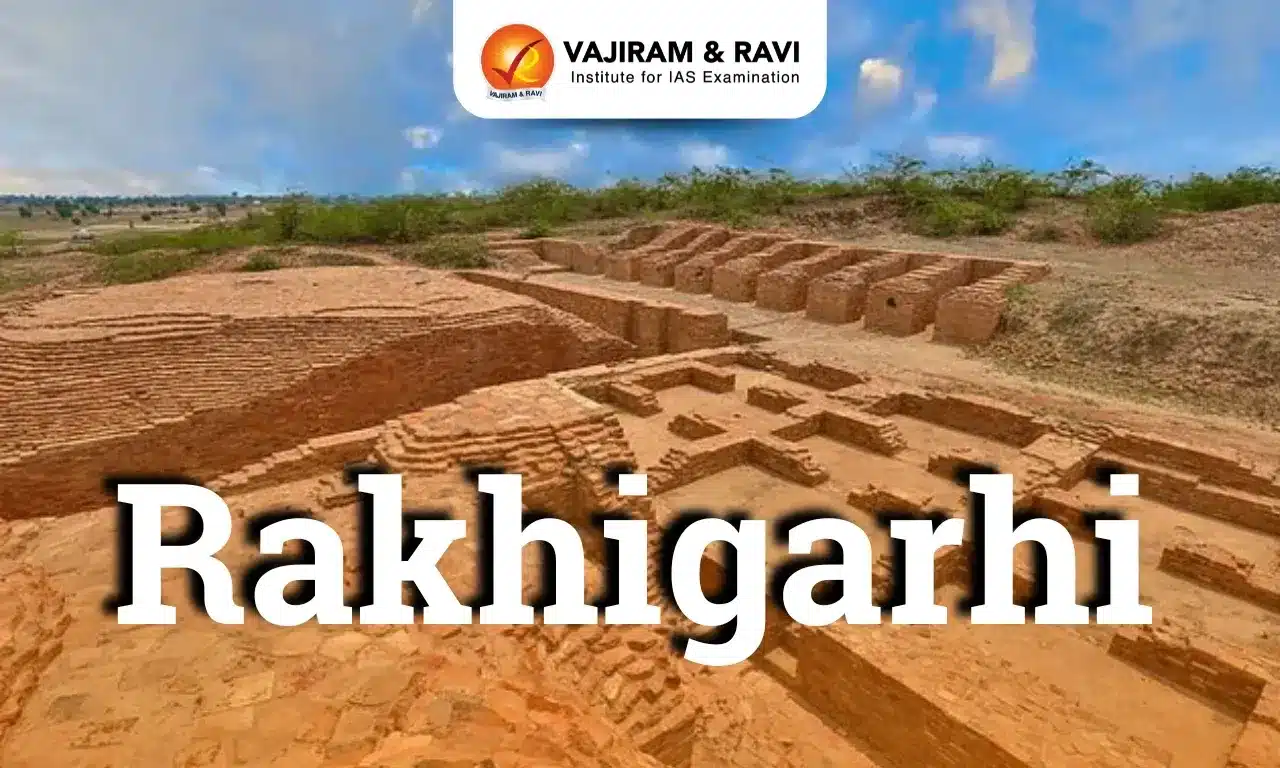
About Rakhigarhi
- Rakhigarhi is an archaeological site located in Hisar district, Haryana, in the Ghaggar-Hakra river plain.
- It is one of the oldest and largest cities of the subcontinent’s earliest known Bronze Age urban culture, the Indus Valley or Harappan Civilization, going back to about 6500 BCE.
- Rakhigarhi constitutes one of the only two cities of the Harappan Era (6th millennium–1900 BC) situated within India’s current political boundary, the other being Dholavira in Gujarat.
- The site was first discovered in the 1960s by the Archeological Survey of India.
- Findings:
- The exploration around this site has clearly identified seven archaeological mounds spread over an area of approximately 350 ha.
- Rakhigarhi primarily yields evidence of occupation during the Early and Mature Harappan periods, with the site being completely abandoned during the Late Harappan period.
- The archaeological excavations revealed the mature Harappan phase, represented by a planned township with mud-brick as well as burnt-brick houses with a proper drainage system.
- The ceramic industry is represented by red ware, which included dish-on-stand, vase, jar, bowl, beaker, perforated jar, goblet, and handis.
- Animal sacrificial pits lined with mud bricks and triangular and circular fire alters on the mud floor have also been excavated, that signifies the ritual system of the Harappans.
- A cylindrical seal with five Harappan characters on one side and a symbol of an alligator on the other is an important find from this site.
- Other antiquities include blades; terracotta and shell bangles; beads of semi-precious stones, terracotta, shell and copper objects; animal figurines, toy cart frame and wheel of terracotta; bone points; inscribed steatite seals, and sealings.
- The excavations have yielded a few extended burials, which certainly belong to a very late stage, maybe the medieval times.
- Rakhigarhi is also well-known as the site which has yielded the only DNA evidence from the Harappan era.
Source :TP
Rakhigarhi Latest FAQs
Q1. On which river is Rakhigarhi civilization?
Ans. Rakhigarhi is situated on the bank of the now dry, Saraswati river
Q2. Who excavated Rakhigarhi first?
Ans. The excavation of Rakhigarhi was first conducted by Dr. V. N. Misra, an Indian archaeologist, in the early 1990s.
Q3. How old is Rakhigarhi?
Ans. Researchers have established that human remains discovered at an ancient site of Rakhigarhi – a village in the Hisar district of Haryana – date back around 8,000 years.
Q4. What is the city of the dead in Harappan civilization?
Ans. Mohenjo-daro! Mohenjo Daro, or “Mound of the Dead” is an ancient Indus Valley Civilization city that flourished between 2600 and 1900 BCE
Last updated on August, 2025
→ UPSC Mains Question Paper 2025 is out for Essay, GS 1 & GS 2.
→ UPSC Mains GS 3 Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Mains GS 4 Question Paper 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi