China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is an infrastructure project initiated in 2015. It aims to enhance China's energy imports and trade while developing Pakistan's infrastructure. The CPEC includes modern transportation networks linking ports in Gwadar and Karachi with northern Pakistan and China's Xinjiang region. Progress on CPEC projects has been slow, with many phase-one initiatives incomplete or not yet started.
However, India opposes CPEC, claiming that some projects infringe upon its sovereignty in territories it considers illegally occupied by Pakistan. CPEC may persist as a major initiative in name, but the realities of economic strain and security risks will likely limit its effectiveness and scope.
About China Pakistan Economic Corridor
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is a 3,000 km infrastructure project that was launched in 2015 to boost China's energy imports and trade while developing Pakistan's infrastructure. The project, valued at $65 billion as of 2022, includes modern transportation networks connecting Gwadar and Karachi ports with Northern Pakistan and the Xinjiang region of China.
CPEC Full Form
Full form of CPEC is China Pakistan Economic Corridor, whose purpose is to act as a development initiative between China and Pakistan that aims to improve trade and connectivity in the region.
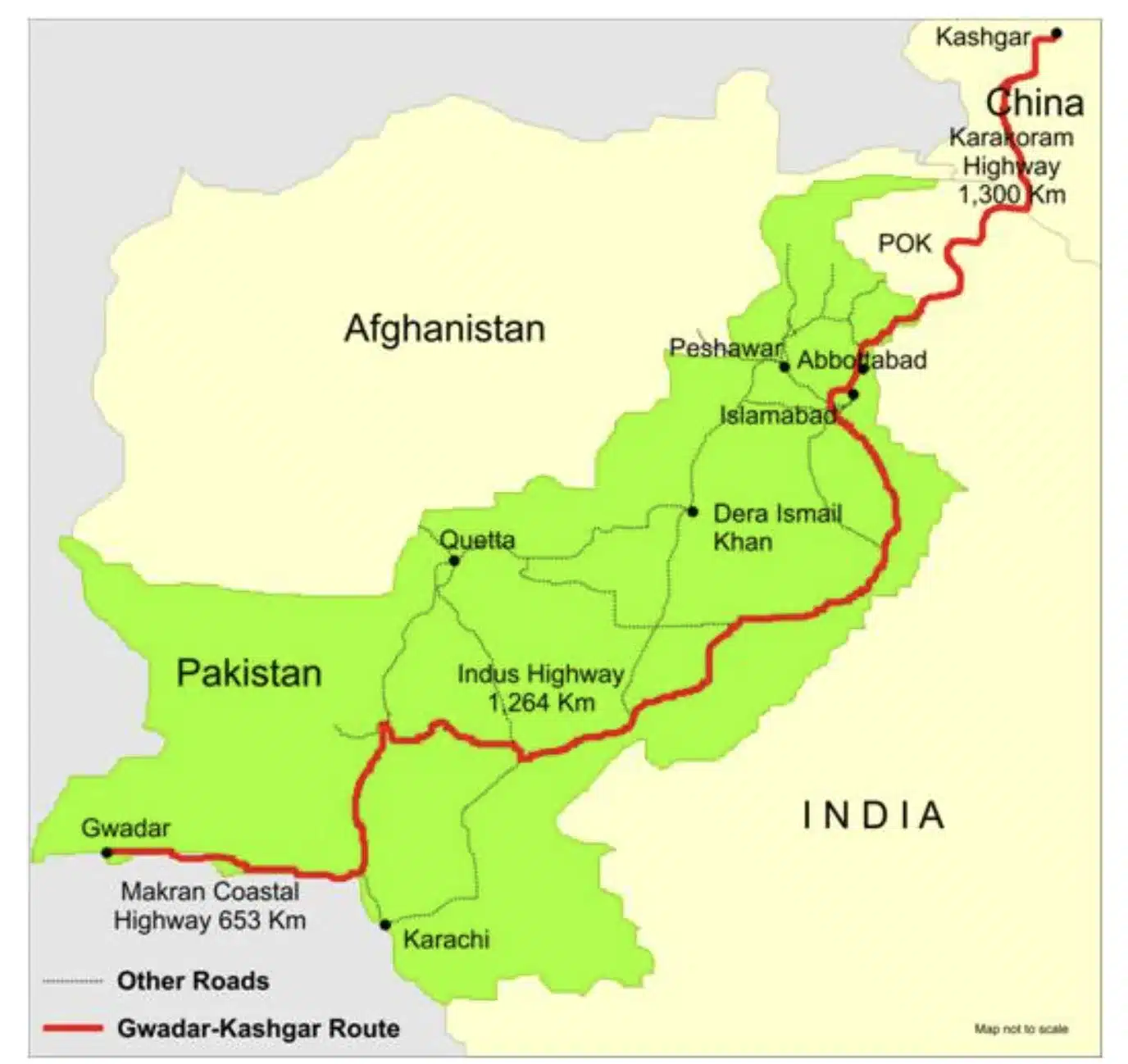
China Pakistan Economic Corridor Map
China Pakistan Economic Corridor Map shows the Gwadar Kashgar Route of CPEC which runs through Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (PoK) and touches some important cities of Pakistan, including Islamabad and Lahore. The map of China Pakistan Economic Corridor is shown below:
China Pakistan Economic Corridor Status
China Pakistan Economic Corridor has been plagued by slow progress due to terrorist attacks on Chinese workers and China’s reluctance to invest further. The status of CPEC is discussed in detail below:
- Investment: The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) has seen an investment of $65 Billion from China.
