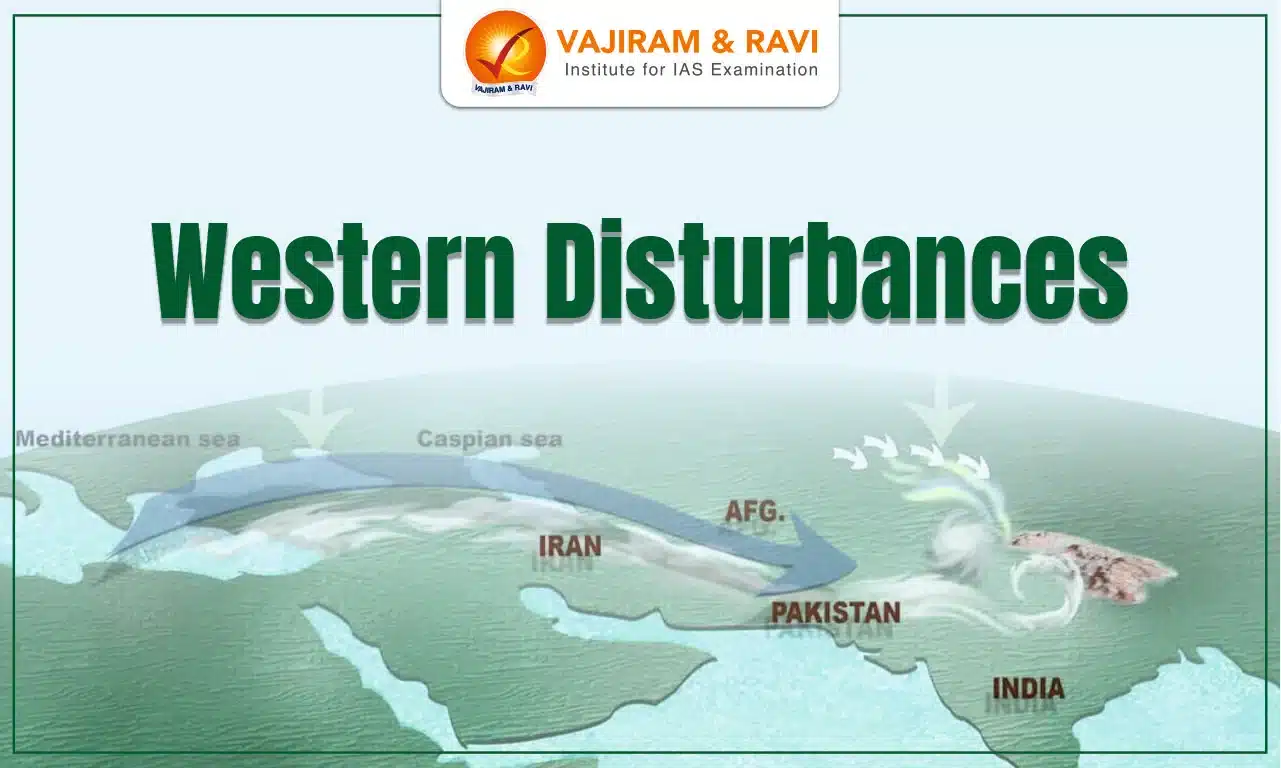
Western Disturbances in India are significant weather phenomena originating from the Mediterranean region, impacting India's climate primarily in winter. These extratropical storms bring crucial rainfall and snowfall, vital for the Rabi crop season, especially in northwestern India, including Punjab, Haryana, and Delhi. They are characterized by low-pressure systems that move eastward, gaining moisture from regions like Iran and Afghanistan before releasing precipitation upon reaching the Himalayas.
Their influence extends beyond winter, affecting agricultural productivity, river flows, and even the onset of the monsoon season, making them critical for India's agricultural and water resources.
What are Western Disturbances?
According to Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), Western Disturbance is the name given to the extratropical storm that forms in the Mediterranean region and provides unexpected winter rains to the northwest of the Indian subcontinent. This precipitation pattern is not monsoonal and is influenced by the westerlies.
- This is not limited to the monsoon season; it can occur in any season. These extratropical storms occur all around the world.
- Unlike their tropical counterparts, where the moisture is carried in the lower layer of the atmosphere, this phenomenon often carries moisture in the upper layer of the atmosphere.
- When a storm system crosses the Himalayas or the Himalayan region, moisture from the storm system occasionally falls as rain on the Indian subcontinent.
Western Disturbances in India Features
Western Disturbances in India are low-pressure cyclonic systems from the Mediterranean that move eastward, bringing precipitation to northwestern India, especially the western Himalayas. Key characteristics include temperature fluctuations, replenishment of soil moisture for rabi crops, and changes in atmospheric pressure, leading to widespread cloud cover and fog.
- Nature: They are low-pressure systems accompanied by clouds, rain in the lower altitudes, and sometimes snow in higher altitudes.
- Weather Patterns: Western Disturbances bring precipitation to the northwestern parts of India, particularly the western Himalayas, including Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, parts of Uttar Pradesh and northern Pakistan.
- Impact on Temperature: They can lead to a sudden drop in temperature in the affected regions due to the influx of cold air masses. Conversely, they can also bring a temporary rise in temperature just before the disturbance.
- Seasonality: Most active during the winter months from December to February but can also occur during other times of the year.
- Influence on Agriculture: The precipitation associated with Western Disturbances is crucial for rabi crops (winter crops) in India, as it helps replenish soil moisture.
- Cyclonic Circulation: These disturbances are often accompanied by cyclonic circulations and associated cloud formations, leading to widespread cloud cover and changes in atmospheric pressure.
- Impact on Air Pressure: They can cause fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, leading to changes in weather patterns, including the potential for fog and mist in the affected regions.
Western Disturbances in India Formation
The formation of Western Disturbances in India involves several steps: they originate in the Mediterranean Sea, move eastward driven by the subtropical westerly jet stream, gain moisture over Iran and Afghanistan, release rain and snow upon reaching the Himalayas, and then dissipate.
- Origin in the Mediterranean Region: Western Disturbances form due to the interaction of different air masses over the Mediterranean Sea. The region's warm air interacts with the colder air masses from Europe, creating low-pressure systems.
- Eastward Movement: These low-pressure systems, driven by the subtropical westerly jet stream, move eastwards towards the Indian subcontinent. The jet stream plays a crucial role in steering these disturbances.
- Passage Over Iran and Afghanistan: As the disturbances move eastward, they gain moisture from the Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea. This added moisture intensifies the system, making it capable of causing significant weather changes.
- Impact on Indian Subcontinent: Upon reaching the Indian subcontinent, these disturbances encounter the Himalayas, which act as a barrier. The interaction with the mountainous terrain causes the disturbances to release their moisture in the form of rain and snow, particularly affecting the northwestern states.
- Dissipation: After causing precipitation, these systems gradually weaken and dissipate, often moving further eastwards and impacting parts of Nepal and Bangladesh before losing their intensity.
Western Disturbances in India Significance
Western Disturbances in India are crucial for northwest India's climate, agriculture, and water resources, bringing vital winter rainfall that supports rabi crops like wheat and barley. These disturbances also deliver significant snowfall in the Himalayas, essential for glacier health and the perennial flow of rivers such as the Indus and Ganges, ensuring a steady water supply year-round. Additionally, they influence temperature patterns, often leading to cold waves, while maintaining soil moisture levels that boost agricultural productivity and overall crop yields.
Climate and Weather
Western Disturbances in India are essential for winter rainfall, temperature regulation, and snowfall in northwestern India, supporting rabi crops like wheat and barley while maintaining the glacial balance in the Himalayas and influencing cold wave conditions.
- Winter Rainfall: Western Disturbances are a primary source of winter rainfall in northwestern India. This rainfall is crucial for rabi crops, such as wheat and barley.
- Temperature Regulation: These disturbances influence temperature patterns, often causing a drop in temperatures in affected regions, leading to cold wave conditions.
- Snowfall: In the higher altitudes of the Himalayas, Western Disturbances bring significant snowfall, which is vital for maintaining the glacial balance and river flows.
Agriculture
Western Disturbances in India are crucial for irrigating rabi crops, preserving soil moisture, and enhancing overall agricultural productivity in northwest India.
- Rabi Crops: The winter rainfall brought by Western Disturbances is essential for the irrigation of rabi crops, which depend on this moisture for growth and yield.
- Soil Moisture: These disturbances help maintain soil moisture levels, benefiting the overall agricultural productivity in the affected regions.
Water Resources
Disturbances in the west contribute to the snowfall in the Himalayas, which maintains glaciers and ensures the continuous flow of rivers such as the Ganges and Indus, which is essential for the year-round supply of water.
- River Flow: Snowfall in the Himalayas due to Western Disturbances contributes to the perennial flow of rivers like the Indus, Ganges, and their tributaries, ensuring a consistent water supply throughout the year.
- Glacial Health: The snowfall helps sustain glaciers, which are crucial for maintaining river flows during the dry months.
Western Disturbances in India Impacts
Western Disturbances in India, significantly affect the Indian subcontinent's monsoon season, climate, agriculture, and water resources. They can delay the monsoon's onset by altering temperature gradients and jet stream patterns, enhancing pre-monsoon rainfall that benefits soil moisture but may also damage crops and delay sowing. Their snowfall in the Himalayas is vital for summer glacial melt, sustaining river flows and replenishing reservoirs, though it can also increase flood risks.
Impact on Weather
Western Disturbances significantly influence the climate and weather patterns of the Indian subcontinent. While they primarily affect the winter months, their implications can extend into the monsoon season as well. Impacts includes:
- Temperature Regulation: The cooling effect of prolonged Western Disturbances can delay the onset of the Indian summer monsoon by influencing the temperature gradient between the Indian Ocean and the subcontinent.
- Jet Stream Interaction: Western Disturbances can alter the position and intensity of the subtropical jet stream, which in turn affects the timing and progression of the monsoon winds.
- Pre-Monsoon Showers: As Western Disturbances dissipate, they often enhance pre-monsoon rainfall in northwestern India, which can provide early moisture beneficial for certain crops.
- Thunderstorms and Hail: Enhanced instability due to residual effects of Western Disturbances can lead to severe thunderstorms and hail, impacting agriculture and infrastructure.
Impact on Agriculture
Western Disturbances positively impact agriculture by retaining soil moisture and controlling pests, but they can also cause crop damage and delayed sowing due to unseasonal rain and hail, affecting the crop calendar.
- Soil Moisture Retention: The rainfall from Western Disturbances helps to retain soil moisture, which is beneficial for the crops sown just before the monsoon season.
- Pest and Disease Control: The cooler temperatures and moisture can help in reducing pest populations and disease incidence in certain crops.
- Crop Damage: Unseasonal heavy rain or hail can cause significant damage to standing crops, especially fruits and vegetables.
- Delayed Sowing: A delayed onset of the monsoon due to prolonged effects of Western Disturbances can postpone sowing activities, affecting the crop calendar.
Impact on Water Resources
Western disturbances are important for river flow and glacial melt, which replenishes groundwater and reservoirs. However, because of heavy precipitation and swift snowmelt, they can also cause flash floods and riverine flooding.
- Glacial Melt Contribution: The snowfall caused by Western Disturbances in the Himalayas is critical for the summer melt that feeds major rivers, ensuring a steady water supply.
- Reservoir Replenishment: Winter and pre-monsoon rains help in replenishing reservoirs and groundwater, which are essential for irrigation and drinking water during the dry months.
- Flash Floods: Intense Western Disturbances can lead to heavy rainfall and rapid snowmelt, causing flash floods in the foothills and downstream areas.
- River Flooding: The combined effect of heavy precipitation and glacial melt can lead to riverine flooding, impacting agriculture, settlements, and infrastructure.
Western Disturbances in India UPSC PYQs
Question 1: Consider the following statements: (UPSC Prelims 2009)
- In the world, tropical deserts occur along the western margins of continents within the trade wind belt.
- In India, the East Himalayan region gets high rainfall from north-east winds.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: (a)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Western Disturbances in India FAQs
Q1. What are Western disturbances?+
Q2. How many Western disturbances are there in India?+
Q3. How do Western disturbances affect India's climate?+
Q4. What is the jet stream and Western disturbance?+
Q5. What is the difference between tropical cyclones and Western disturbances?+
Tags: quest UPSC Geography Notes western disturbances in india