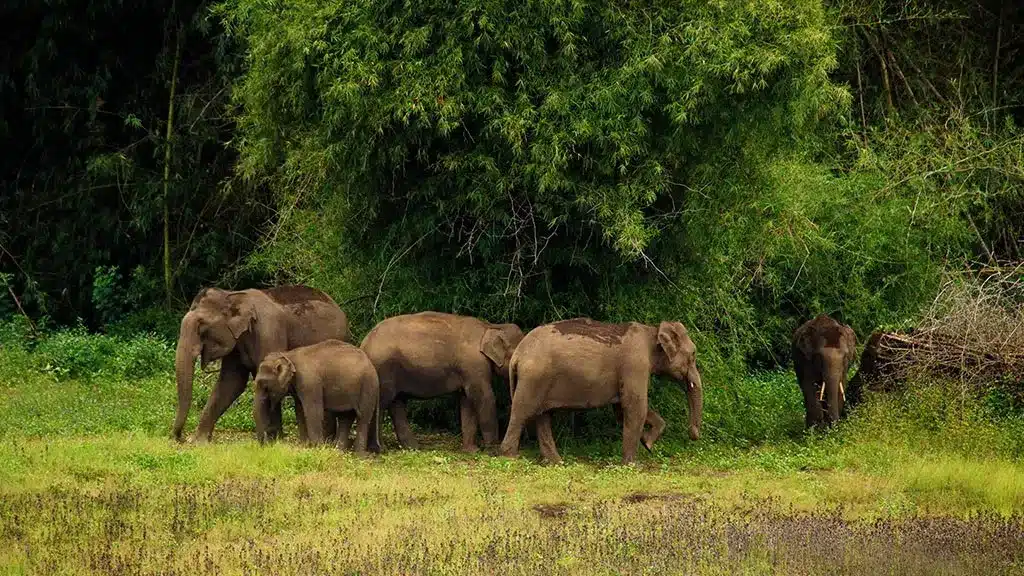
About Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Location: It is located in Wayanad, Kerala, in the southern trenches of the Western Ghats.
- It is an integral part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- It is bordered by the protected areas of Nagarhole and Bandipur in Karnataka on the northeastern side and Mudumalai in Tamil Nadu on the southeastern side.
- Tribes living in these forests include some scheduled adivasis, such as Paniyas, Kattunaikkans, Kurumas, Ooralis, Adiyans, and Kurichiyas.
- Flora:
- It is a mosaic of the Western Ghats’ significant vegetation types, ranging from moist deciduous to dry deciduous and semi-evergreen patches.
- Teak, rosewood, eucalyptus, and silver oak plantations cover roughly one-third of the sanctuary.
- Fauna:
- It is also home to animals like elephants, panthers, tigers, jungle cats, civet cats, monkeys, wild dogs, bison, deer and bears.
- It is known for having the largest population of tigers in Kerala.
Q1: What are Biosphere Reserves (BR)?
BR is an international designation by UNESCO for representative parts of natural and cultural landscapes extending over a large area of terrestrial or coastal/marine ecosystems or a combination thereof.
Source: Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary’s vulture survey records 80 birds
Last updated on August, 2025
→ UPSC Mains Admit Card 2025 has been released on 14th August at www.upsc.gov.in.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi