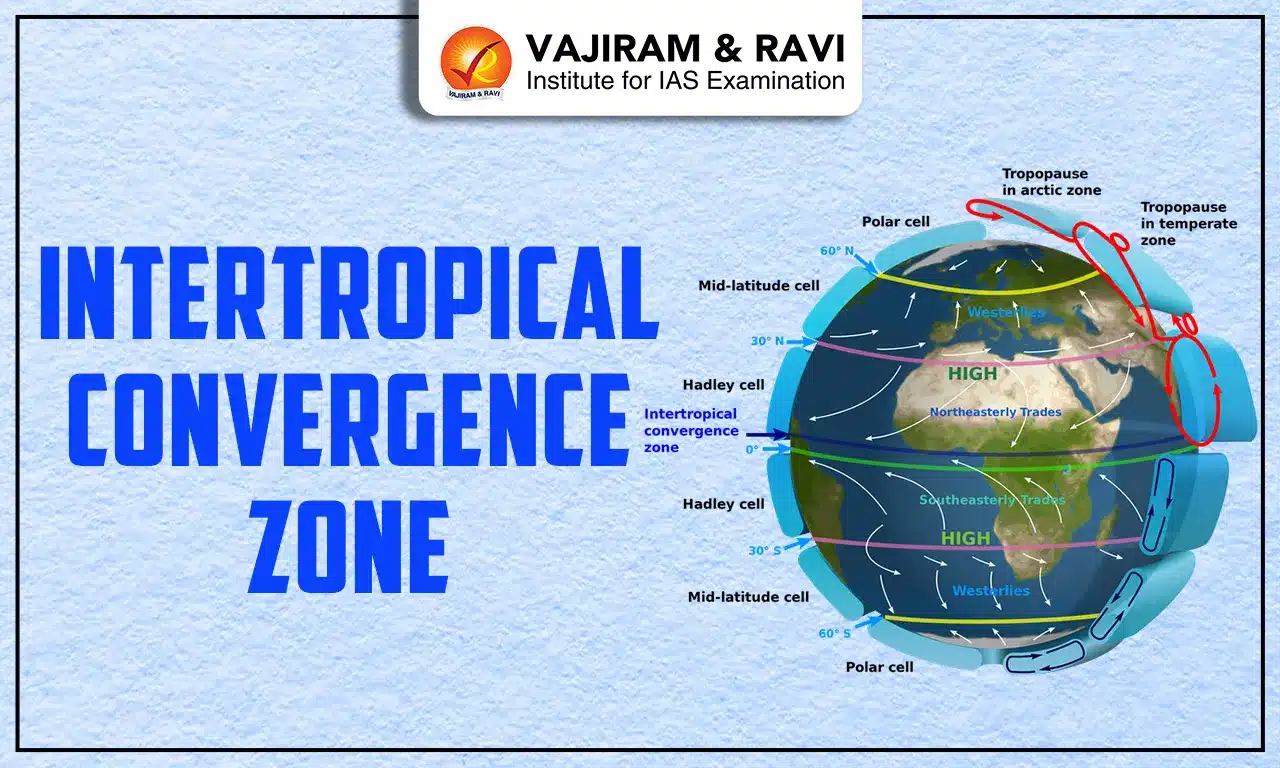
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is one of the most important elements in the study of meteorology and climatology. It plays an important role in shaping global weather systems and long-term climatic patterns. The ITCZ refers to a belt near the equator where the northeast and southeast trade winds converge, forcing warm, moist air upward. This upward movement triggers convection, leading to the formation of cumulonimbus clouds, frequent thunderstorms, and heavy rainfall. For this reason, it is also often referred to as the Equatorial Convergence Zone or simply the doldrums.
The position of the ITCZ is not fixed. It oscillates northward and southward in tune with the seasonal migration of the overhead sun. This shifting character makes it a dynamic system that directly impacts weather and climate across tropical and subtropical regions. For instance, the northward movement of the ITCZ plays a critical role in triggering the Indian summer monsoon.
In this article, we are going to cover the Intertropical Convergence Zone, its characteristics, impact and its importance.
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone is essentially a thermal low-pressure belt encircling the Earth near the equator. It forms as a result of intense solar heating in equatorial latitudes. The sun’s rays fall almost vertically on the equator, heating the surface air and causing it to rise. As the moist, warm air ascends, it cools, condenses, and produces towering cloud formations followed by heavy rainfall.
Thus, the ITCZ is not just a meteorological zone but a dynamic system that shifts with the apparent movement of the sun. In the Northern Hemisphere summer, it moves northward over Asia and Africa, while during the Southern Hemisphere summer, it shifts southward, influencing weather over South America and parts of Africa.
Intertropical Convergence Zone Causes
The development and shifting of the ITCZ are driven by multiple interconnected factors:
- Solar Heating: The equatorial region receives maximum insolation throughout the year. This extreme heating generates rising air currents, creating a zone of low pressure that draws in the trade winds from both hemispheres.
- Earth’s Rotation: The Coriolis effect resulting from Earth’s rotation alters the path of trade winds, making them converge around the equatorial region. This convergence sustains the ITCZ.
- Seasonal Shifts of the Sun: The tilt of the Earth’s axis causes the sun’s direct rays to migrate north and south of the equator, dragging the ITCZ along. This is responsible for seasonal rainfall patterns in the tropics.
- Ocean Currents and Surface Temperatures: Warm ocean currents intensify convection and enhance rainfall in the ITCZ belt, while cold currents suppress rainfall. For instance, the Benguela Current reduces rainfall in parts of southwestern Africa.
Intertropical Convergence Zone Characteristics
The ITCZ can be identified by many features including:
- Heavy Rainfall: Precipitation often exceeds 2000 mm annually in regions under its influence. Rainfall is frequent and intense due to continuous convection.
- Thunderstorms: Deep convection leads to regular thunderstorms, making the zone highly unstable.
- Cloud Cover: Cumulonimbus and stratocumulus clouds dominate the ITCZ region, creating a near-constant overcast sky.
- Seasonal Migration: The ITCZ shifts northward in June–July and southward in December–January, corresponding to the sun’s position.
- Low Pressure Zone: It remains a belt of weak, variable winds and calm conditions, historically referred to as the doldrums by sailors.
Intertropical Convergence Zone Impact
The ITCZ is not just an equatorial phenomenon; its shifting belt has far-reaching consequences for global and regional climates.
- Influence on Monsoons: In India and Southeast Asia, the northward migration of the ITCZ during summer brings monsoon rains. Conversely, its southward retreat signals the withdrawal of the monsoon.
- Support for Tropical Rainforests: Regions like the Amazon Basin, Congo Basin, and parts of Southeast Asia owe their dense rainforest ecosystems to the high rainfall generated by the ITCZ.
- Droughts and Floods: Any irregularity in ITCZ positioning can cause extreme weather. A delayed northward shift may weaken the Indian monsoon, leading to drought, while excessive rainfall may cause floods.
- Part of Global Circulation: The ITCZ forms an important component of the Hadley Cell circulation, which governs global atmospheric circulation and redistribution of heat.
- Impact on Agriculture: Farmers in tropical regions depend on the seasonal migration of the ITCZ for planning, sowing and harvesting. Its predictable rainfall ensures agricultural cycles.
ITCZ Importance in India
For India, the Intertropical Convergence Zone is specially important because of its connection with the Southwest Monsoon. The northward migration of the ITCZ towards the Tropic of Cancer in June draws in moisture-laden winds from the Indian Ocean, resulting in heavy rains across the subcontinent. Similarly, its retreat southwards in October-November signals the onset of the Northeast Monsoon, especially over Tamil Nadu.
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Intertropical Convergence Zone FAQs
Q1. What is the Intertropical Convergence Zone?+
Q2. What is the ITCZ zone?+
Q3. What is the cause of the ITCZ?+
Q4. How is ITCZ connected with the southwest monsoon?+
Q5. What is the impact of the Intertropical Convergence Zone?+