What’s in today’s article?
- Historical Ties
- Bilateral Trade
- Strategic Significance and Cooperation
- Common Groupings and Multilateral Cooperation
- Indian Diaspora in Nigeria
- Challenges and Opportunities
- News Summary
Historical Ties
- The historical relationship between India and Nigeria dates back to the colonial era, with both countries sharing a common struggle against colonialism.
- India’s independence in 1947 and Nigeria’s in 1960 created a foundation for solidarity and cooperation.
- Both nations have been members of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), advocating for a world free of geopolitical blocs during the Cold War era.
- Over the decades, their shared experiences and values have cemented a relationship built on mutual respect and shared aspirations.
Bilateral Trade
- Economic engagement is a cornerstone of India-Nigeria relations, with trade being a key driver.
- Trade Volume: Bilateral trade between the two countries exceeds USD 14 billion annually, making Nigeria India’s largest trading partner in Africa.
- Key Imports and Exports:
- India’s Imports from Nigeria: Crude oil dominates, accounting for over 70% of India’s imports from Nigeria. India is one of the largest buyers of Nigerian oil.
- India’s Exports to Nigeria: Pharmaceuticals, engineering goods, automobiles, agricultural machinery, and textiles are significant exports.
- Investment: Indian companies have invested in Nigeria’s energy, manufacturing, and services sectors, contributing to local economic development. Prominent Indian firms such as Tata, Mahindra, and Bharti Airtel operate extensively in Nigeria.
Strategic Significance and Cooperation
- Energy Security: Nigeria’s status as Africa’s largest oil producer is critical for India, a major energy consumer. The partnership ensures a stable supply of crude oil and natural gas.
- Defense and Security: Both nations collaborate on counterterrorism, maritime security, and defense training programs. India’s experience in defense manufacturing and Nigeria’s strategic location in West Africa make this a mutually beneficial partnership.
- Agriculture and Technology: India supports Nigeria’s efforts to modernize its agriculture and improve food security. Joint ventures in ICT and technology transfer further bolster Nigeria’s industrialization.
- Education and Capacity Building: India has offered scholarships and technical training programs under the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) initiative, strengthening Nigeria’s human resource development.
Common Groupings and Multilateral Cooperation
- India and Nigeria collaborate in several international and regional organizations:
- United Nations (UN): Both nations advocate for reforms in global governance structures, including the UN Security Council.
- Commonwealth: Shared membership promotes cultural and political exchanges.
- African Union (AU) and India-Africa Forum: India’s outreach to Africa finds resonance with Nigeria, a prominent player in the AU.
- South-South Cooperation: India and Nigeria work together to promote development in the Global South through platforms like BRICS (India) and the G-77.
Indian Diaspora in Nigeria
- The Indian community in Nigeria, numbering over 60,000, plays a significant role in strengthening bilateral ties:
- Economic Contributions: Indian expatriates are prominent in Nigeria’s trade, industry, and healthcare sectors. Indian-owned businesses contribute to Nigeria’s GDP and job creation.
- Cultural Exchange: The Indian diaspora has introduced cultural elements like cuisine, festivals, and Bollywood to Nigeria, fostering mutual appreciation and understanding.
- Healthcare Services: Indian doctors and healthcare professionals have earned respect in Nigeria for their contributions to the medical field.
Challenges and Opportunities
- While the relationship is strong, challenges persist, including:
- Security Issues: Concerns over piracy and insurgency in Nigeria’s regions can affect Indian investments and diaspora safety.
- Economic Diversification: Overreliance on oil trade needs diversification into other sectors like renewable energy, manufacturing, and infrastructure.
News Summary
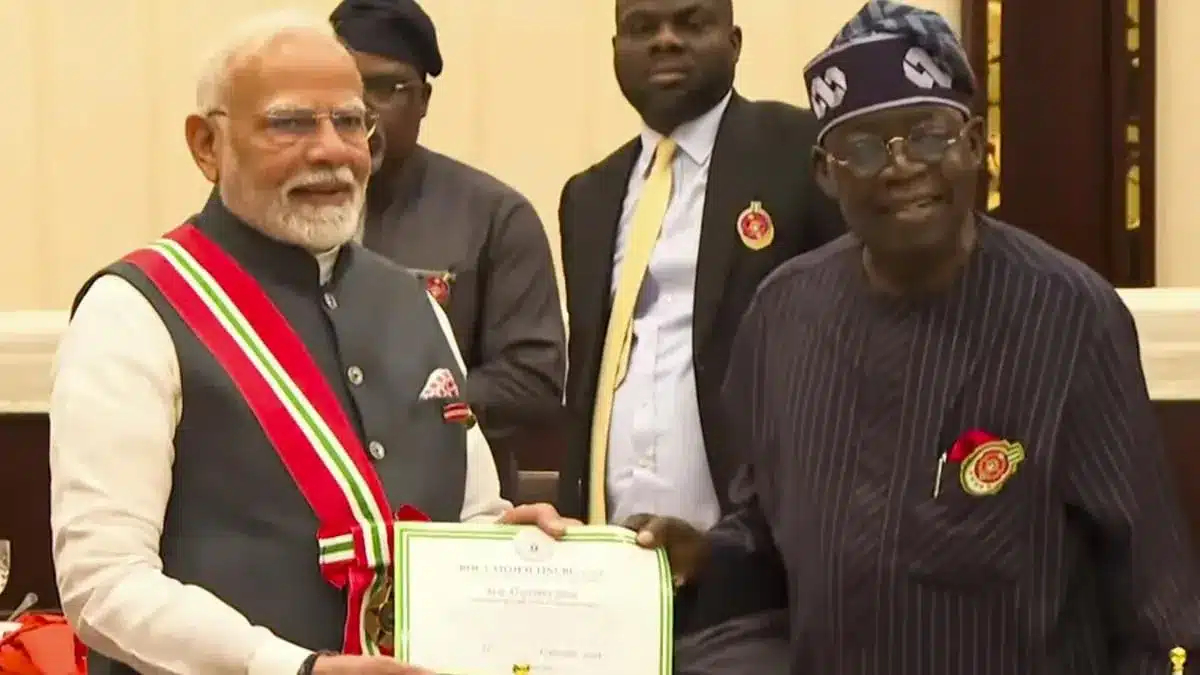
- Nigeria conferred its second-highest national honour, the Grand Commander of the Order of the Niger (GCON), on Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his historic visit—the first by an Indian PM to Nigeria in 17 years.
- PM Modi highlighted the strategic partnership between the nations, focusing on collaboration in defense, energy, trade, technology, health, and education.
- Three MoUs were signed on cultural exchange, customs cooperation, and survey collaboration, alongside India’s provision of 20 tonnes of relief supplies for flood victims.
- With over 200 Indian companies investing $27 billion in Nigeria, PM Modi acknowledged their economic contributions and the role of the 60,000-strong Indian diaspora in strengthening bilateral ties.
- His visit included discussions on counter-terrorism, developmental cooperation, and Africa’s role in global platforms, cementing a robust and multifaceted partnership.
Q1. What is the difference between Embassy and Consulate?
Embassy: Due to its broader range of responsibilities, an embassy is generally larger and staffed with more diplomats and support personnel than a consulate. Consulate: Consulates are smaller in size and have fewer staff members, focusing primarily on providing consular assistance.
Q2. What is the Horn of Africa?
The Horn of Africa, also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa. Located on the easternmost part of the African mainland, it is the fourth largest peninsula in the world. It is composed of Somalia, Djibouti, Ethiopia, and Eritrea.
News: PM Modi receives Nigeria’s second-highest national award
Last updated on February, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India