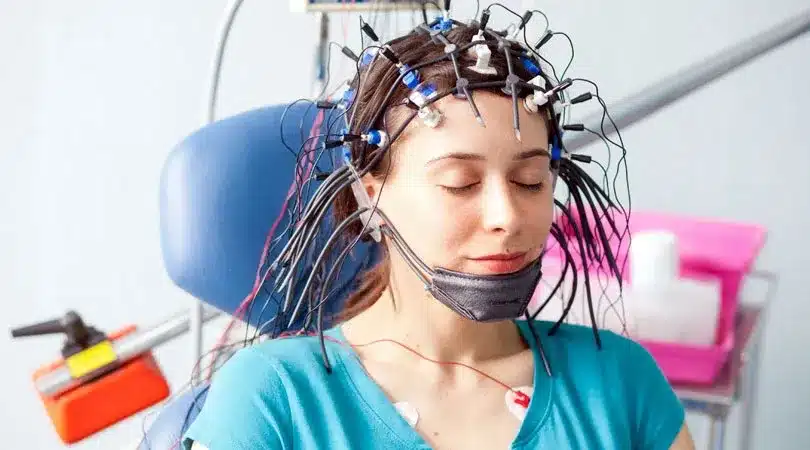
About Electroencephalogram (EEG):
- An EEG is a recording of brain activity.
- It is a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain.
- Procedure:
- The procedure may be short, often just a 30-minute recording.
- During the procedure, electrodes consisting of small metal discs with thin wires are pasted onto your scalp.
- The electrodes detect tiny electrical charges that result from the activity of your brain cells.
- The charges are amplified and appear as a graph on a computer screen or as a recording that may be printed out on paper.
- The EEG procedure is usually carried out by a highly trained specialist, called a clinical neurophysiologist.
- Applications:
- The EEG is used to evaluate several types of brain disorders. Examples:
- When epilepsy is present, seizure activity will appear as rapid spiking waves on the EEG.
- People with lesions of their brain, which can result from tumors or strokes, may have unusually slow EEG waves, depending on the size and location of the lesion.
The EEG may also be used to determine the overall electrical activity of the brain (for example, to evaluate trauma, drug intoxication, or extent of brain damage in comatose patients).
The EEG may also be used to monitor blood flow in the brain during surgical procedures.
Q1: What are electrodes?
An electrode is a solid electric conductor that carries electric current into non-metallic solids, or liquids, or gases, or plasmas, or vacuums. Electrodes are typically good electric conductors, but they need not be metals.
Source: A century after the EEG was discovered, it remains a crucial tool for understanding the brain
Last updated on November, 2025
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is scheduled to be released on January 14, 2026.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Mains Question Paper 2025 is out for Essay, GS 1, 2, 3 & GS 4.
→ UPSC Mains Indian Language Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Mains Optional Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi