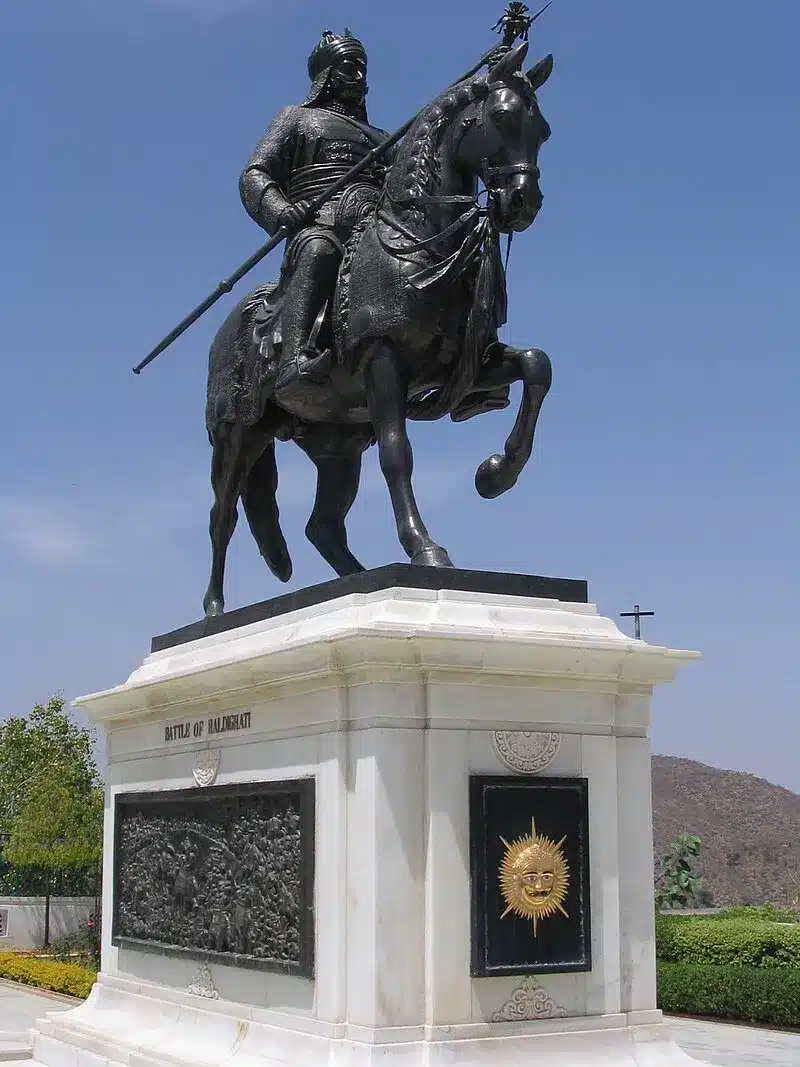
Battle of Haldighati, which took place on June 18, 1576, was fought between Maharana Pratap and the Mughal forces of Akbar led by Raja Man Singh I. Despite Akbar's diplomatic efforts, Maharana Pratap refused to submit to Mughal rule, fearing independence of Mewar and Rajput honor. The Mughal army, with more troops and resources, faced a brave Rajput army led by Maharana Pratap.
The Battle of Haldighati was indecisive, and the Mughals claimed tactical victory and secured the trade route from Gujarat to Mewar. However, it did not break Maharana Pratap's spirit, and he continued to resist Mughal control through guerrilla warfare. The battle is remembered for Maharana Pratap's bravery and determination, as demonstrated by his resistance to the Mughal Empire.

Battle of Haldighati Overview
Battle of Haldighati was fought on 18 June 1576 between the ruler of Mewar, Maharana Pratap Singh, and Mughal forces led by Raja Man Singh I of Amber. The battle was fought at Rajasthan's Haldighati Pass, a section of the Aravalli mountain range that connects the districts of Pali and Rajsamand.
- The Mughals had a force of approximately 28000 troops, while Mewar had a cavalry of about 4000 along with 3000 Bhil tribesmen.
- The battle, despite not being won by either side, symbolized Rajputana's valor and the ongoing struggle for sovereignty against the expanding Mughal Empire.
Battle of Haldighati Background
Battle of Haldighati was fought in the background of Akbar assuming the throne and attempting to usurp all the Rajput Kingdoms under his control. The developments which led to the Battle of Haldighati are discussed in detail below:
- Akbar’s Strategy: Emperor Akbar forged a strong alliance with most Rajput Kingdoms except Mewar, a prominent state in Rajasthan.
- Siege of Chittorgarh: The Rana of Mewar, Udai Singh II, refused to submit to the Mughal Emperor Akbar, leading to the Siege of Chittorgarh in 1568, resulting in the loss of a significant portion of Mewar to the Mughals.
- Maharana Pratap's succession: When Maharana Pratap inherited the throne of Mewar from his father, Udai Singh II, in 1572, Akbar dispatched several diplomatic missions to persuade Maharana Pratap to support Mughal rule by becoming an ally and resolving the ongoing conflict between the Mughals and the Rajput Kingdoms.
- Failure of Diplomatic missions: All diplomatic missions of Akbar under Jalal Khan Qurchi, Man Singh of Amber, Raja Bhagwant Das, and Todar Mal failed, leading to the Battle of Haldighati.
Causes of the Battle of Haldighati
Battle of Haldighati happened due to several reasons. The reasons include the rejection of Mughal authority by Maharana Pratap, the failure of Akbar’s diplomatic missions, a lucrative trade route along Mewar, historically hostile relations between Rajputs and Mughals, etc.
- Rejection of Mughal Authority: The primary cause of the Battle of Haldighati was Maharana Pratap's rejection of the Mughal Emperor Akbar’s authority. Akbar sought to consolidate Mughal authority by bringing all Rajput states under control.
- Failure of Diplomatic Missions: Akbar attempted to make Mewar a tributary state of the Mughal Empire, but Maharana Pratap rejected these offers, viewing them as a compromise on Rajput's dignity and a threat to Mewar's sovereignty.
- Lucrative Trade Route: Akbar was determined to establish an essential and stable trade route to Gujarat from Mewar, but Maharana Pratap refused to sign a treaty.
- Hostile Relations: The relationship between the Mughals and Maharana Pratap was already strained as a result of previous battles, such as Akbar's Siege of Chittorgarh in 1568.
Battle of Haldighati Events
Battle of Haldighati was fought on 18 June 1576 between Maharana Pratap’s Mewar forces and the Mughal army led by Man Singh I. The battle symbolized bravery, determination, valor, and strategic retreats. It was a turning point in Mughal-Rajput history. The various events can be summarized as follows:
- Mughal’s Planned move: Under the command of Man Singh, the Mughal army moved in a planned direction towards Mewar’s soldiers who were preparing defenses at Gogunda, close to Haldighati.
- The Mughals had almost 28000 troops consisting of 16000 cavalry, 8000 infantry, an elephant corps, and guns.
- Composition of Mahrana’s Force: Maharana Pratap had a smaller force but was strengthened by 3000-4000 Rajput cavalry, a few elephants, and about 3000 Bhil tribal men without any guns or muskets.
- Maharana’s van also consisted of the Afghan contingent led by Hakim Khan Sur.
- Guerilla tactics of Mahrana: Maharana Pratap’s army's fierce attack initially led many Mughal soldiers to flee the battlefield. The Rajputs took advantage of the rugged terrain and used successful guerilla tactics.
- Strategic Retreat & Continued assault: Although fighting bravely with the Mughal forces, Maharana Pratap's army was outnumbered by the Mughal army. As casualties rose, Maharana Pratap strategically retreated to prevent further losses.
Battle of Haldighati Why in Haldighati?
Haldighati got its name because of the rocks it had that gave a yellowish colour similar to haldi (turmeric) when crushed. The pass had hilly terrain, thorny bushes, and several trees, which provided necessary cover for Maharana Pratap’s soldiers. This area gave Maharana Pratap’s army a tactical edge over the Mughal army. The area of Haldighati also offered an easy exit for Maharana Pratap’s army in case of defeat.
Battle of Haldighati Outcome
The Battle of Haldighati failed to break the stalemate between Akbar and Rana Pratap, prompting Rana Pratap to retreat into the southern Mewar hills. This secured the Mughal Empire's vital route from Mewar to Gujarat. Akbar expected to capture or kill Maharana Pratap during the battle, but Maharana Pratap's heroic escape won the hearts of all his followers. The Battle of Haldighati was not a great victory for Akbar because Maharana Pratap continued to fight valiantly, and Akbar had to launch several additional campaigns to defeat him but failed.
Battle of Haldighati Significance
The Battle of Haldighati signifies the glorious saga of Rajput valor and the spirit of sacrifice for cherished principles. It also reflects the will of the Rajput rulers to fight foreign subjugation and maintain their independence. The battle highlighted the effectiveness of guerilla warfare as a strategy to resist a powerful enemy. Shivaji and the Deccani General, Malik Ambar, later developed Maharana Pratap’s method of intermittent warfare.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Battle of Haldighati FAQs
Q1. What was the Battle of Haldighati?+
Q2. What is the significance of the Battle of Haldighati?+
Q3. Who won the Battle of Haldighati?+
Q4. Who led the Mughal forces in the Battle of Haldighati?+
Q5. How did the Battle of Haldighati impact Mewar?+