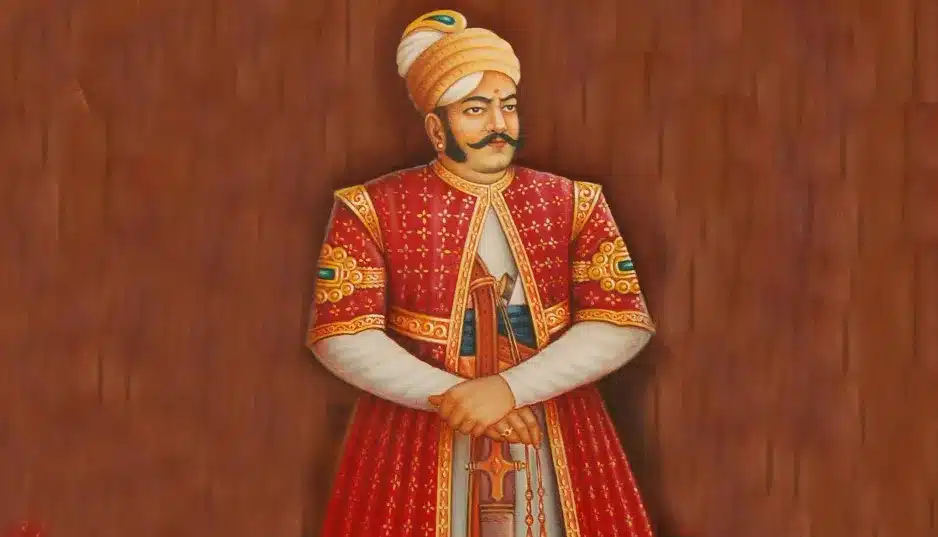
Velayudhan Thampi, known as Velu Thampi Dalawa, was born on May 6th, 1765, into an aristocratic Nair family in Kalkulam, near Trivandrum. His integrity and leadership earned him the position of Mulukumatissila Karyakkar (Commerce Minister for Pepper) in 1801. Recognized for his efforts, he was appointed Prime Minister (Diwan) of Travancore in 1802, where he introduced significant reforms to improve governance, eliminate corruption, and stabilize the state's finances.
In 1805, the Treaty of Perpetual Friendship placed Travancore under British control, reducing its autonomy. In response, Velu Thampi led a revolt in 1809, including the Attack on Cochin and the Kundara Proclamation. Though the rebellion failed, his legacy endures.
Velu Thampi Dalawa History
Velayudhan Thampi, known as Velu Thampi Dalawa, was born on May 6th, 1765, in an aristocratic Nair family in Kalkulam near Trivandrum. At 19, he started his career as Karyakkar (Thahsildar) and gained a reputation for honesty and efficiency. During Balarama Varma's weak reign, the state was mismanaged by Jayantahan Nambudiri and Mathu Tharakan, pushing the state towards financial collapse.
- When forced to pay a heavy contribution, he rallied the people against the corrupt administration through his powerful oratory.
- His leadership inspired a mass uprising, which resulted in the dismissal of the unpopular Diwan and his associates.
- Recognised for his efforts, he was appointed Mulukumatissila Karyakkar (Commerce Minister for Pepper) and, in 1801, was elevated to Diwan of Travancore, playing a pivotal role in restoring stability to the state.
Velu Thampi Dalawa Administration
Velu Thampi Dalawa was the Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Travancore from 1802 to 1809. He was an efficient administrator who reformed Travancore's governance. He dismissed corrupt officials, eliminated crime through strict punishments, and strengthened the central government.
- He reorganized the revenue department, ensuring prompt collection and minimizing misappropriation, and improved the state's financial condition by issuing new pattas (title deeds) after a land survey. He also cleared state debts and paid overdue salaries.
- Velu Thampi focused on urban development, improving towns like Trivandrum and Quilon, and constructing key public buildings like the Huzur Kacheri in Quilon. His reforms left a lasting mark on Travancore's administration.
Velu Thampi Dalawa Revolt
Velu Thampi's revolt (1808-1809) stemmed from Travancore's decline after the death of Raja Bala Rama Varma in 1798, which was exacerbated by British interference through the Subsidiary Alliance and the appointment of the corrupt Dewan, Jayantahan Namboothiri. Velu Thampi, appointed Dalawa (Prime Minister) in 1801, led efforts to combat corruption in Travancore. However, his strict governance alienated some allies, leading to challenges within his administration.
- The Treaty of Perpetual Friendship (1805) further diminished Travancore's autonomy under British control, prompting Velu Thampi to lead a revolt in 1809.
- He spearheaded the Attack on Cochin and issued the Kundara Proclamation to rally people against British Rule in India.
Despite early successes, the rebellion ultimately failed, but Velu Thampi’s legacy endures as an early symbol of India's freedom struggle.
Treaty of Perpetual Friendship and Alliance (1805)
The Treaty of Perpetual Friendship treaty (1805) made Travancore a subsidiary ally of the British, requiring the state to pay an increased annual tribute of Rs. 8 lakhs and accept British protection. This led to the loss of Travancore's political autonomy, allowing the British to intervene in internal matters, especially during rebellions.
- Although Velu Thampi initially maintained good relations with British Resident Colin Macaulay, tensions arose due to Macaulay’s interference in governance.
- The frustration with British control eventually led Velu Thampi to organize a revolt, aiming to resist British domination and restore Travancore's independence.
Velu Thampi Dalawa Attack on Cochin (1809)
Velu Thampi formed a strong alliance with Paliath Achan, and together they planned a revolt against the British. They gathered men and arms on a large scale. Assurance of help came from the French and the Zamorin. The uprising began in Cochin on the night of December 18, 1808, when their combined forces surrounded the British Resident’s house.
- Although Col. Macaulay and his associate Kunhikrishna Menon narrowly escaped, the rebels looted the residence and killed the British sepoys.
- They also broke into the Cochin jail, freeing all the prisoners, marking a significant escalation in their revolt.
Velu Thampi Dalawa Kundara Proclamation
The Kundara Proclamation was issued by Velu Thampi on January 11, 1809, calling upon the people of Travancore to rise against British colonial rule. However, the British garrison at Quilon (Kollam) withstood his attack, and with reinforcements, they dealt a significant blow to the Travancore forces, weakening their morale.
- Velu Thampi's struggle was further strained when his ally, Paliath Achan, was forced to abandon their alliance and support the British, creating additional challenges.
- The British, led by Colonel St. Leger, soon invaded Travancore, capturing key forts such as Udayagiri and Padmanabhapuram, and advancing towards Trivandrum.
- Velu Thampi fled from the capital and sought refuge at the Bhagavathi Temple in Mannadi.
- Surrounded by British forces, he chose to commit suicide rather than face capture.
- Despite his failure, Velu Thampi is remembered as one of the earliest pioneers of India’s freedom struggle, honoured for his patriotism, leadership, and ultimate sacrifice.
Velu Thampi Dalawa Legacy
Velu Thampi Dalawa’s 200-year-old sword, a double-edged weapon, is currently displayed at the Napier Museum in Kerala. After being forgotten for nearly 150 years, the Kilimanoor family identified its significance and handed it over to President Rajendra Prasad in 1957. It was kept at the National Museum in New Delhi for 53 years before being ceremoniously returned to Kerala in 2010.
- Velu Thampi Dalawa is renowned for leading the 1809 rebellion against the British East India Company in Travancore.
- Although the uprising was ultimately crushed and Thampi was captured and executed, his legacy as a visionary leader endures.
- He is remembered for his efforts to protect his people and for his role in modernizing Travancore’s administration.
| Other Related Posts | |
| Civil Uprisings Before 1857 | Velu Thampi Dalawa (1765–1809) |
| Moplah Rebellion | Ramosi Rebellion 1822-1829 |
| Poligar Revolt | Rampa Rebellion of 1922 |
| Alluri Sitarama Raju | |
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Velu Thampi Dalawa FAQs
Q1. How did Veluthambi Dalawa died?+
Q2. Who was Velu Thampi?+
Q3. Where was Veluthambi born?+
Q4. Who issued the Kundara Proclamation?+
Q5. What was the reason for the revolt of Diwan Velu Thambi?+