- Slow Progress: The progress on CPEC projects has been slow, with many phase-one initiatives incomplete or not yet started.
- COVID-19 hindered progress: The COVID-19 pandemic's economic impact further slowed CPEC projects, worsened Pakistan's economic crisis, and prompted China to hesitate in granting debt relief.
- Reduced Focus of China: Key projects such as the Mainline One Railway and upgrades to the Karakoram Highway received a limited commitment from China.
China Pakistan Economic Corridor Impact on India
China Pakistan Economic Corridor has raised issues of sovereignty and security for India since it passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, which falls under the Territory of India. The work on CPEC has progressed without India’s involvement, which has become a matter of serious concern. The details of the impact are discussed below:
- Against India’s Sovereignty: India is against this project because it violates its sovereignty and territorial integrity as it passes through Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
- Against International Norms: India has consistently opposed the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) of which CPEC is a part, arguing that connectivity initiatives must be based on universally recognized international norms, good governance, rule of law, openness, transparency, and equality.
- Debt-Trap Diplomacy: India has also been concerned with the economic non-viability of many of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) projects that have led to “debt trap” situations in countries like Sri Lanka.
- Naval blockade: India's concerns are heightened by the Gwadar port's closeness to the Strait of Hormuz, a vital international trade route, which could allow China to control maritime trade and interfere with Indian naval operations.
- Military Alliance: India's defense readiness is called into question by the possible military presence along the corridor.
CPEC Counter Measures by India
China Pakistan Economic Corridor and its broader Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) have been proactively countered by India in the Indian Ocean. The Indian strategy involves economic, military, and diplomatic strategies. The details are discussed below:
- Necklace of Diamonds: India initiated the Necklace of Diamonds strategy, aiming to encircle China by increasing its naval presence and extending its military base and diplomatic ties.
- Chabahar Port: India is constructing the Chabahar port (Iran) to counter Pakistan's Gwadar port, a key component of CPEC, offering a strategic position and a direct trade route to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
- QUAD: The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) formation has enhanced India's strategic cooperation with the US, Japan, and Australia, contributing to the freedom, openness, and inclusivity of the Indo-Pacific region, while not directly addressing China.
- Act East Policy: The Act East Policy helps to counter Chinese influence by establishing India's bilateral and multilateral security and strategic cooperation with Southeast Asian countries.
India perceives the Chinese CPEC project as a strategic plan to reduce its regional and global power. It is believed that China's policy is to balance Indo-US strategic cooperation in the region.
China Pakistan Economic Corridor UPSC PYQs
Q.1 The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is viewed as a cardinal subset of China’s larger ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative. Give a brief description of CPEC and enumerate the reasons why India has distanced itself from the same. (UPSC Mains 2018)
Q.2 “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (UPSC Mains 2017)
Q.3 China and Pakistan have entered into an agreement for the development of an economic corridor. What threat does this pose to India’s security? Critically examine. (UPSC Mains 2014)
Q.4 Belt and Road Initiative is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (UPSC Prelims 2016)
(a) African Union
(b) Brazil
(c) European Union
(d) China
Ans. (d)
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
China Pakistan Economic Corridor FAQs
Q1. What is the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor Agreement?+
Q2. What is the main purpose of CPEC?+
Q3. When was the CPEC launched?+
Q4. Who started CPEC?+
Q5. Who is paying for CPEC?+
Tags: china pakistan economic corridor cpec quest UPSC International Relations and Institutions Notes