About Migratory Bird Species:
- Delhi-NCR accounts for almost one-third of the total bird species found in India.
- The region has about 1,800 species of fauna out of which 446 are bird species.
- There are nine protected areas, including one national park, six wildlife sanctuaries, one reserve forest and one conservation reserve.
- There are eight important bird areas, including Okhla Bird sanctuary (Gautam Budh Nagar), Sultanpur National Park (Gurgaon), Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary (Muzaffarnagar, Meerut, Ghaziabad, Bijnor), Basai Wetlands (Gurgaon) etc. None of them are in Delhi.
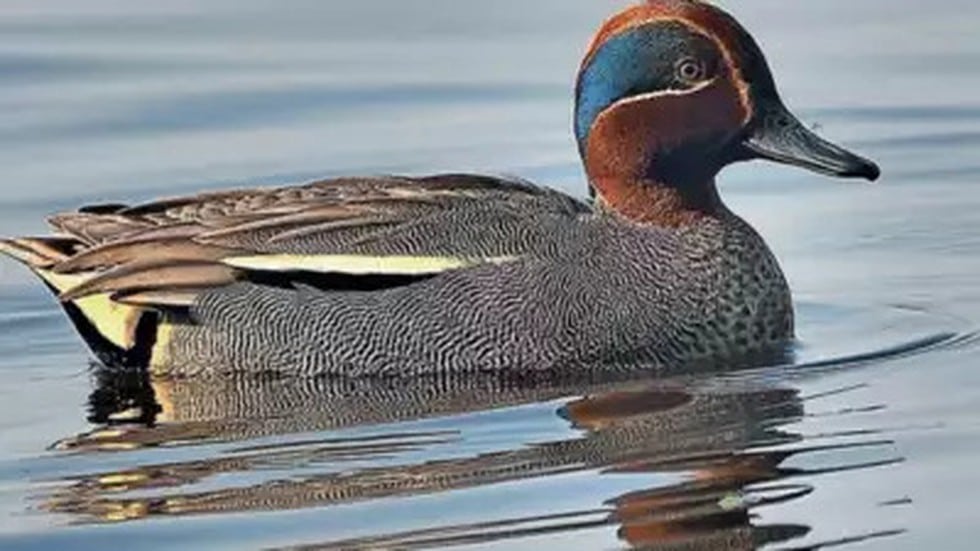
- Some of the major migratory ducks are Northern shoveler, Gadwall, Greylag geese, Pallas’s gulls, brown-headed and black-headed gulls, coots, etc.
- India is a winter home for most of the Siberian birds such as the Siberian Cranes, Greater Flamingo, and Demoiselle Crane, also numerous species of birds from other regions of the world.
- They migrate to India every year during the winter and summer season for food, breeding, and nesting.
The major global flyways:
- Americas Flyway: three flyways that connect North America with Caribbean and Central and South America.
- African-Eurasian Flyway: three flyways that connect Europe and northern Asia with Mediterranean, Middle East, and Africa.
- Central Asian Flyway: connects northern Asia with southern Asia and Middle East.
- East Asian-Australasian Flyway: connects north-east Asia with south-east Asia, Australia and New Zealand.
Source : Times of India