About Pompe disease
- It is a rare inherited disorder that affects one child per million.
- Causes
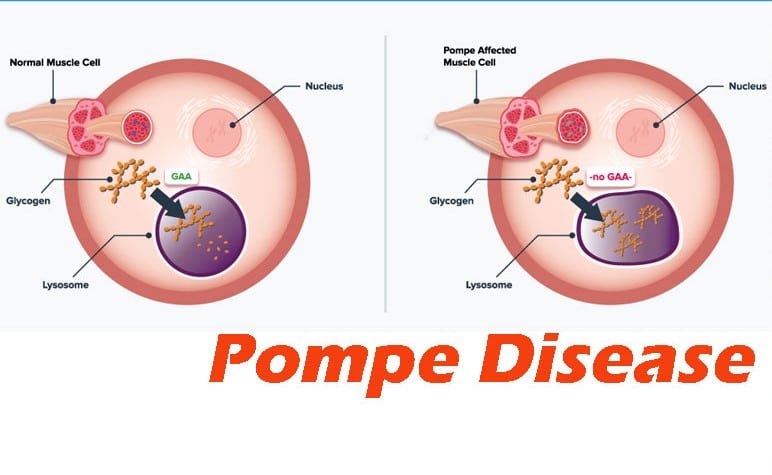
- Mutations in the GAA gene cause Pompe disease.
- The GAA gene provides instructions for producing an enzyme called acid alpha-glucosidase (also known as acid maltase).
- This enzyme is active in lysosomes, which are structures that serve as recycling centers within cells.
- The enzyme normally breaks down glycogen into a simpler sugar called glucose, which is the main energy source for most cells.
- Mutations in the GAA gene prevent acid alpha-glucosidase from breaking down glycogen effectively, which allows this sugar to build up to toxic levels in lysosomes.
- This buildup damages organs and tissues throughout the body, particularly the muscles, leading to the progressive signs and symptoms of Pompe disease.
- Some common side effects and symptoms include muscle weakness, respiratory issues, heart problems and difficulty swallowing.
- This disease can be:
- Infantile-onset: symptoms begin in the first few months after birth.
- Late-onset or delayed-onset: symptoms appear later in childhood or in adulthood.
- It affects males and females equally.
- Treatment: The treatment includes enzyme replacement therapy (ERT).
Q1) What is enzyme?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst and is almost always a protein. It speeds up the rate of a specific chemical reaction in the cell. The enzyme is not destroyed during the reaction and is used over and over.
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi