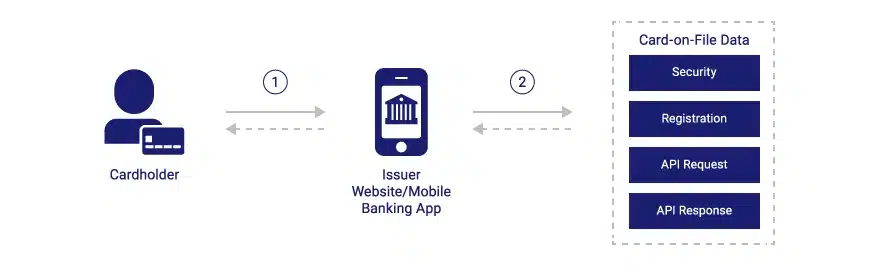
About Card-on-File Tokenization
- Tokenisation refers to replacement of actual credit and debit card details with an alternate code called the “token”.
- It is a combination of card, token requestor and device.
- The card detail when stored with a merchant is known as card-on-file (CoF).
- This token is a randomly generated string of characters that has no intrinsic value and is meaningless outside of the context of a specific transaction.
- The token is used as a surrogate for the actual card details, making it more secure to store and transmit.
- Requirements for enabling CoFT through card issuers:
- Generation of CoFT tokens for a card can be enabled through mobile banking and internet banking channels.
- The token can be generated only on explicit customer consent and with AFA (additional factor authentication) validation.
- The cardholder may tokenise the card at any time of their convenience, either on receipt of the new card or at a later stage
- The cardholder can select the merchants with whom he/she wishes to maintain tokens.
- The card token so issued may be either by the card network or the issuer or both.
- Advantage
- Tokenisation replaces a debit or credit card’s 16-digit number with a unique token that is specific to just your card and is valid for one merchant at a time.
- The token masks the true details of your card, so in case there is a data leak from the merchant website, the fraudster cannot misuse the card.
Q1) What is a Card-on-File transaction?
It is a transaction where cardholders authorizes merchants to store their payment information securely and bill cardholders’ stored accounts for future purchases.
Source: Tokenisation: RBI expands the scope of CoFT to debit cards issuing banks. Details here
Last updated on November, 2025
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is scheduled to be released on January 14, 2026.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Mains Question Paper 2025 is out for Essay, GS 1, 2, 3 & GS 4.
→ UPSC Mains Indian Language Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Mains Optional Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi