Indus Water Treaty, signed in 1960, divides the Indus River system between India and Pakistan. Pakistan controls the Western rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab), while India controls the Eastern rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej). The treaty includes a Permanent Indus Commission and a three-tier dispute resolution mechanism.
Recently, India suspended the treaty following the Pahalgam attack in April 2025, affecting Pakistan's vital water supply for agriculture and urban areas. This suspension has granted India greater control over the Western rivers, enabling increased hydropower generation and improved flood management. The shift in water dynamics has heightened tensions and reshaped regional geopolitics, further impacting Indo-Pakistani relations.
Also Read: Pahalgam Terror Attack
Indus Water Treaty Overview
Indus Water Treaty is a landmark water-sharing agreement between India and Pakistan, established to govern the use of water from the Indus River system. Signed in Karachi in 1960 and mediated by the World Bank, the treaty allocates the usage of six rivers—three to India and three to Pakistan—ensuring equitable distribution for agricultural, domestic, and industrial purposes.
Indus Water Treaty River Distribution
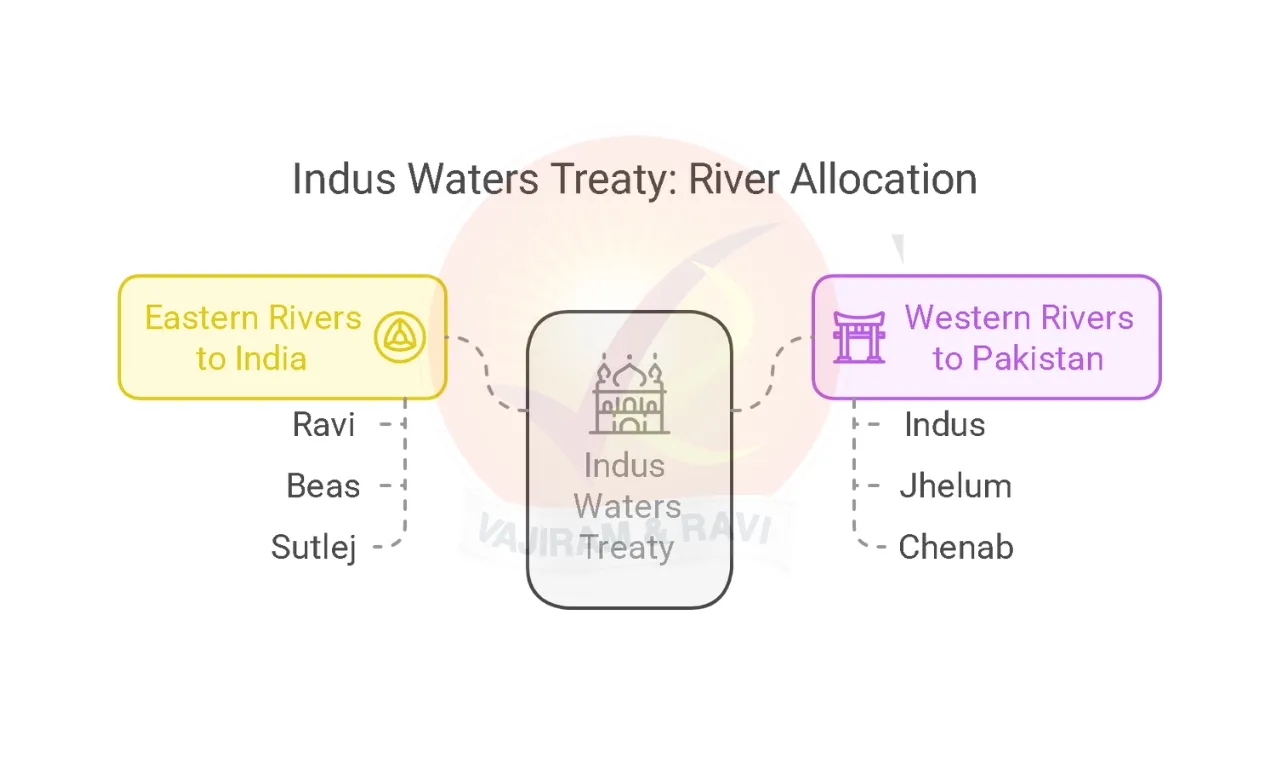
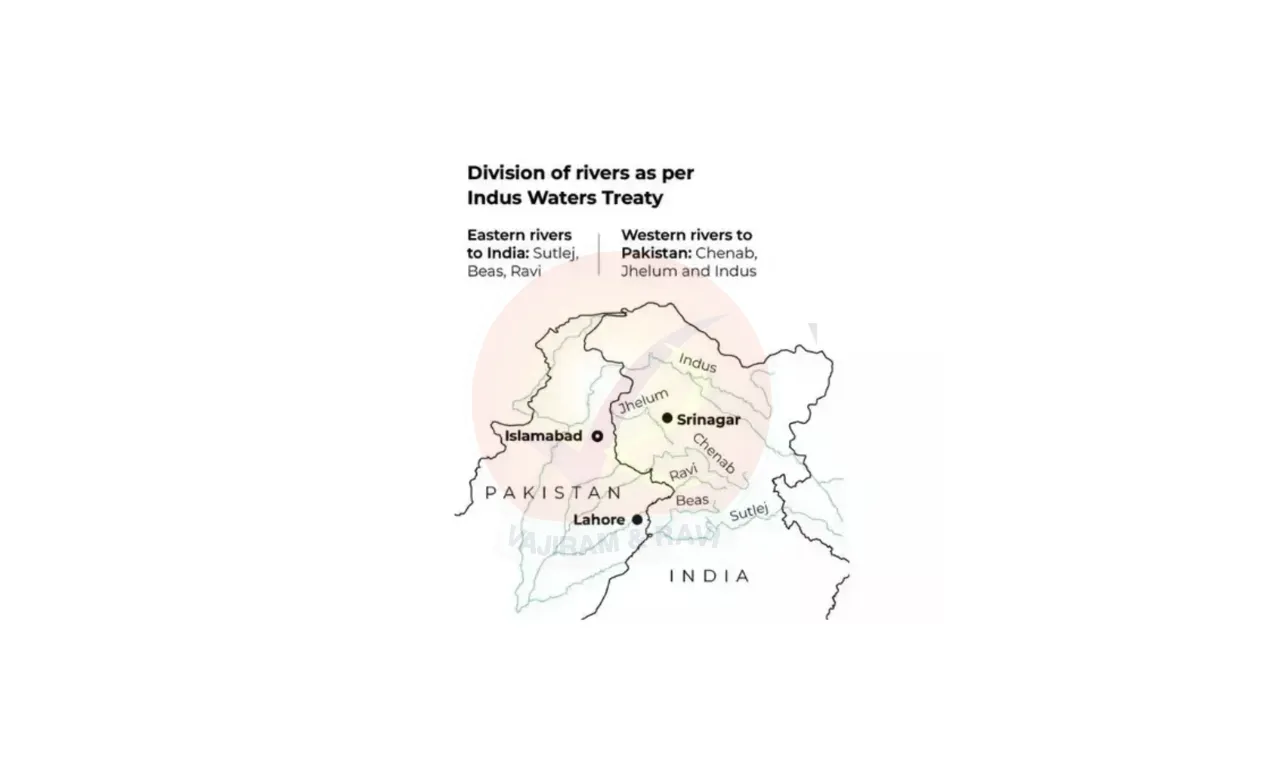
Indus Water Treaty River Distribution is done to ensure a fair division of river water and ensure peaceful cooperation among the neighbors. The Indus Water Treaty ensures a sustainable water division between India and Pakistan by allocating the Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) to Pakistan and the Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) to India.
Indus Water Treaty History
The History of the Indus Water Treaty goes back to the time of India’s Independence when the boundary line between Pakistan and India was being drawn. The details are mentioned below:
- Drawing of Boundaries: During the time of India’s independence, the boundary line between Pakistan and India was drawn across the Indus Basin, leaving Pakistan as the lower riparian.
- Beginning of conflict: Post partition, two crucial irrigation head works in Madhopur and Ferozepur, which were dependent on Punjab's irrigation canal supplies, were left in the Indian Territory, leading to a dispute over water usage.
- Mediation by World Bank: The negotiations with the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (World Bank) led to the signing of the Indus Waters Treaty in 1960.
- Signing of Treaty: The treaty was signed by Mohammad Ayub Khan of Pakistan, Jawaharlal Nehru, and W.A.B. Iliff of the World Bank and is effective from April 1, 1960.
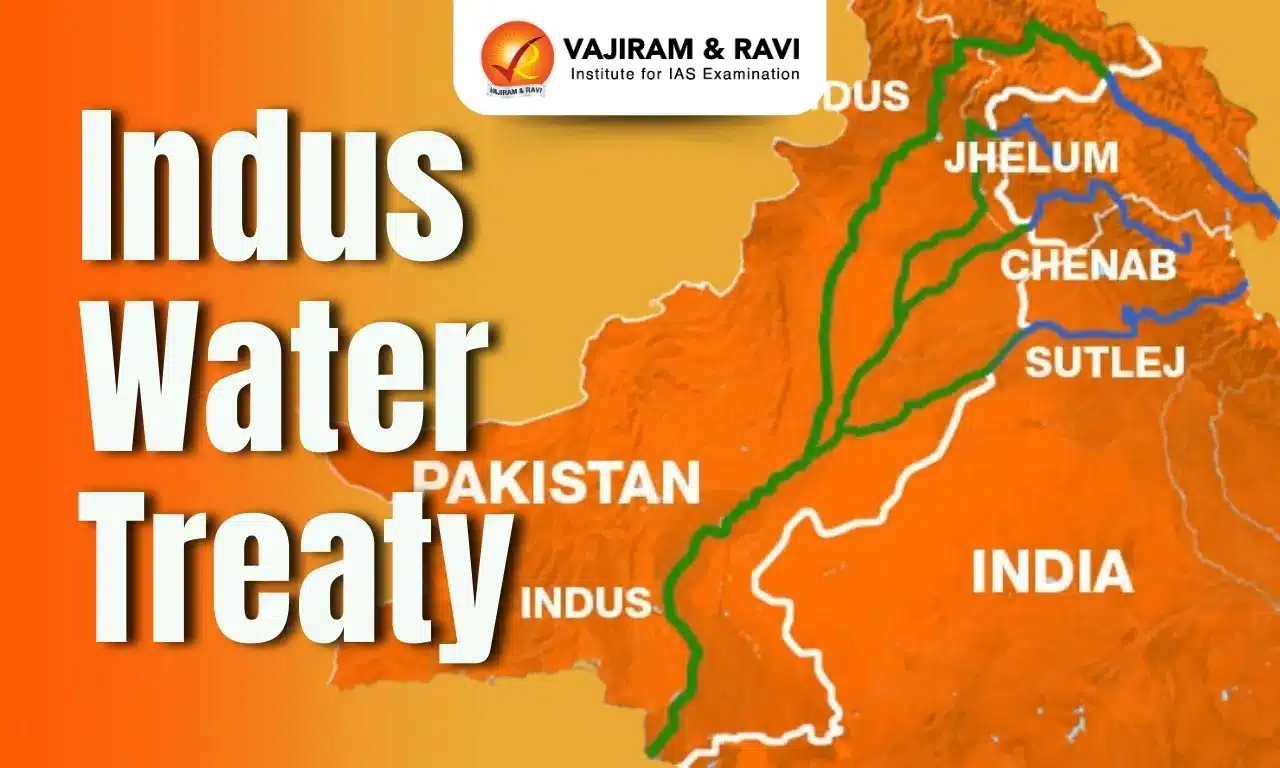
Indus Water Treaty Map
Indus Water Treaty Map below shows the route of the Indus River and its tributaries. The details analyzed through the map are mentioned below:
- Indus River: It originates in Tibet, flows through India (Ladakh), and then into Pakistan.
- Jhelum and Chenab: They flow through Jammu and Kashmir before entering Pakistan.
- Sutlej, Beas, and Ravi: They flow through northern India and Punjab before entering Pakistan.
Indus Water Treaty Key Features
Indus Water Treaty, which was signed in 1960, was brokered by the World Bank. It has several important provisions to ensure continued peaceful sharing of the Indus River System among the neighbors. The important features of the treaty are discussed below in detail:
- Water-Sharing: Under Indus Water Treaty Pakistan was granted the western rivers Indus, Chenab, and Jhelum for unrestricted use, while India was granted the eastern rivers Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej for unrestricted use.
- Permanent Indus Commission: The Treaty required to set up a Permanent Indus Commission, mandated to meet annually.
- It acts as a mechanism for cooperation and information exchange between the two countries regarding their use of the rivers. It consists of a Commissioner from each country.
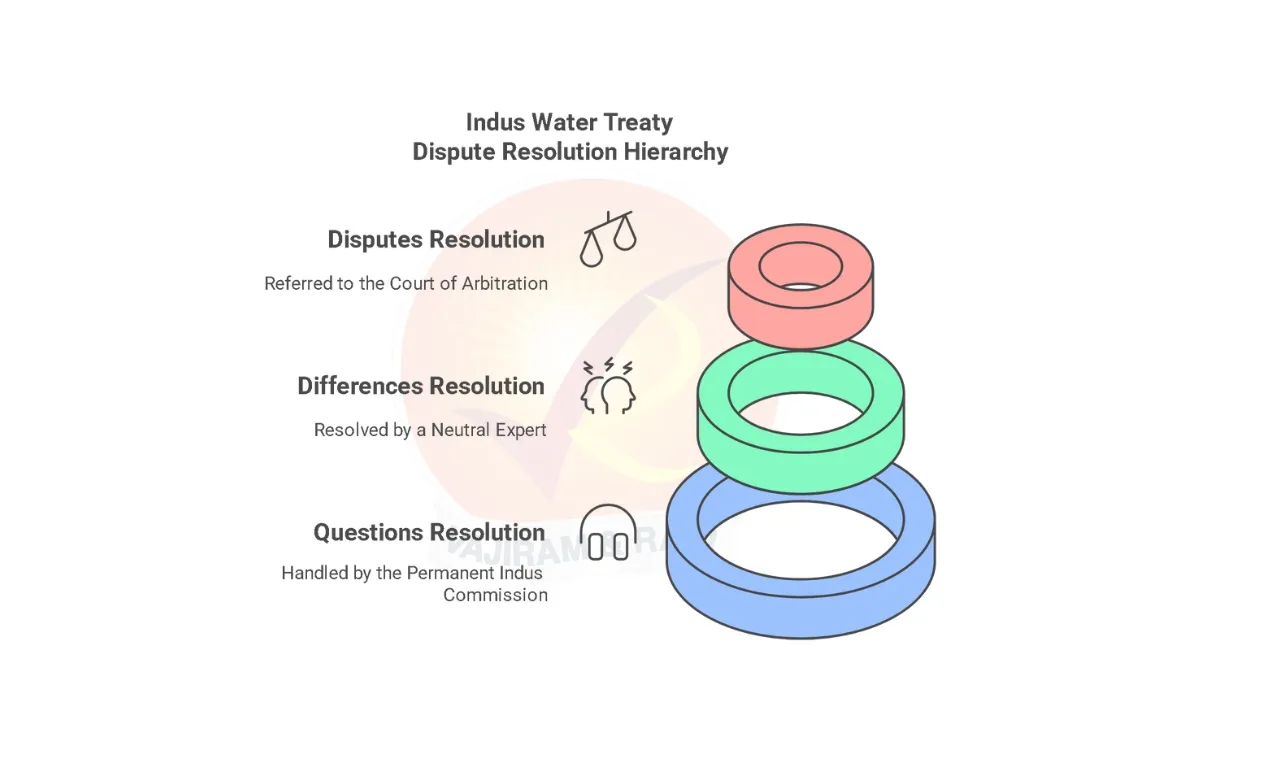
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism: The Indus Water Treaty provides for a three-tier dispute resolution mechanism. This structure ensures that disputes over the Indus waters are addressed in a graduated manner, with efforts focused first on cooperation and technical expertise before moving to formal arbitration.
- Level 1: “Questions” are handled by the Permanent Indus Commission;
- Level 2: “Differences” are to be resolved by a Neutral Expert (appointed by the World Bank)
- Level 3: “Disputes” are referred to an ad hoc arbitral tribunal called the “Court of Arbitration.”
- Exchange of Data: Both parties must indulge in the Monthly exchange of data on river water usage.
- Future Co-operation: Both countries must cooperate to set up hydrologic observation stations and undertake new drainage work to preserve the rivers.
Indus Water Treaty Timeline
The Indus Waters Treaty, signed in 1960, regulates water-sharing between India and Pakistan. Over the years, water usage has become increasingly linked to national security and geopolitical tensions.
- 2013: A Court of Arbitration rules that India must maintain minimum flows from the Kishanganga Dam (a Jhelum tributary) and cannot draw down its reservoir below a certain level, safeguarding Pakistan’s downstream rights.
- 2016: After the Uri attack, India suspends Indus Commission meetings and pledges to maximize its share under the treaty, marking the first direct linkage between water policy and security.
- 2019: In response to the Pulwama attack, India reiterates full utilization of eastern rivers. Although legal, the move highlights growing politicization of the treaty.
- 2022: Due to stalled dispute resolution, the World Bank appoints both a Neutral Expert and a Court of Arbitration, reflecting deep procedural disagreement.
- 2023: India invokes Article XII(3) to propose treaty modifications, citing climate change, national development, and Pakistan’s alleged obstruction. Pakistan rejects the proposal.
- 2024: India issues formal notice to amend the treaty, calling it outdated and biased toward Pakistan. No agreement is reached.
- 2025: Post-Pahalgam attack, India announced a suspension of treaty obligations, demanding action from Pakistan against cross-border terrorism.
Indus Water Treaty Dispute
In recent years, India and Pakistan have been in disagreement over the design of the Kishenganga and Ratle hydroelectric power plants on the Jhelum and Chenab Rivers, respectively. The dispute revolves around the issue of whether the plants' technical design violates the Indus Water Treaty, which designates the Jhelum and Chenab Rivers as the "Western Rivers" for Pakistan's unrestricted use. India is allowed to construct hydroelectric facilities on these rivers, subject to design specifications as provided in the treaty.
Indus Water Treaty Legal Framework
Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) is a permanent agreement with no exit clause or enforcement mechanism. Amid rising tensions, its limitations leave Pakistan with no peaceful or legal recourse if India chooses to suspend or revoke the treaty.
- No Exit Clause in the treaty: The Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) does not permit unilateral termination by either India or Pakistan. It is a perpetual agreement with no expiration date. Any amendment or revision requires mutual consent between the two nations.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism: Article IX, along with Annexures F and G, outlines a three-tiered dispute resolution process:
- Initial resolution via the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC)
- Escalation to a Neutral Experts
- Final arbitration through a designated Court of Arbitrators
- No Peaceful Mechanism for Enforcement: If India revokes the treaty, it essentially steps outside its legal framework. The dispute resolution mechanism becomes irrelevant, as it only applies within the bounds of the treaty.
- There is no provision in the IWT to enforce or revive the treaty after suspension.
- Pakistan cannot approach the International Court of Justice (ICJ) due to India’s reservation under the ICJ statute.
- As a result, no peaceful or legal pathway remains for Pakistan to compel treaty compliance from India.
Indus Water Treaty After Pahalgam Attack
The suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty by India, following the Pahalgam terror attack, marks a turning point in regional water diplomacy. It poses severe challenges for Pakistan’s water-dependent agriculture and urban supply, while granting India enhanced control over western rivers, hydropower potential, and flood management, altering regional water dynamics significantly.
Indus Water Treaty Suspension Implication for Pakistan
India has taken a series of strong measures following the Pahalgam terror attack, including suspending the Indus Waters Treaty, 1960. The treaty's suspension would have serious consequences for Pakistan.
- Water Dependency: Pakistan receives nearly 80% of Indus water flow, crucial for agriculture, irrigation, and drinking water in Punjab and Sindh.
- Urban Water Supply: Major cities like Karachi, Lahore, and Multan depend directly on these rivers for daily water needs.
- Agricultural Economy: Agriculture contributes 23% to GDP and supports 68% of the rural population, relying on 93% of water for irrigation.
- Irrigation Backbone: The Indus basin delivers around 154.3 million acre-feet of water annually, essential for food security and farming.
- Economic Impact: Disruption in water flow can lower crop production, increase food scarcity, and strain rural economies.
- Existing Water Crisis: Pakistan already struggles with groundwater depletion, soil salinity, and weak water storage infrastructure.
- Limited Storage: Reservoirs like Mangla and Tarbela together hold only 14.4 million acre-feet—just 10% of the annual allocation.
- Loss of Security: Treaty suspension removes guaranteed water supply, worsening water management challenges and national vulnerability.
Indus Water Treaty Suspension Implications for India
The implications for India following changes in the Indus Waters Treaty are significant. India now enjoys greater control over the western rivers—Jhelum, Chenab, and Indus—enabling increased flexibility in water usage, hydropower generation, and flood control. These developments mark a shift in regional water-sharing dynamics, reducing Pakistan’s oversight and potentially impacting bilateral relations.
- Increased Control Over Western Rivers: Greater flexibility in the use of water from the Jhelum, Chenab, and Indus rivers.
- Hydropower Generation: Potential for increased hydroelectric power generation without treaty-imposed design and operational limitations.
- Flood Control and Water Storage: Ability to undertake flood control measures and mitigate floods in the Kashmir Valley. No restriction on storage in reservoirs on western rivers, particularly the Jhelum.
- Non-Obligation to Share Flood Data: India may stop sharing flood data with Pakistan, affecting Pakistan's flood preparedness, particularly during the monsoon season.
- Suspension of Site Visits: India can deny access to Pakistani officials seeking to inspect Indian hydro projects, which were earlier mandated under the treaty’s provisions.
- Limited Immediate Impact: Despite these expanded powers, the short-term impact is minimal because India currently lacks adequate infrastructure to halt or divert river flows effectively.
Indus Water Treaty Conclusion
The waters of the Indus, once a symbol of cooperation, now stand at the heart of an emerging conflict where 'blood and water cannot flow together,' as Prime Minister Narendra Modi stated, highlighting the complexities of the evolving Indo-Pakistani relationship. The suspension of the Indus Water Treaty signals a strategic shift in India’s posture, linking water diplomacy to national security imperatives. What was once a framework for peace is now being re-evaluated in light of persistent cross-border terrorism, marking a turning point in regional geopolitics.
Indus Water Treaty UPSC PYQs
Q.1 The interlinking of rivers can provide viable solutions to the multi-dimensional inter-related problems of droughts, floods, and interrupted navigation. Critically examine. (UPSC Mains 2020)
Q.2 “The situation today is far different to that prevalent fifty years back when the Indus Water Treaty was signed.” Highlight the complexity of the current challenges on both sides of the border in this regard. Do you think that a review of the Treaty is in India’s best interests? (UPSC Mains 2012)
Q.2 With reference to the Indus river system, of the following four rivers, three of them pour into one of them which joins the Indus directly. Among the following, which one is such a river that joins the Indus directly? (UPSC Prelims 2021)
(a) Chenab
(b) Jhelum
(c) Ravi
(d) Sutle
Ans. (d)
Q.3 Consider the following pairs: (UPSC Prelims 2019)
|
Glacier |
River |
|
1. Bandarpunch |
Yamuna |
|
2. Bara Shigri |
Chenab |
|
3. Milam |
Mandakini |
|
4. Siachen |
Nubra |
|
5. Zemu |
Manas |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 2 and 5
(d) 3 and 5
Ans. (a)
Q.4 Consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2009)
- The Baglihar Power Project had been constructed within the parameters of the Indus Water Treaty.
- The project was completely built by the Union government with loans from Japan and the World Bank.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. (a)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Indus Water Treaty FAQs
Q1. What were the objectives of the Indus Water Treaty?+
Q2. What are the main points of Indus Water Treaty?+
Q3. Who created Indus Water Treaty?+
Q4. What does the Indus Water Treaty highlight?+
Q5. What happened on 19 September 1960?+
Tags: indus water treaty quest UPSC International Relations and Institutions Notes