Proton Emission Latest News
An international collaboration of researchers recently detected and measured the half-life of the heaviest proton emitter, the 188At (astatine) isotope, which decayed by emitting a proton.
About Proton Emission
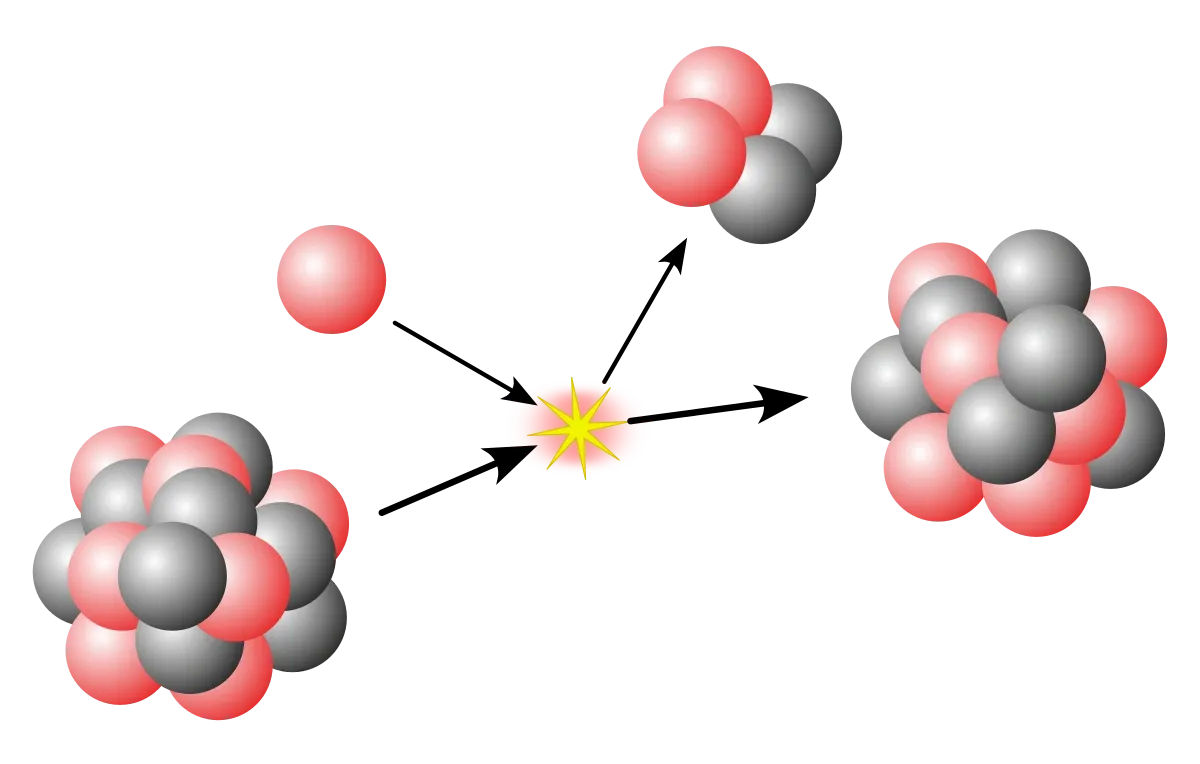
- Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare form of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus.
- Radioactive decay is the process of an unstable atom transitioning to a more stable form.
- It may do so by releasing subatomic particles and energy or by capturing an orbital electron into the nucleus and releasing energy.
- Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay, in which case the process is known as beta-delayed proton emission, or can occur from the ground state (or a low-lying isomer) of very proton-rich nuclei, in which case the process is very similar to alpha decay.
- Alpha decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an unstable nucleus emits an alpha particle. An alpha particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, which is the same as a helium nucleus (⁴₂He).
- Beta decay occurs when a nucleus emits a beta particle, which can be an electron (β⁻) or a positron (β⁺).
- For a proton to escape a nucleus, the proton separation energy must be negative – the proton is therefore unbound, and tunnels out of the nucleus in a finite time.
- Proton emission is not seen in naturally-occurring isotopes; proton emitters can be produced via nuclear reactions, usually utilising some kind of particle accelerator.
- The rate of proton emission is governed by the nuclear, Coulomb, and centrifugal potentials of the nucleus, where centrifugal potential affects a large part of the rate of proton emission.
- The half-life of a nucleus with respect to proton emission is affected by the proton energy and its orbital angular momentum.
- Half-life is the time that it takes for half of the original value of some amount of a radioactive element to decay.
Proton Emission FAQs
Q1. What is proton emission?
Ans. It is a rare form of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a nucleus.
Q2. In which condition does proton emission typically occur?
Ans. In proton-rich nuclei.
Q3. What is required for a proton to be emitted from the nucleus?
Ans. Negative proton separation energy.
Source: TH
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi
Tags: Prelims Pointers proton emission upsc current affairs upsc prelims current affairs