Self Respect Movement or Suya Mariyadhai Iyakkam, a social movement in South India aimed at achieving social equality and challenging the caste system. Self Respect Movement was founded by Periyar E.V. Ramaswamy Naicker, along with S. Ramanathan in 1925. Self Respect Movement aimed to challenge and dismantle the dominance of Brahminism and caste-based discrimination and promote self-respect among lower castes.
Self Respect Movement emphasized the dignity and equality of all individuals, advocating for social justice and rational thinking. It significantly impacted the socio-political landscape of South India, leading to the rise of Dravidian ideologies and influencing subsequent political developments.
Self Respect Movement About
Self Respect Movement was a reform movement aimed at giving non-Brahmins a sense of pride in their Dravidian heritage. E.V Ramaswami Naicker gave the movement its concrete shape in 1925. The movement denied the Brahmins' superiority and implicit belief in the present system.
- Targeted Brahmanical Dominance: The Movement denied Hindu mythology, claiming that innocent people had been victimized by it, and because the Brahims were regarded as social and religious leaders in Tamil Nadu, they were targeted by the Self-Respect movement.
- Participation: The movement focused almost entirely on the Tamil districts. It primarily covered low-status groups such as Vanniya Kula Kshatriyas and untouchables. The movement also saw the participation of women and youth including illiterate and semi-educated.
- Role of Kudi Arasu: Kudi Arasu, a Tamil weekly founded in 1924, became the Self-Respect Movement's organ. Ramaswami Naicker later started Viduthalai (Freedom) and Pakkuthariuu (commonsense) daily, but in the late 20s, Kudi Arasu remained the movement's propaganda weapon.
Self Respect Movement Background
Self Respect Movement emerged in a period of intense social and political turmoil. The oppressive caste system, particularly in Tamil Nadu, marginalized non-Brahmin communities, denying them basic rights and opportunities. Inspired by the Anti-caste movements led by Jyotirao Phule and B.R. Ambedkar in other parts of India, Periyar sought to create a society free from caste hierarchies and religious orthodoxy, where self-respect and human dignity were paramount. Periyar left Congress in 1925 for the formation of the Self Respect movement.
Self Respect Movement Objectives
Self Respect Movement's primary objectives were to abolish the caste system, promote rational thought, and challenge the hegemony of Brahminical traditions. The Self-Respect Movements has two pamphlets: Namathu Kurikkol and Tiravitak kalaka Lateiyam, that outline its objectives:
- Eradicating Social Hierarchies: The program aims to eliminate the social structure of superiority and birthplace biases.
- Gender Equality: The goal was to ensure equal opportunities for all individuals, regardless of community. This included achieving equal status for men and women in life and under the law.
- Equal growth opportunities: Everyone deserves equal opportunities for growth and development. Everyone should naturally feel a sense of friendship and belonging.
- Brotherhood and Unity: The goal is to eradicate the concept of untouchables and create a brotherhood-based society.
- Orphans and Widows: Create a home for orphans and widows and operate educational institutions.
- Prevention of New Religious Institutions: Prevent the construction of new temples, mutts, or Vedic schools. People should remove the caste title from their names.
- Education and Employment: Public funds should support education and job creation for the unemployed.
Self Respect Movement Significance
Self Respect Movement brought significant changes to South Indian society, particularly in Tamil Nadu. It weakened the caste system, promoted secularism, and encouraged rationalism and scientific thinking. The movement's legacy is evident in Tamil Nadu's progressive social policies, including reservations for backward classes and state support for education and welfare programs, contributing to the state's social advancement.
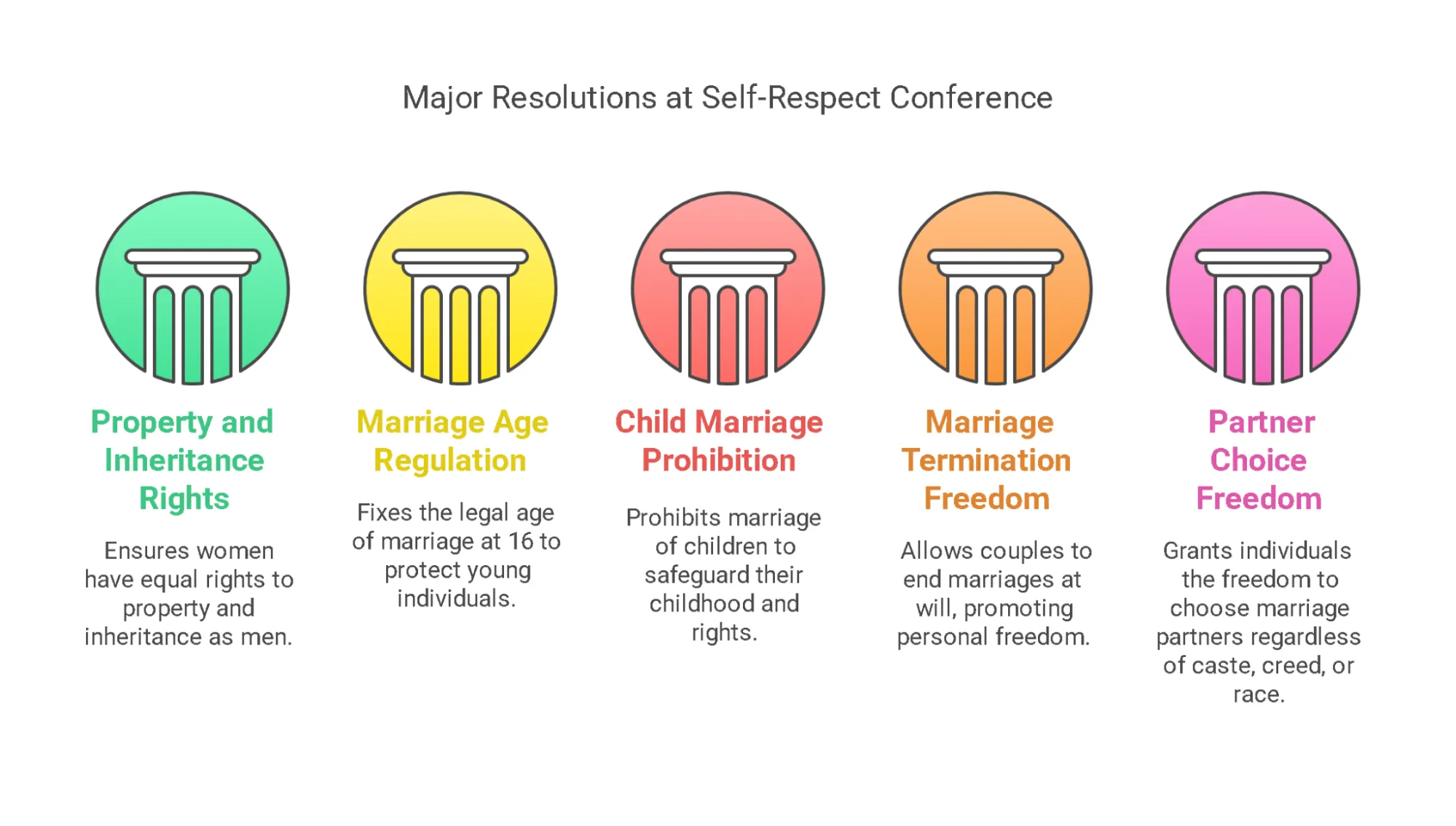
- Self-Respect marriages: The movement enabled Self-Respect weddings which were Hindu weddings to be conducted without the presence of a Hindu priest, making such ceremonies legally permissible for the first time in the country.
- Social Advances: The movement opposed the Devdasi system, caste-based discrimination, and the practice of widow remarriage, advocating for more equitable social norms.
- Political Change: The Self Respect Movement fostered a sense of nationalism among the people of Tamil Nadu. E.V. Ramasamy (Periyar) asserted that genuine intellectual freedom was essential for achieving complete liberation, thereby intertwining social reform with political activism.
- Self-Respect Conference: In February 1929, Periyar organized the first provincial Self-Respect Movement conference in Chengalpattu, presided over by W.P.A. Soundara Pandian.
-
- Periyar’s Self-Respect conference was a landmark event for its sheer focus on women’s issues.
- Dravidian Movement: It laid the foundation for the Dravidian movement, which later culminated in the forming of political parties like Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) and All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (AIADMK).
Self Respect Movement Feminist Perspective
Self Respect Movement in India has significantly influenced feminist discourse, advocating for women's rights, education, employment, and freedom from patriarchal norms. It challenged traditional marriage practices and advocated for women's autonomy in choosing partners.
- Female leaders Veeramal and Annai Meenanmbal, who persistently sought information on Dalit women's rights, contributed to the broader feminist movement.
- The movement aimed to end societal discrimination against women and seek their rights.
Self Respect Movement and Political Freedom
Self Respect Movement primarily focused on social reform, but it also had political implications. Periyar’s ideas influenced the demand for political autonomy in South India, particularly in opposing the dominance of North Indian political ideologies. The movement’s call for Dravidian identity and cultural pride eventually translated into a demand for political freedom, leading to the rise of Dravidian political parties that played a pivotal role in Tamil Nadu's political landscape.
Self Respect Movement Impact
Self Respect Movement challenged Brahmanical dominance, promoted Tamil Nationalism, and advocated for social equality. It emphasized equal rights for marginal groups, fostered self-respect, and significantly impacted South India’s political, social, and religious landscape.
- Impact on Brahmins: The movement directly challenged the social and religious privileges enjoyed by Brahmins, leading to a significant decline in their socio-political influence in Tamil Nadu.
- Self-Respecting Organizations: The movement inspired the creation of various organizations dedicated to promoting rationalism, social justice, and the abolition of caste-based discrimination. These organizations played a key role in spreading Periyar’s ideas across South India.
- Intercaste and Interreligious Dynamics: The Self Respect Movement aimed to dismantle caste boundaries and promote inter-caste and inter-religious marriages, challenging orthodox norms and promoting a more inclusive society by addressing intra-caste inequalities.
- Legal Reforms: When the Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam(DMK) formed the government in 1967, self-respect marriages became law, marking the Self-Respect Movement's first legislative achievement.
Self Respect Movement UPSC PYQs
Question 1: Consider the following pairs: (UPSC Prelims 2019)
Movement/organization Leader
- All India Anti-Untouchability League: Mahatma Gandhi
- All India Kisan Sabha : Swami Sahajanand Saraswati
- Self-Respect Movement: E.V.Ramaswami Naicker
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Question 2: Who among the following was the founder of the 'Self-Respect Movement?
a) Periyar E.V.Ramaswamy Naicker
b) Dr. B. R. Ambedkar
c) Bhaskarrao Jadhav
d) Dinkarrao Javalkar
Ans: (a)
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the first week of March 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Self Respect Movement FAQs
Q1. What is the principle of the Self Respect Movement?+
Q2. What were the objectives of the Self Respect Movement?+
Q3. Who was the father of the Self Respect Movement?+
Q4. What is the 1930 Self Respect Movement?+
Q5. What is the golden rule of Self Respect?+