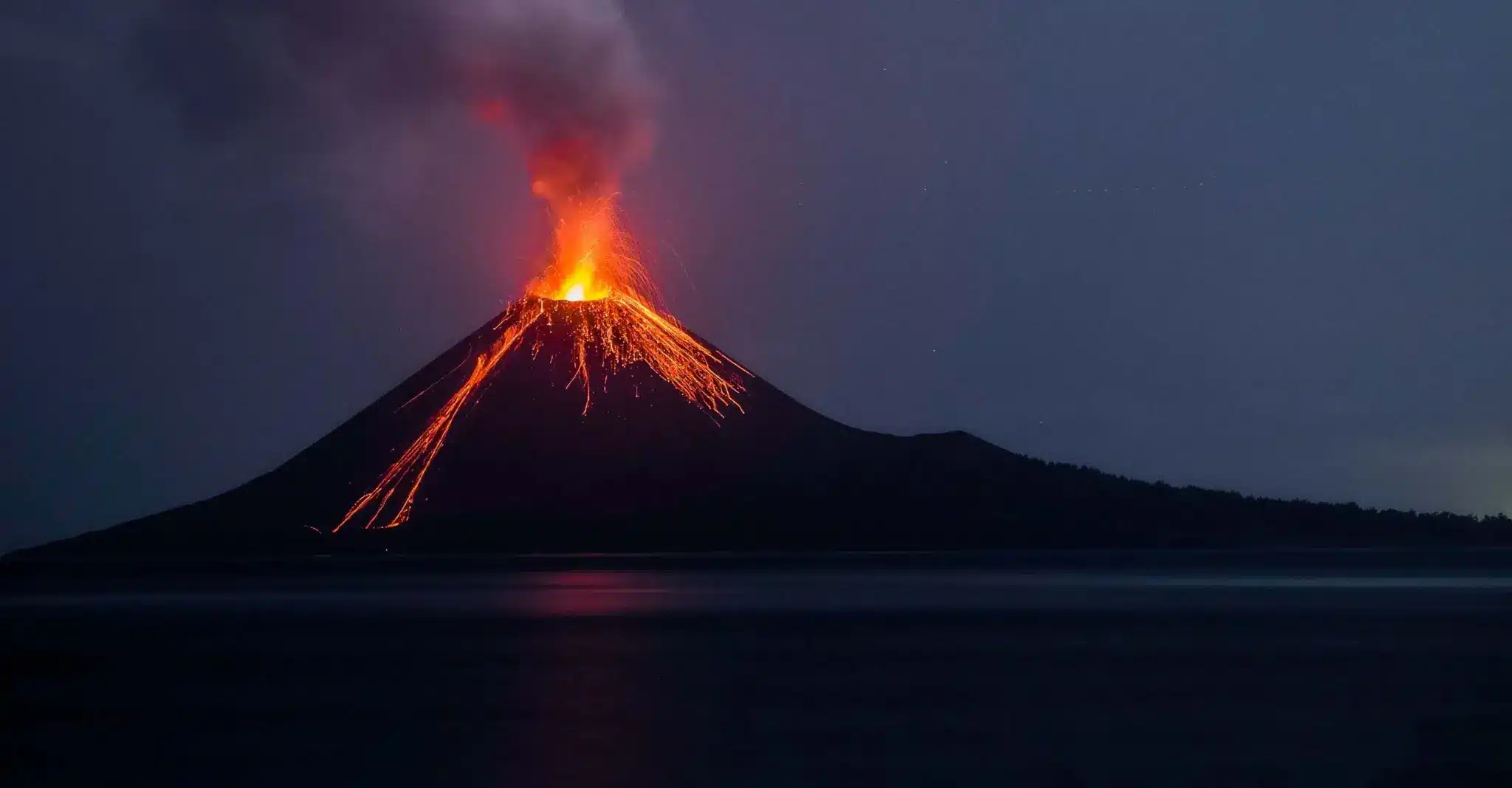
About Mount Ruang
- It is a stratovolcano located in Indonesia’s North Sulawesi province.
- It is a 725-meter (2,400-foot) volcano.
- The summit of Ruang stands 10,932 feet above sea level, with a caldera that is about two miles wide.
What is a Stratovolcano?
- It is a tall, steep, and cone-shaped type of volcano.
- Unlike flat shield volcanoes, they have higher peaks.
- They are typically found above subduction zones, and they are often part of large volcanically active regions, such as the Ring of Fire that frames much of the Pacific Ocean.
- Strato Volcanoes comprise the largest percentage (~60%) of the Earth’s individual volcanoes, and most are characterized by eruptions of andesite and dacite, lavas that are cooler and more viscous than basalt.
- These more viscous lavas allow gas pressures to build up to high levels. Therefore, these volcanoes often suffer explosive eruptions.
- They are usually about half-half lava and pyroclastic material, and the layering of these products gives them their other common name of composite volcanoes.
At the peak, stratovolcanoes usually have a small crater. The crater may be filled with water or ice, or it may contain a volcanic dome during a period of relative inactivity.
Q1: What are Pyroclasts?
Pyroclasts (or “tephra’) are any volcanic fragments that were hurled through the air by volcanic activity. A pyroclastic eruption is one in which the great majority of activity involves fountaining or explosions. A pyroclastic deposit is the resulting layer or pile of material that has fallen to the ground by one or many pyroclastic eruptions. A pyroclastic rock is the hardened, solidified, or compressed version of an originally loose pyroclastic deposit.
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi