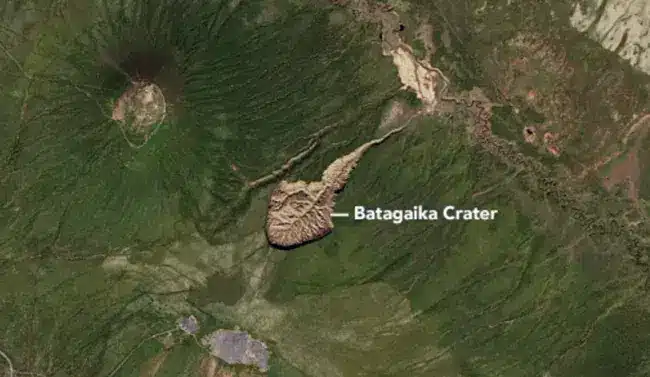
About Batagay Crater:
- It is also called the “gateway to the underworld,” by some locals in Russia’s Sakha Republic.
- Location: It is located in Russia’s Far East that forms the world’s biggest permafrost crater.
- It is a crater or megaslump, features a rounded cliff face that was first spotted on satellite images in 1991 after a section of hillside collapsed in the Yana Uplands of northern Yakutia in Russia.
- Scientists believe that the crater is the result of a melting permafrost land, which was frozen during the Quaternary Ice Age 2.58 million years ago.
What is Permafrost?
- Permafrost is any ground that remains completely frozen—32°F (0°C) or colder—for at least two years straight.
- Global Distribution
- These permanently frozen grounds are most common in regions with high mountains and in Earth’s higher latitudes—near the North and South Poles.
- It covers large regions of the Earth. Almost a quarter of the land area in the Northern Hemisphere has permafrost underneath.
Q1: What is Snowpack?
Snowpack refers to the snow that has fallen on the ground and does not melt for months due to below-freezing temperatures is called a snowpack. Snowpacks can consist of multiple layers of snow, each one from a different snowfall, that become compacted under the weight of the subsequent layers that lie on top.
Source: Gateway to the underworld’ in Siberia is growing at a staggering rate every year: Study
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi