About Gulf of Mannar
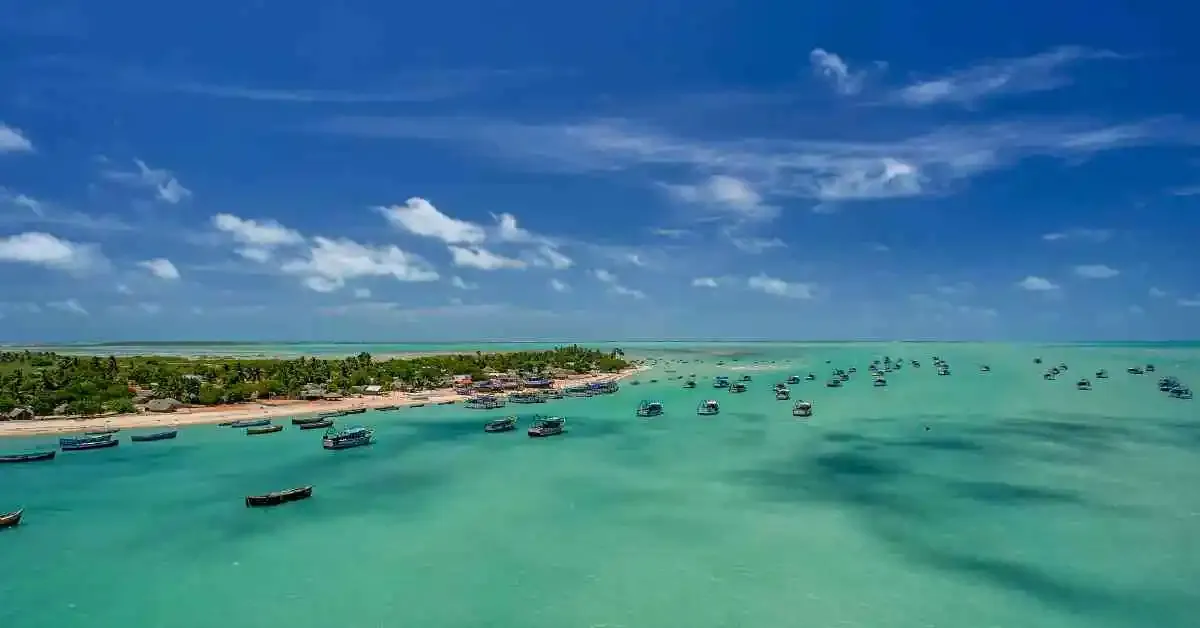
- Along the southeast coast of India lies the Gulf of Mannar, a part of the Laccadive Sea of the Indian Ocean, containing 21 islands.
- It spans a total distance of around 125 miles in breadth and 100 miles in length between the northwest coast of Sri Lanka and the southeast coast of India.
- It is bounded to the northeast by Rameswaram (island), Adam’s (Rama’s) Bridge (a chain of shoals), and Mannar Island.
- It receives several rivers, including the Tambraparni (India) and the Aruvi (Sri Lanka).
- The port of Tuticorin is on the Indian coast. The gulf is noted for its pearl banks and sacred chank (a gastropod mollusk).
Key facts about the Gulf of Mannar Marine National Park
- The Gulf of Mannar is one of the biologically richest coastal regions in all of the mainland of India.
- It is the first Marine Biosphere Reserve in South and South East Asia.
- In India, the Gulf of Mannar region in Tamil Nadu is one of the four major coral reef areas, and the others are the Gulf of Kutch in Gujarat, Lakhsadweep and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- It is designated as a Biosphere Reserve.
- This Biosphere Reserve encompasses a chain of 21 islands (2 islands already submerged) and adjoining coral reefs off the coasts of the Ramanathapuram and Tuticorin districts.
Q1) What is a Gulf?
The Gulf is a portion of the sea that is almost surrounded by land except one narrow opening. Gulfs are formed when a giant rock collapses or when a piece of land sinks. This causes a big indentation in the area, and the water eventually fills it up. Gulfs are also formed through a natural process of erosion.
Last updated on July, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi