What’s in today’s article?
- Why in news?
- Pompe disease
- What is Pompe Disease?
- How does Pompe disease affect an individual?
- How is Pompe disease diagnosed?
- Is Pompe disease curable?
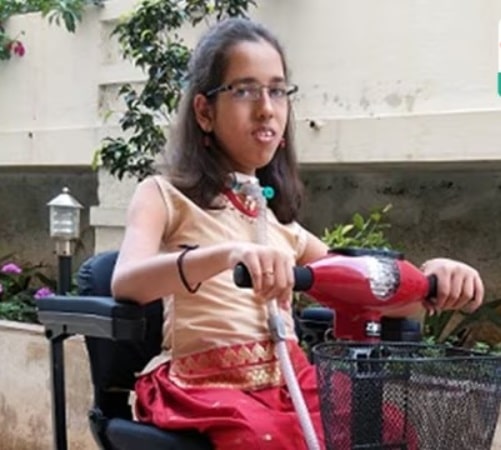
Why in news?
- Nidhi Shirol, India’s first Pompe disease patient, passed away last month at the age of 24 years after battling the disease.
- She spent the last six years in a semi-comatose state.
What is Pompe Disease?
- Also known as Glycogen Storage Disease Type II, Pompe disease is a rare genetic disorder.
- It is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA).
- This enzyme is crucial for breaking down glycogen into glucose within the lysosomes of cells.
- Its prevalence estimates range from 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 300,000 births. It occurs across diverse ethnicities and populations.
How does Pompe disease affect an individual?
- Muscle weakness:
- Progressive muscle weakness is a primary feature of Pompe disease.
- It affects both skeletal and smooth muscles, leading to difficulties in mobility and daily activities.
- Weakness in the respiratory muscles can result in breathing difficulties, especially during physical exertion or even while lying down.
- Motor skill delay:
- Children with the disease may experience delays in achieving motor milestones, such as sitting, crawling, and walking.
- The degree of motor skill delay can vary, and some individuals may never attain certain motor milestones.
- Degenerative impact on bones:
- Prolonged muscle weakness and reduced mobility can have a degenerative impact on bones, leading to joint contractures and skeletal deformities.
- Respiratory complications:
- The weakening of respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm, can have an impact.
- Patients may experience shortness of breath, respiratory infections, and in severe cases, respiratory failure.
- Cardiac involvement:
- In some cases, Pompe disease can affect the heart muscles, leading to complications.
- Symptoms such as heart palpitations, fatigue, and chest pain, may manifest.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy:
- Pompe disease can cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, characterised by the thickening of the heart muscle walls.
- This can lead to impaired heart functions and cardiovascular symptoms.
- Implications for daily living:
- Patients may face challenges in performing daily activities independently due to muscle weakness and respiratory limitations.
- Assistive devices such as wheelchairs and respiratory support equipment may become necessary.
How is Pompe disease diagnosed?
- It involves a multi-faceted approach.
- Enzyme assays are conducted to measure the activity of acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA), the deficient enzyme.
- Enzyme tests, often performed on blood or skin cells, provide crucial insights into GAA deficiency.
- Genetic testing identifies mutations in the responsible GAA gene.
- Genetic analysis confirms the presence of specific mutations associated with Pompe Disease.
- The combination of these diagnostic tools enables healthcare professionals to accurately identify and confirm the disease.
Is Pompe disease curable?
- While there is currently no cure, there are treatment options available to manage symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) is a standard treatment, involving the infusion of the missing enzyme to alleviate glycogen buildup.
- ERT is a medical treatment that replaces a missing or deficient enzyme in the body.
Q1) What is Glycogen storage disease type II (GSD2)?
Glycogen storage disease type II (GSD2), also known as Pompe disease, is a metabolic disorder that causes glycogen to build up in muscle tissue. It’s caused by a deficiency of the enzyme α-glucosidase.
Q2) What is Alpha-glucosidase?
Alpha-glucosidase is an enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates into monosaccharides, which can then be absorbed by the small intestine. It’s located in the brush border of the small intestine.
Source: India’s first Pompe disease patient passes away: What is this rare genetic disorder?
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released in the second week of April 2026.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India