Gobar Dhan Scheme or Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources Dhan Scheme (GOBARdhan), launched in 2018, is an umbrella initiative aimed at converting waste to wealth and promoting a circular economy. GOBARdhan scheme encompasses a wide range of schemes and policies to facilitate the conversion of organic waste such as cattle dung and agricultural residues into biogas, Compressed Bio Gas and Bio-CNG (Compressed Natural Gas).
The Gobar dhan scheme promises effective waste management, employment generation, and reduction of fossil fuel import. Thus, Gobar Dhan scheme has the potential to contribute to India’s Net-Zero targets.
About Gobar Dhan Scheme
GOBAR Dhan, Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources- Dhan is a scheme to improve village cleanliness and generate wealth and energy from cattle and organic waste. It was launched in 2018 as part of the Biodegradable Waste Management component under Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen). It aims to improve village cleanliness, increase rural household income, and generate energy and organic manure from cattle waste.
Gobar Dhan Scheme Ministry
Gobar dhan scheme (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources- Dhan) is under the nodal Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
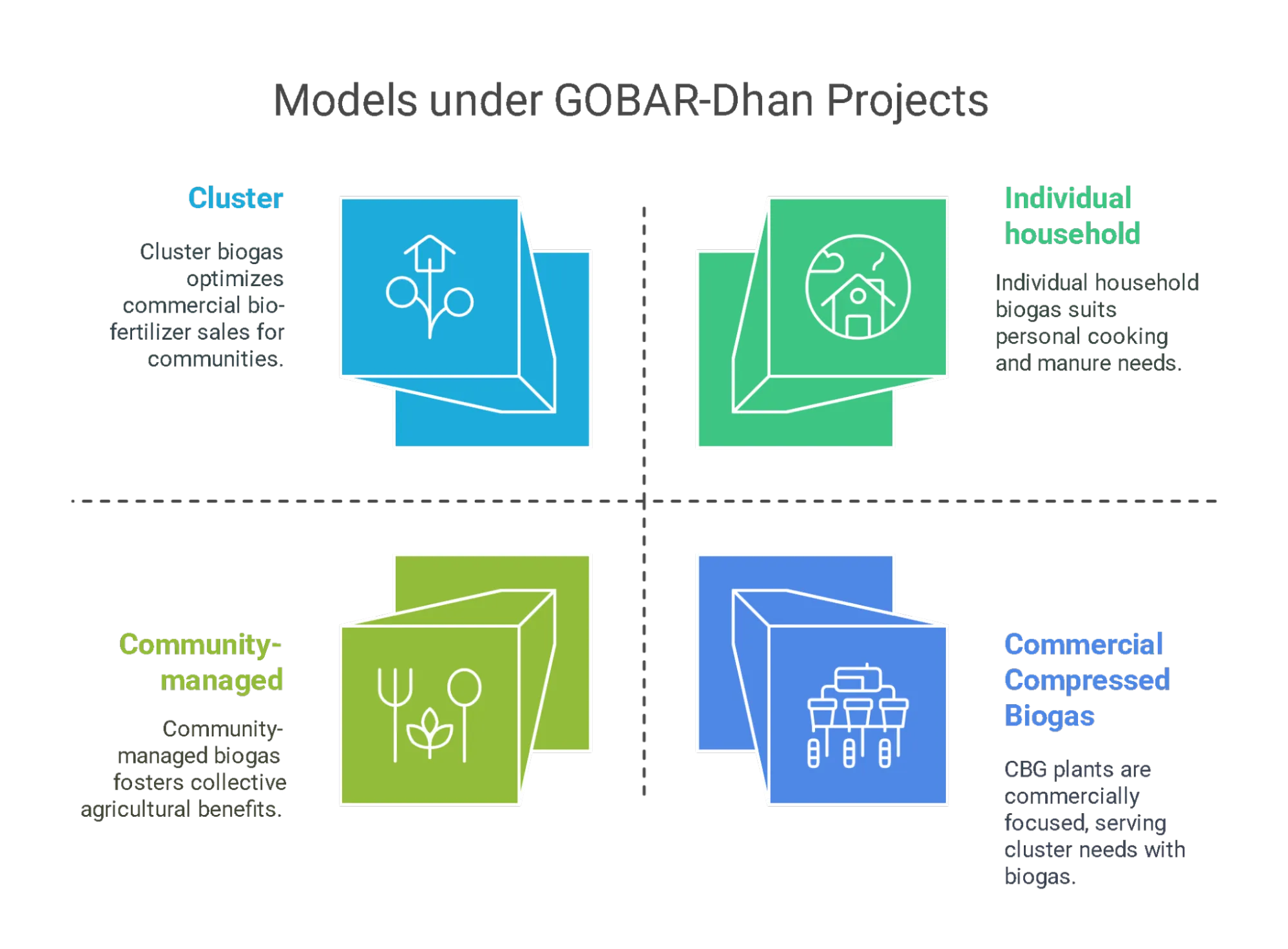
Gobar dhan Scheme Models
Gobar dhan Scheme has various models under it for the development of Biogas plants. The models include Individual, Cluster, community-managed, and commercial plants. The various models are discussed in detail below:
- Individual Household: This model is suitable for households with three or more cattle, where biogas and slurry from plants are used for cooking and as manure.
- Community: Biogas plants can be constructed for a minimum of five to ten households, operated and managed by Gram Panchayats/Self Help Groups.
- The gas generated is supplied to households, restaurants, and institutions, while slurry can be used as organic manure or sold to farmers.
- Cluster: This model involves installing biogas plants in individuals' households within a village or group of villages.
- The biogas produced by households is used, and the resulting slurry is collected, separated into solid and liquid parts, fortified, and sold as bio-fertilizers.
- Commercial Compressed Biogas (CBG): CBG plants can be established by entrepreneurs, cooperative societies, or Gaushalas, producing compressed raw biogas for vehicular fuel or industries and converting slurry into organic manure or bio-fertilizer for farmers.
Gobar dhan Scheme Objectives
Gobar dhan scheme was launched to utilize cattle and agricultural waste. Other objectives include Waste-to-Wealth conversion, disease prevention, farm input generation, etc. The objectives of Gobardhan are as follows:
- Waste Management: To help villages safely manage cattle waste, agricultural waste, and organic waste over time.
- Waste-to-Wealth: To assist communities in converting cattle and organic waste into wealth through decentralized systems.
- Disease Prevention: To improve environmental sanitation and prevent vector-borne diseases in rural areas, waste should be disposed of properly.
- Farm input generation: To convert organic waste, particularly cattle waste, into biogas and fertilizer for rural areas.
- Rural entrepreneurship: To promote rural entrepreneurship by involving entrepreneurs, Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Youth Groups in the setting up, operation, and management of biogas plants
Gobar dhan Scheme Need
Gobar dhan scheme is needed because in rural India, bio-waste is often burned or used inefficiently, posing environmental and public health risks. Gobar dhan’s implementation aims to increase community awareness and ownership while also assisting villages in managing organic waste, such as cattle dung and agricultural residues.
Gobar dhan Scheme Guiding Principles
Gobar dhan scheme aims to utilize animal dung in villages through grassroots efforts. The community will lead the planning, implementation, and management of the Gobar-Dhan scheme. The guiding principles of Gobar dhan scheme are discussed below:
- Role of Administration: The State, District, and Block administration should promote the safe management of cattle dung and organic waste to raise awareness of the Gobar dhan initiative among rural communities.
- Infrastructure: Gobar dhan infrastructure would be community-owned, operated, and managed.
- Financial support: Villages with a high cattle population would be given priority in financial support. The available financial resources will be optimally utilized to benefit all households.
- Intensive IEC: Intensive Information, Education, and Communication (IEC) at the local level must be done to promote the benefits of Gobar dhan and encourage community action.
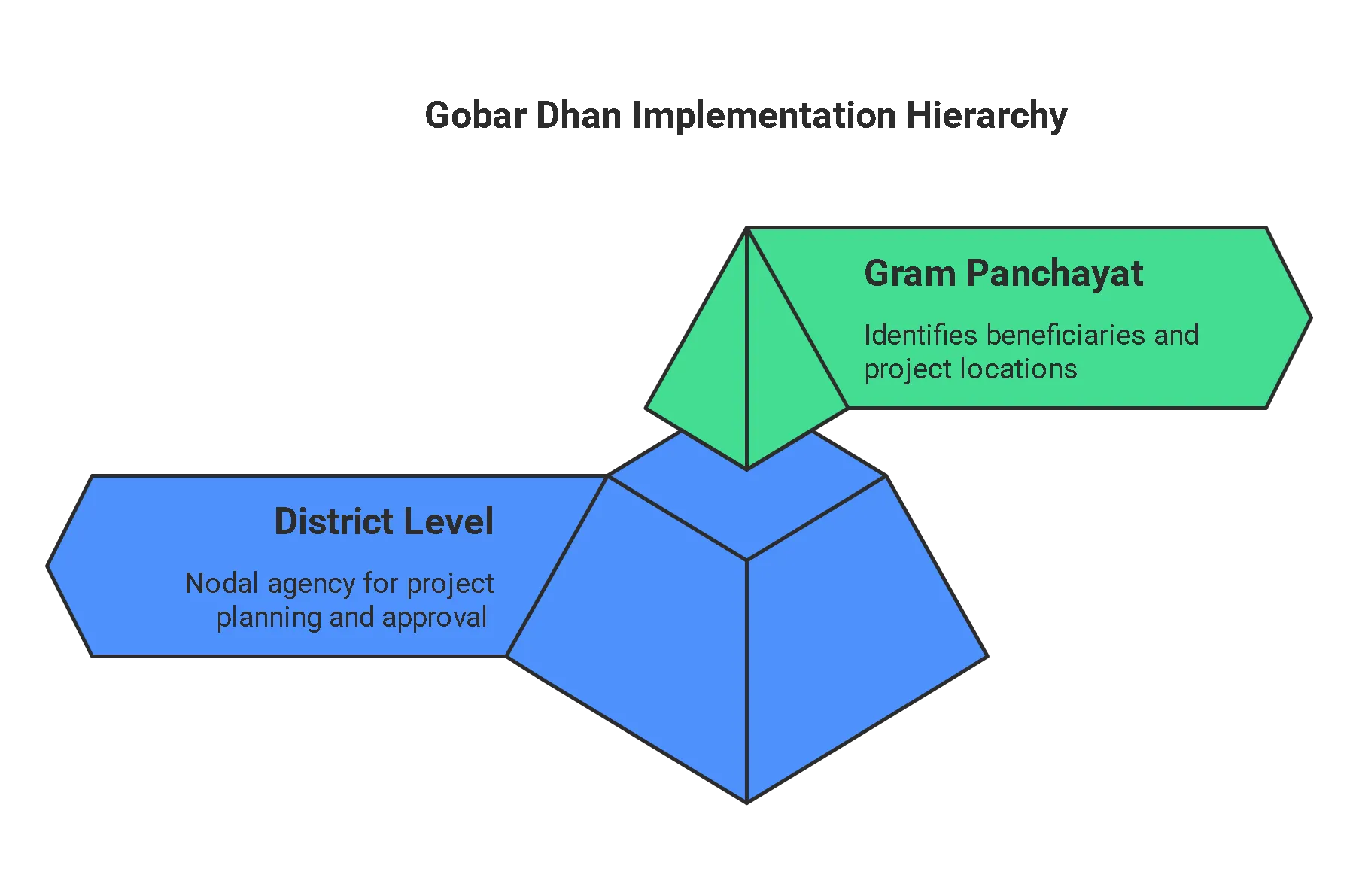
Gobar dhan Scheme Implementation
Gobar dhan scheme is implemented by the State/Union Territories in coordination with the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS). DDWS also provides financial support to the States/Union Territories for implementation of Gobar dhan projects under Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen).
Gobar dhan Scheme Benefits
Gobar dhan scheme helps support the circular economy and promote sustainable growth. The scheme provides diverse benefits, including public health protection, increased public savings, employment generation, improved productivity, and more. The benefits of the scheme are as follows:
- Environmentally Friendly: Gobar dhan effectively manages solid waste in villages, including cattle dung and agricultural waste, while also promoting environmental sanitation.
- Protects Public Health: Provides public health protection by substantially reducing vector-borne diseases.
- Increases Savings: Promotes biogas use, which increases household income and saves money on Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
- Improves productivity: The scheme helps in producing organic manure, which increases agricultural productivity.
- Employment Generation: It promotes job and income opportunities for Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and farmers.
- Reduces Carbon emissions: It also helps to reduce carbon footprint while promoting environmental sustainability.
- Forex Reserves Improve: It will indirectly boost forex reserves by reducing the import of natural gas.
Gobar dhan Scheme Challenges
Gobar dhan scheme, aimed at transforming organic waste into valuable resources, faces several challenges, such as lack of feedstock, delay in identification of biogas plant site, vagaries of monsoon, and lack of awareness, among others. The details are discussed below:
- Feedstock Supply: A Continuous supply of cattle waste to run the Gobar dhan biogas plant remains a challenge.
- Site identification: Finding a Suitable location and land acquisition for the biogas plant is difficult.
- Timely waste processing: It becomes challenging to timely process the waste in the monsoon season for the biogas plant and other use cases.
- Awareness & Education: Lack of awareness among farmers about the benefits of the scheme and resources provided by it.
Gobar dhan Scheme Way Forward
Gobar dhan scheme has the potential to substantially contribute towards India’s Net-Zero emission targets. The need is to provide timely financial support, infrastructure development in villages, capacity building of farmers and awareness generation through Gram Panchayats for increased adoption of the scheme. The Gobar dhan scheme can play a crucial role in India’s transition towards clean energy and contribute to the Government of India’s Mission LiFE.
Gobar dhan Scheme UPSC PYQs
Q.1 Do you think India will meet 50 percent of its energy needs from renewable energy by 2030? Justify your answer. How will the shift of subsidies from fossil fuels to renewables help achieve the above objective? Explain. (UPSC Mains 2022)
Q.2 Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (UPSC Mains 2018)
Q.3 Write a note on India’s green energy corridor to alleviate the problems of conventional energy. (UPSC Mains 2013)
Q.4 In the context of which one of the following are the terms ‘pyrolysis and plasma gasification’ mentioned? (UPSC Prelims 2019)
(a) Extraction of rare earth elements
(b) Natural gas extraction technologies
(c) Hydrogen fuel-based automobiles
(d) Waste-to-energy technologies
Ans: (d)
Q.5 Consider the following: (UPSC Prelims 2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into the atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the second week of April 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Gobar dhan Scheme FAQs
Q1. Which ministry is responsible for GOBARdhan scheme?+
Q2. What is the Gobar Dhan scheme?+
Q3. What is the full form of GOBARdhan?+
Q4. What are the benefits of GOBARdhan?+
Q5. Who are eligible for gobardhan scheme?+