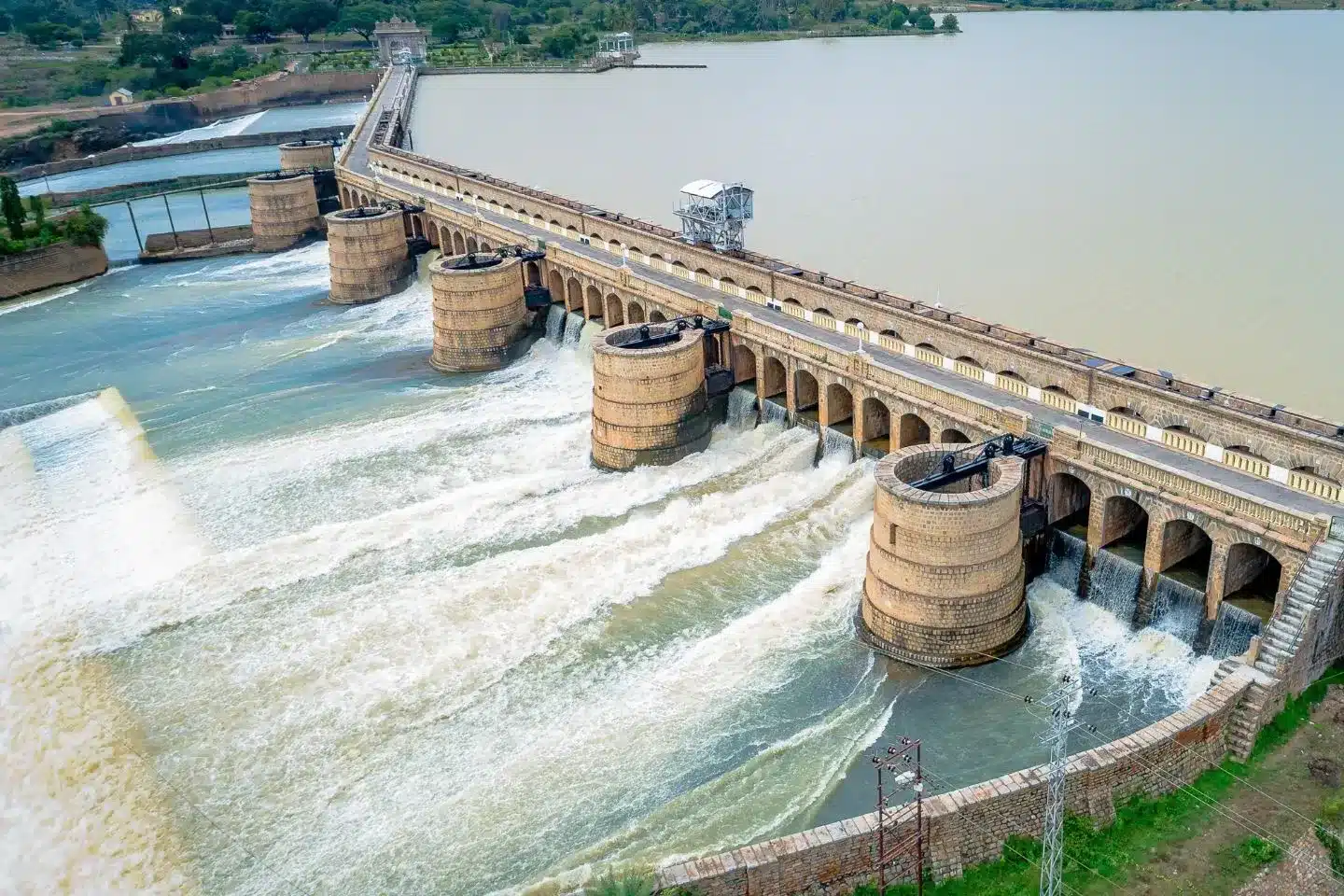
About Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) Dam:
- It is a type of gravity dam.
- Location: It is located below the confluence of river Kaveri with its tributaries, Hemavati and Lakshmana Tirtha, in the district of Mandya in Karnataka.
- Usage:
- The water from the Dam is used for irrigation in Mysore and Mandya and is the main source of drinking water for Mysore, Mandya and Bengaluru city.
- It also ensures power supply to the Shivanasamudra hydroelectric power station.
- The water released from this dam flows into the state of Tamil Nadu and is stored in the Mettur dam in the Salem district.
- History:
- The dam was constructed during the rule of the Maharaja of Mysore, Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV, and it was named in his honor.
- The construction of the KRS Dam began in 1911 and it was completed in 1931.
- The dam was designed by Sir M. Visvesvaraya, a famous Indian engineer.
- Features:
- It was built using a mixture of surki mortar and limestone.
- It is 2,621 meters (8,600 ft) long and 40 meters (130 ft) high.
- It has arch type 177 Iron sluices, and some of them have automatic doors.
- Its reservoir is about 130 Sq. Kms, which was the largest in Asia at the period when it was built.
- Brindavan Gardens, an ornamental garden, is attached to the dam.
Key Facts about Kaveri river:
- Kaveri, also spelt Cauvery, is a sacred river of southern India. It is known as the Ganga of South India.
- Origin: It rises on Brahmagiri Hill of the Western Ghats in southwestern Karnataka state.
- It flows in a southeasterly direction for 765 km through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu and descends the Eastern Ghats in a series of great falls.
- The Cauvery basin extends over the states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala and the Union Territory of Puducherry.
- The river drains into the Bay of Bengal at Poompuhar in the Mayiladuthurai district of Tamil Nadu.
- Major left bank tributaries: Harangi, the Hemavati, the Shimsha and the Arkavati.
- Major right bank tributaries: Lakshmantirtha, the Kabbani, the Suvarnavati, the Bhavani, the Noyil and the Amaravati.
Q1) What is a Gravity Dam?
A gravity dam is a type of dam structure designed to withstand the force of water pressure solely through its weight. It relies on its massive weight and resistance to sliding to hold back the force of the water and maintain stability. Gravity dams are commonly built in locations where there is a solid foundation of bedrock or rock formations that can support their weight effectively.
Last updated on August, 2025
→ UPSC Mains Admit Card 2025 has been released on 14th August at www.upsc.gov.in.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi