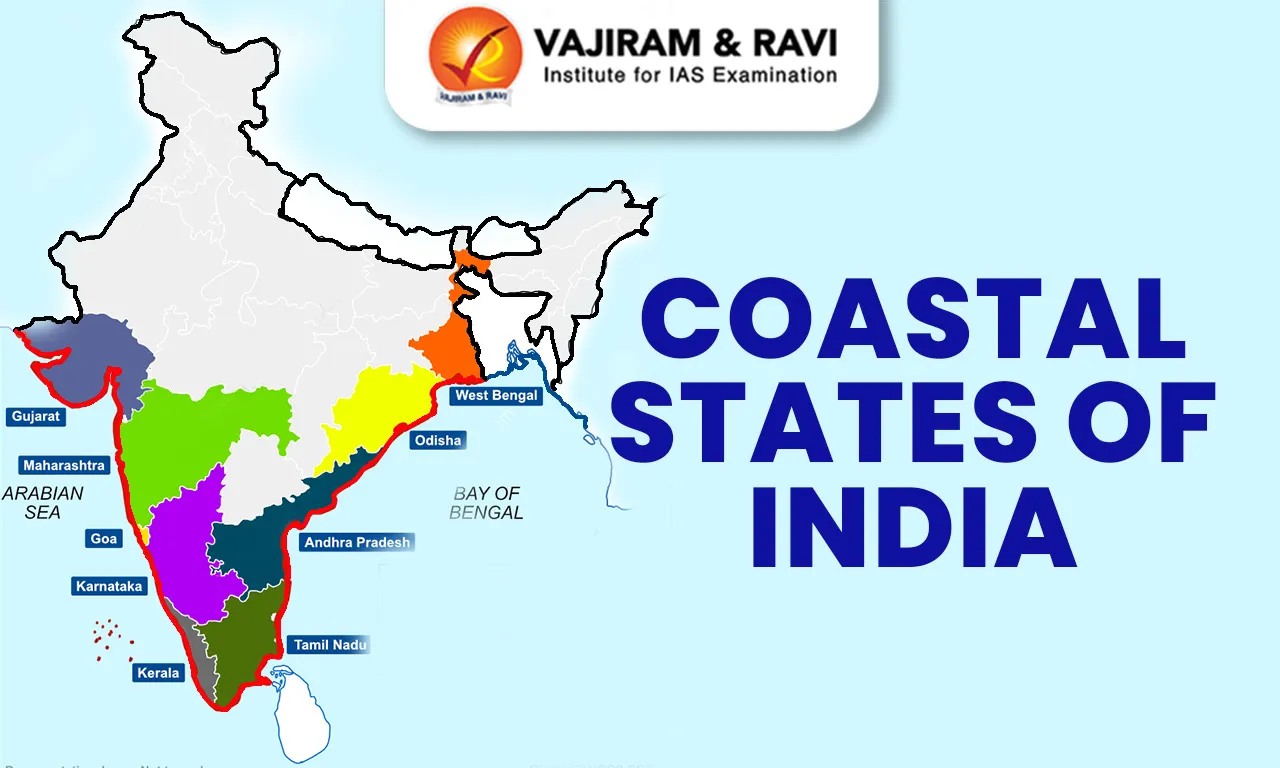
The coastal states of India include Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, West Bengal, Goa, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha. The coastal union territories are Daman & Diu, Puducherry, Lakshadweep Islands, and Andaman & Nicobar Islands. India’s extensive coastline, measuring 7,516.6 km, includes 5,422 km of mainland coastline and 2,094 km belonging to island territories.
This coastline spans 9 states and 4 union territories, bordered by the Arabian Sea and Indian Ocean on the west and the Bay of Bengal on the east. Among the coastal states, Gujarat has the longest coastline, while Andaman & Nicobar Islands lead among union territories.
Coastal States in India Features
India's coastline is geographically diverse, featuring extensive coastal plains, sandy beaches, rocky shores, mangrove forests, and fertile deltas nourished by prominent rivers such as the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri. It serves as a significant ecological zone supporting marine life, ecosystems and Economic activities like fishing, tourism, and port-based trade.
East Coast of India
The Eastern Coast is characterised by plains that are expansive and flat along the Bay of Bengal. Compared to the western coast, the eastern coastal plain is wider and is considered an emergent coast.
- Divisions: The Northern Circar refers to the northern part of this coastline, while the southern section is known as the Coromandel Coast.
- Delta: The eastern rivers, such as the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri, create extensive deltas along the coastline.
- Ports: Due to its emergent nature, the eastern coast has fewer ports and harbours in comparison to the western coast.
- Continental shelf: It extends up to 500 kilometres, presenting challenges in the development of major ports and harbours.
- Monazite, a mineral-rich in rare earth and thorium, is primarily found in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, and inland areas of Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Tamil Nadu.
West Coast of India
The Western Coastal Plains stretch from Gujarat in the north to Kerala in the south, passing through Maharashtra, Goa, and Karnataka. These plains are narrower and more rugged than the eastern plains. Key features:
- This coastal region is a submerged coastal plain, which influences its geography.
- The width of the plains narrows in the centre and widens towards the northern and southern ends.
- Rivers flowing through this region do not form deltas, unlike other plains.
- Due to submergence, the coast provides ideal natural conditions for developing ports and harbours.
Eastern Coastal States of India
The Eastern Coastal Plains stretch from West Bengal in the north to Tamil Nadu in the south, encompassing Odisha and Andhra Pradesh. These plains are wider and flatter than their western counterparts.
| West Bengal |
|
| Odisha |
|
| Andhra Pradesh |
|
| Tamil Nadu |
|
Western Coastal States of India
The Western Coastal Plains stretch from Gujarat in the north to Kerala in the south, passing through Maharashtra, Goa, and Karnataka. These plains are narrower and more rugged than the eastern plains. It is roughly divided into Kachchh and Kathiawar Coast, Konkan Coast, Malabar Coast.
| Gujarat |
|
| Maharashtra |
|
| Goa |
|
| Karnataka |
|
| Kerala |
|
The Islands of India
India is home to two major island groups, situated in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea, which add significant strategic and ecological value to the country. Key island groups:
- Bay of Bengal Islands: This group consists of around 572 islands and islets.
- Arabian Sea Islands: These include the Lakshadweep Islands and Minicoy.
- Classification of islands: India’s islands are broadly divided into Andaman & Nicobar Islands (Bay of Bengal) and Lakshadweep Islands (Arabian Sea).
| Andaman & Nicobar Islands |
|
| Lakshadweep Islands |
|
Coastal Regions in India Geomorphology
The coastal regions of India exhibit diverse geomorphological features influenced by a combination of geographical, geological, and climatic factors. These characteristics vary significantly between the eastern and western coasts of India.
- Physiography of the Indian Coastline (Mainland): The physiography of India’s mainland coastline comprises various geomorphic features: Sandy Beaches: 43%, Muddy Flats: 36%, Rocky Coasts: 11%, Marshy Coasts: 10%.
- Additionally, 1821.7 kilometres (33.6%) of the mainland coastline is currently affected by erosion.
- Coastal Statistics:
- Total Length of Coastline: 7,516.60 km
- Total Land Area: 3,287,263 km2.
- Continental Shelf Area: 372,424 km2.
- Territorial Sea Area (up to 12 nautical miles): 193,834 km2
- Population in Coastal States and Union Territories: Approximately 560 million.
Difference Between Eastern and Western Coastal States of India
The coastal states of India are divided into two regions: the Eastern Coastal States along the Bay of Bengal and the Western Coastal States along the Arabian Sea. Following is the comparison highlighting their distinctions:
| Feature | Eastern Coastal States | Western Coastal States |
| Location | Along the Bay of Bengal | Along the Arabian Sea |
| Characteristics | Longer coastline with broader plains | Shorter coastline with narrower plains |
| Major rivers inflow | Ganges, Brahmaputra, Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna | Narmada, Tapti, Mandovi, Zuari, Godavari |
| Delta | Prominent deltas | Less prominent deltas |
| Climatic influence | Dominated by the Bay of Bengal | Regulated by the Arabian Sea and Western Ghats |
| Biodiversity | Includes Sundarbans mangrove forests and diverse flora and fauna | Features the Western Ghats biodiversity hotspot with rich ecosystems |
Coastal States of India UPSC PYQs
Question 1: Comment on the resource potentials of the long coastlines of India and highlight the status of natural hazard preparedness in these areas. (UPSC Mains 2023)
Question 2: With reference to India, consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2022)
- Monazite is a source of rare earths.
- Monazite contains thorium.
- Monazite occurs naturally in the entire Indian coastal sands in India.
- In India, Government bodies only can process or export monazite.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, and 3 only
(b) 1, 2, and 4 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b)
Question 3: Consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2018)
- The Barren Island volcano is an active volcano located in the Indian territory.
- Barren Island lies about 140 km east of Great Nicobar.
- The last time the Barren Island volcano erupted was in 1991, and it has remained inactive since then.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3
Answer: (a)
Question 4: Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the 'Ten Degree Channel'? (UPSC Prelims 2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Answer: (a)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Coastal States of India FAQs
Q1. What are the 9 coastal states of India?+
Q2. What are the 4 coasts of India?+
Q3. Which is the largest coastal state in India?+
Q4. How many states have coastlines?+
Q5. Which state has the smallest coastline in India?+
Tags: coastal states of india quest