly of dry deciduous type.
- Flora:
- The vegetation of Bandhavgarh is specially filled with Sal forest in the valleys, and Bamboo stretches on the lower slopes of the region.
- Some of the most famous floral species include Saj (Terminalia tomentosa), Dhaora (Anogeissus latifolia), Tendu, Arjun (Terminalia arjuna), Amla (Emblica officinalis), Palas (Butea monosperma) etc.
- Fauna:
- The important prey species consists of chital, sambhar, barking deer, nilgai, chinkara, wild pig, chowsingha, langur and rhesus macaque.
- Dependent upon them are the major predators like tiger, leopard, wild dog, wolf and jackal.
Q1) What is a National Park?
National Parks in India are discussed here along with the Wildlife Sanctuaries. These are suitable places for biodiversity conservation. National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries are protected areas declared by Government with the primary objective to preserve wildlife, save flora & fauna and restore the natural ecological balance.
Source: Madhya Pradesh: 2000-year-old modern society unearthed from Bandhavgarh National Park
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi