The Tapti River, also known as the Tapi, is a significant west-flowing river in central India. Originating from the Satpura range in Madhya Pradesh, it flows through Maharashtra and Gujarat before emptying into the Arabian Sea. With a total length of approximately 724 kilometers, the Tapti is one of the few rivers in peninsular India that flows from east to west, along with the Narmada and Mahi rivers.
It serves as an essential water source for agriculture, industry, and domestic use in the regions it travels. The river’s basin is characterized by fertile plains, and it plays a crucial role in the economy of the surrounding areas. Major cities along its course include Burhanpur, Bhusawal, and Surat. The Tapti River, along with its tributaries, supports diverse ecosystems and contributes significantly to the region’s hydrology.
Tapti River System Origin
The Tapti River, also known as the Tapi, is the second-largest west-flowing river in Peninsular India and is often regarded as the "twin" or "handmaid" of the Narmada River. It originates from the Multai reserve forest in Madhya Pradesh at an elevation of 752 meters and flows for approximately 724 kilometers before emptying into the Arabian Sea via the Gulf of Cambay.
The river and its tributaries travel the plains of Vidarbha, Khandesh, and Gujarat, covering large parts of Maharashtra and smaller sections of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat. The Tapti River basin spans an area of 65,000 square kilometers across these three states. It is located on the Deccan Plateau and is bordered by the Satpura Range to the north, the Mahadev Hills to the east, the Ajanta Range and Satmala Hills to the south, and the Arabian Sea to the west.
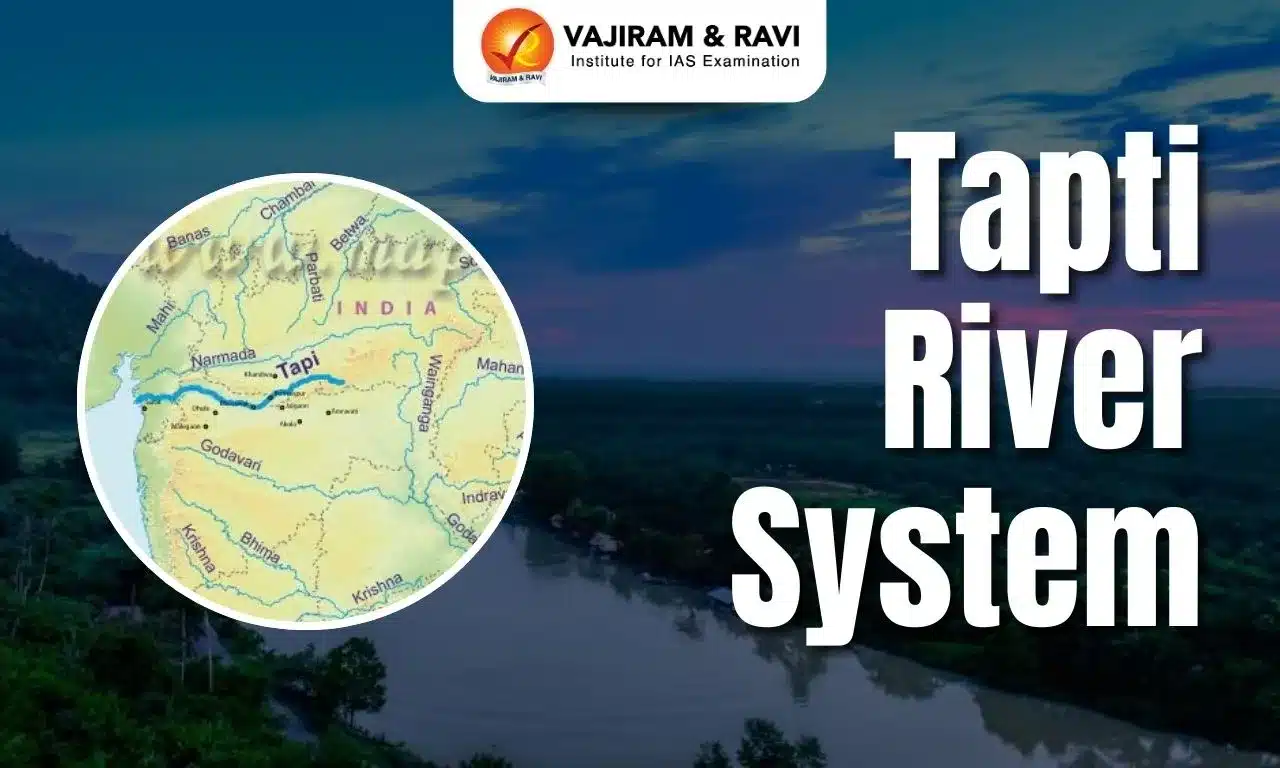
Tapti River System Map
The Tapti River System Map helps visualize the complete course of the river as it flows westward across Central India before draining into the Arabian Sea. It highlights the Tapti’s origin, major tributaries, adjoining states, and key cities located along its basin.

Tapti River System Tributaries
The Tapti River System includes the Tributaries spans over 50km, with a greater drainage area on the left bank than on the right. The table below includes the list of Tapti River System Tributaries:
| Tapti River System Tributaries | ||||
| Tributary | Description | Drainage Area (sq. km) | Length (km) | Direction of Flow |
|
Purna |
Major left-bank tributary; only river flowing in the upper basin of peninsular India |
18,929 |
- |
Left bank |
|
Girna |
Named after Goddess Parvati; originates in the Western Ghats and flows north |
10,061 |
- |
North |
|
Bori |
Originates in Nashik, Maharashtra; flows east and then north to meet Tapti |
2,580 |
- |
East, then North |
|
Panjhra |
Originates near a small town; Latiapada Dam built near its source |
3,257 |
- |
- |
|
Aner |
Largest right-bank tributary of Tapti |
1,702 |
- |
Right bank |
|
Arunavati |
Flows from Satpura range to southern slopes, covering 64 km on the left bank before merging with Tapti |
- |
64 |
Left bank |
|
Gomai |
Originates in Satpura range and flows towards the southern slopes; right-bank tributary |
1,148 |
58 |
Right bank |
|
Waghur |
Originates in the Ajanta range and flows north; left-bank tributary |
2,592 |
96 |
Left bank |
|
Burray |
Originates in the Satmala range and flows east before meeting Tapti |
1,419 |
64 |
East |
Tapi River Basin
- The Tapti River Basin extends across the states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat, covering an area of 65,145 square kilometers, with a maximum length of 534 kilometers and a breadth of 196 kilometers.
- Situated on the Deccan Plateau, the basin is bordered by the Satpura Range to the north, the Mahadev Hills to the east, the Ajanta Range and Satmala Hills to the south, and the Arabian Sea to the west.
- The upper reaches of the basin are steep and densely forested, while the lower areas consist of vast, fertile lands suitable for agriculture.
- Farming dominates the basin, covering approximately 66.19% of the total area, while water bodies account for around 2.99%.
Tapi River Soil Type
- The Tapti River basin primarily consists of black soils, while the coastal plains of Gujarat feature alluvial clays with a top layer of black soil.
- The soil composition in the basin, up to the Ukai Dam, can be categorized into three types: coarse shallow soils, medium black soils, and deep black soils.
- These soil variations influence the region's agricultural productivity, with black soils being particularly suitable for cotton cultivation and other crops.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Tapti River System FAQs
Q1. Where does Tapi River start and end?+
Q2. What is the drainage system of Tapti?+
Q3. Does Tapti River form delta?+
Q4. What is the largest tributary of Tapti?+
Q5. Which city is famous on Tapi river?+
Tags: tapti river system