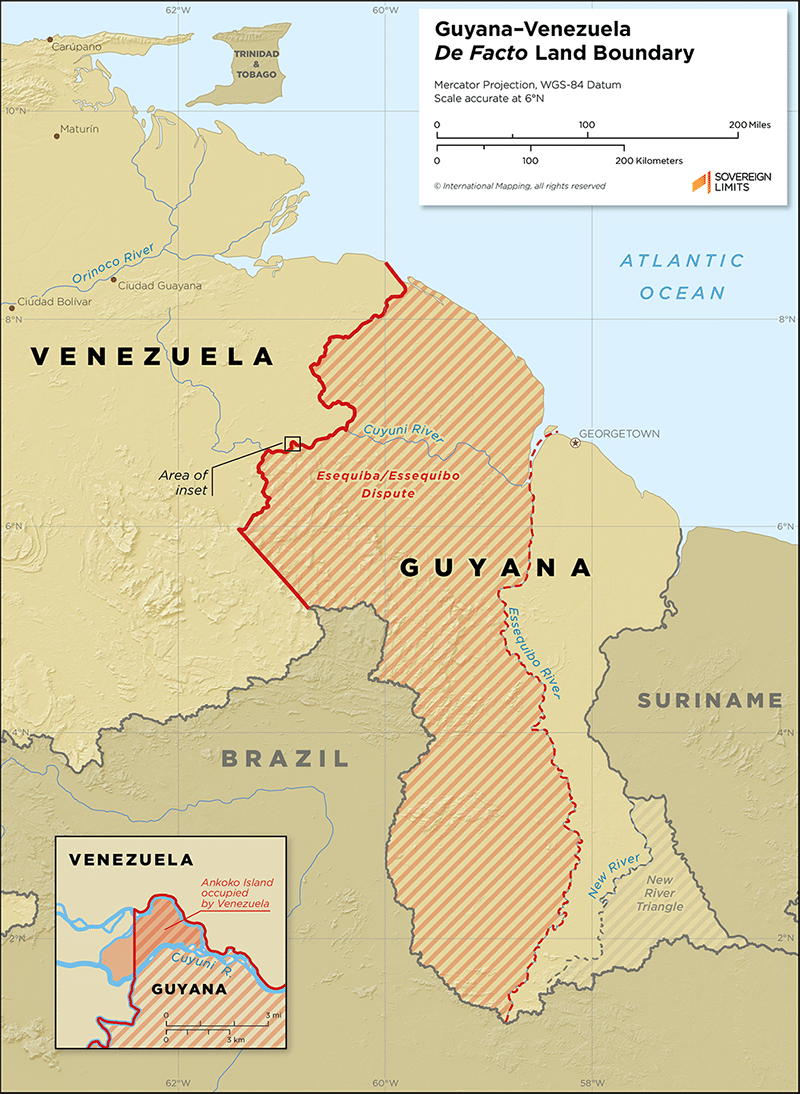
About Guyana-Venezuela Border Dispute:
- History:
- The land boundary between Guyana and Venezuela has been disputed since its colonial inception between British and Spanish powers in South America.
- In the 1840s, the British government had the border unilaterally surveyed, but the proposed line encroached on Venezuelan territorial claims.
- The boundary has since been arbitrated (1899) and bilaterally agreed upon following demarcation (1905) but remains in conflict.
- While the British line, accepted by Guyana, is the current de facto boundary, Venezuela maintains a historic claim to all territory currently administered by Guyana west of the Essequibo River.
- Venezuelan contents that the Arbitral Award of 1899 about the frontier between British Guiana and Venezuela is null and void.
- Disputed Area:
- Venezuela’s claim along the Essequibo River extends for 1,034 kilometers before reaching Brazilian territory.
- At stake is approximately 142,795 square kilometers that is currently administered by Guyana.
- Offshore the disputed land territory is maritime space that was recently discovered to be rich in hydrocarbon resources, upping the stakes of the land boundary dispute.
- Current Status:
- Guyana submitted the dispute to the International Court of Justice in 2018.
- Despite Venezuela’s withdrawal from the case, proceedings are currently ongoing.
Q1) What is the International Court of Justice (ICJ)?
The International Court of Justice, which has its seat in The Hague,is the principal judicial organ of the United Nations. The Court’s role is to settle, in accordance with international law, legal disputes submitted to it by States and to give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by authorized United Nations organs and specialized agencies.
Source: World Court says it can rule on Guyana-Venezuela border dispute
Last updated on June, 2025
→ UPSC Notification 2025 was released on 22nd January 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Result 2025 is out now for the CSE held on 25 May 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims Question Paper 2025 and Unofficial Prelims Answer Key 2025 are available now.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 is released on 15th May, 2025.
→ The UPSC Vacancy 2025 were released 1129, out of which 979 were for UPSC CSE and remaining 150 are for UPSC IFoS.
→ UPSC Mains 2025 will be conducted on 22nd August 2025.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ UPSC Result 2024 is released with latest UPSC Marksheet 2024. Check Now!
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best IAS Coaching in Delhi