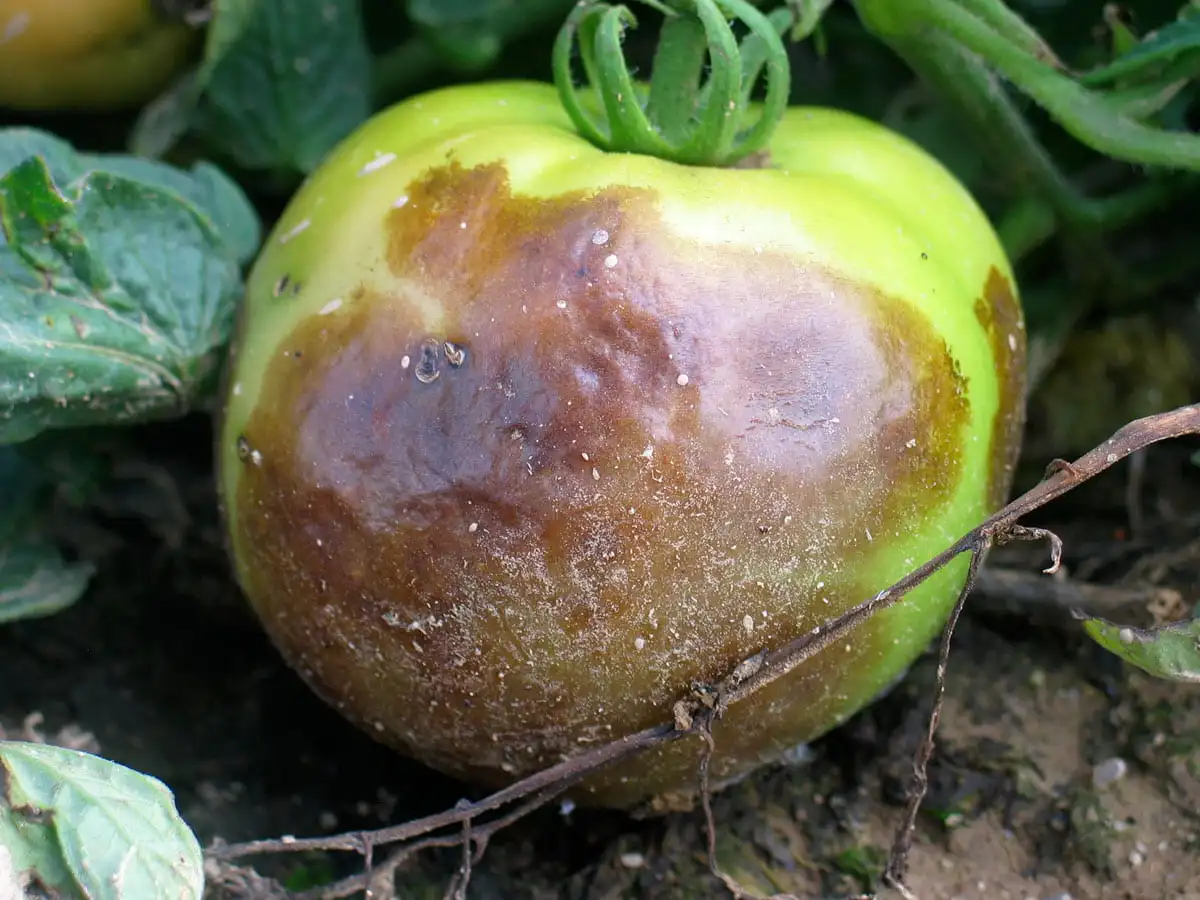
About Fruit Rot Disease:
- It is a plant disease that can cause significant losses for farmers, as it can reduce the quality of the crop and make it unmarketable.
- In some cases, fruit rot can also lead to the death of the plant.
- It is caused by a number of different fungi, bacteria, and viruses, and it can be difficult to prevent and treat.
- Continuous heavy rainfall coupled with low temperature (20 to 23 °C), high relative humidity (>90%), and intermittent rain and sunshine hours favour the occurrence of fruit rot.
- Symptoms:
- Brown or black spots on the fruit
- Softening of the fruit
- Shrivelling of the fruit
- Mould growth on the fruit
- There are many different types of fungi that can cause fruit rot, but the most common type is Botrytis cinerea.
- This fungus affects a wide range of fruits, including grapes, strawberries, tomatoes, and peppers.
- The fungus enters the plant through wounds in the leavesor fruit lesions, and it proliferates in humid conditions.
- Once established, the fruit infections can spread rapidly through the crop, causing rot.
- The fungi that cause fruit rot can also produce toxins that are harmful to humans and animals.
Q1: What are Fungi?
Fungi (singular-Fungus) are eukaryotic organisms that include moulds, yeasts, and related organisms like mushrooms within the kingdom Fungi. Fungi come in both unicellular and multicellular forms, with yeast representing the simplest unicellular type and moulds like Rhizopus, Mucor, and Penicillium are examples of multicellular fungi. They exhibit greater complexity and size compared to bacteria and can function as either saprophytes or parasites.
Source: CPCRI issues advisory to control koleroga disease in arecanut plantations
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi