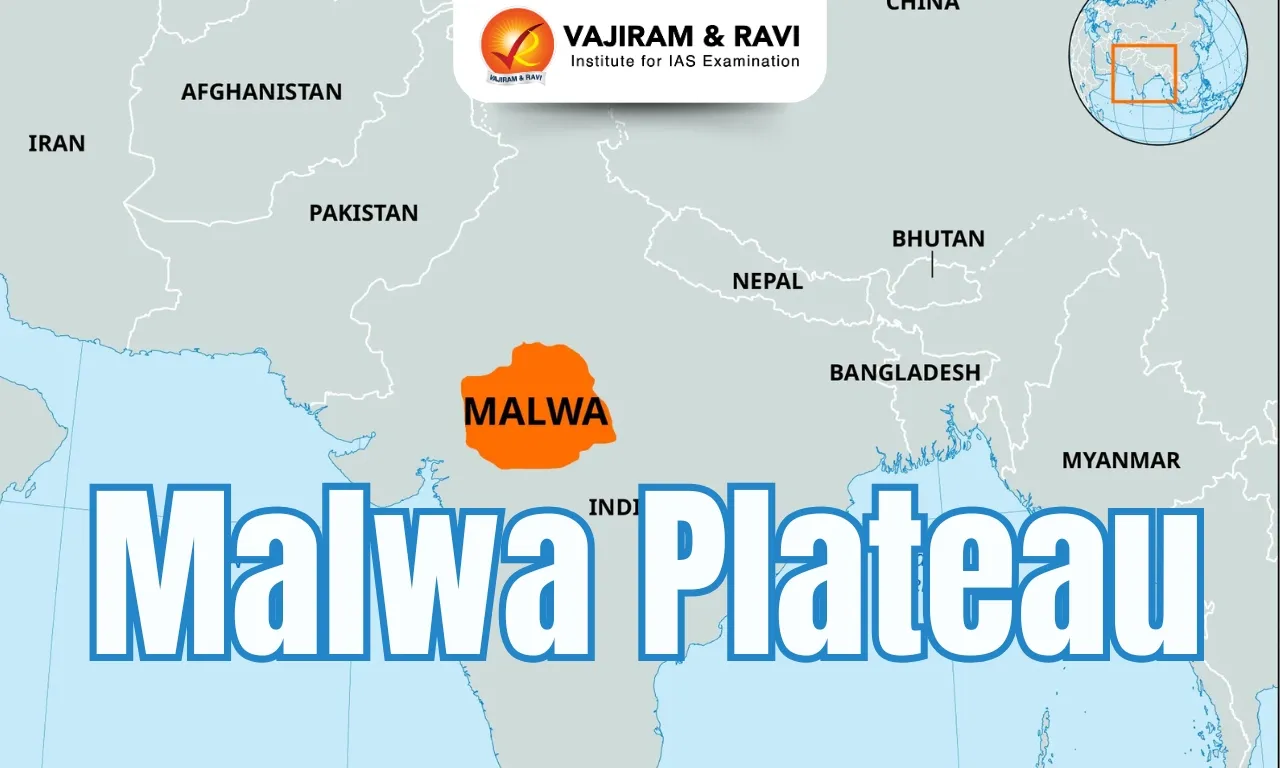
The Malwa Plateau, spanning western Madhya Pradesh and southeastern Rajasthan, is a volcanic upland formed from the Deccan Traps, with an average elevation of 500 m and peaks like Sigar (881 m). It features black, brown, and stony soils, retaining moisture for agriculture. Key rivers like Chambal, Betwa, and Shipra drain the region, supporting ecosystems and irrigation. Its tropical dry forests, dominated by teak and sal, adapt to seasonal rains.
The climate includes hot summers (30–45°C), monsoons (900–1,200 mm rainfall), and mild winters (10–25°C). Historically, it flourished under Maurya, Gupta, and Maratha empires, reflecting its rich legacy.
Malwa Plateau Geographical Features
The Malwa region spans western Madhya Pradesh and southeastern Rajasthan, bordered by Gujarat to the west, the Vindhya Range to the south and east, and the Bundelkhand upland to the north. It is part of the Deccan Traps, formed 60–68 million years ago during the Cretaceous period.
- Elevation: The plateau is elevated, with an average height of about 500 meters above sea level.
- Terrain: It is characterised by volcanic lava flows, making the soil fertile and suitable for agriculture.
- Soil: Its rich iron volcanic soil retains moisture, reducing irrigation needs.
- Rivers: Several rivers, including the Chambal, Shipra, and Kali Sindh, originate or flow through this region.
Region
The Malwa Plateau is a prominent geographical feature of north-central India, mainly in Madhya Pradesh, and extends into southeastern Rajasthan.
- Madhya Pradesh: It hosts the majority of the Malwa Plateau, encompassing key districts such as Indore and Ujjain.
- Other significant areas include Dewas, Dhar, Jhabua, and Mandsaur, each contributing to the state's economy through agriculture and industry.
- Rajasthan: The plateau extends into southeastern Rajasthan, covering districts like Jhalawar, known for its cotton and wheat agriculture, and Kota, an industrial and educational center.
- Chittorgarh, with its UNESCO World Heritage Site fort, and Banswara, the "City of Hundred Islands," also lie within the plateau.
- Geographical Boundaries: The Malwa Plateau is bordered by the Vindhya Range to the east and south, which separates it from the Gangetic plains.
- To the north, it transitions into the Madhya Bharat Plateau and Bundelkhand Upland,
- The Gujarat Plains to the west influence its climatic conditions.
Malwa Plateau Historical Significance
The name Malwa is derived from the Sanskrit term "malav," meaning "part of the abode of Lakshmi," the goddess of wealth.
- Ancient Kingdom: Malwa has been an important cultural and political center since ancient times. It was part of the Avanti kingdom, one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas.
- Ujjain: The city of Ujjain, located on the plateau, was an important center for trade, learning, and astronomy. It is also one of the seven sacred cities in Hinduism.
- Medieval Period: During the medieval period, Malwa was ruled by various dynasties, including the Paramaras, the Delhi Sultanate, the Mughals, and the Marathas.
Malwa Plateau Rivers
The Malwa Plateau is drained by several major rivers that play a crucial role in the region's ecology, agriculture, and economy.
- Mahi River drains the western part
- Chambal River flows through the central region
- Betwa River runs through the east, along with the headwaters of the Dhasan and Ken rivers.
- Other important rivers include the Parbati, Shipra, Gambhir, and Choti Kali Sindh, which contribute to irrigation and water supply, support local ecosystems and hold cultural significance, especially the Shipra River in Ujjain.
These rivers, with their terraced valleys, are integral to the region's hydrology and agricultural practices.
Malwa Plateau Climate
The Malwa Plateau, located in north-central India, spans Madhya Pradesh and southeastern Rajasthan, with an average elevation of 500-600 meters (1,650 to 2,000 feet) above sea level, influencing its climate.
- Climate Classification: Classified as tropical wet and dry (Aw) under the Köppen-Geiger system, the region experiences hot summers, a significant monsoon season, and mild winters.
- Climate of Malwa Plateau: The Malwa Plateau experiences hot summers (30°C to 45°C), a monsoon season with 900 mm to 1,200 mm of rainfall essential for agriculture, and mild winters (10°C to 25°C) with colder nights dropping to 6°C.
Malwa Plateau Vegetation
The Malwa Plateau has tropical dry forests dominated by deciduous trees like teak and sal, which adapt to seasonal rainfall by shedding leaves in dry periods. The undergrowth includes shrubs like Grewia and Ziziphus, and grasslands support grazing livestock. The region's black soil, rich in iron and moisture-retaining, supports agriculture, with crops such as wheat, rice, pulses, oilseeds, and cash crops like cotton and sugarcane.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Malwa Plateau FAQs
Q1. Where is Malwa Plateau located?+
Q2. Which states are in Malwa region?+
Q3. Which is the highest peak of Malwa?+
Q4. Which river originates from Malwa Plateau?+
Q5. Which drainage system drains the Malwa Plateau?+
Tags: quest upsc modern history