Komagata Maru incident of 1914 marked a pivotal moment in the Indian freedom struggle, highlighting racial discrimination against Indian immigrants. Gurdit Singh chartered the Japanese ship to transport 376 passengers to Canada, but they were denied entry due to Canada’s discriminatory immigration laws. The ship was forced to return to India, underscoring the injustices of colonial rule.
Komagata Maru incident fueled the Ghadar Movement, with revolutionaries highlighting colonial injustices and mobilizing support for Indian independence. It ignited unrest in Punjab, strengthening anti-colonial sentiment and becoming a powerful symbol of resistance against racial discrimination. The incident’s legacy inspired future generations to continue the fight for India's freedom.
Komagata Maru Incident Overview
Komagata Maru Incident of 1914 was a key moment in the Indian freedom struggle, symbolizing resistance against racial discrimination. Gurdit Singh, a Singapore-based Indian businessman and activist, chartered the Japanese ship Komagata Maru (renamed Guru Nanak Jahaz) to transport 376 Indian passengers, mostly Sikhs, from East and Southeast Asia to Canada.
- However, the passengers were denied entry upon arriving in Vancouver due to Canada's discriminatory immigration laws.
- The ship was forced to return to India, highlighting racial injustice and rallying Indian immigrants to support the nationalist movement against British colonial rule.
Reasons for Komagata Maru's Denial of Entry
Canadian government immediately amended the legislation and reinstated the Continuous Journey Regulation three months before the departure of Komagata Maru to Vancouver. After arriving in Vancouver, the Canadian authorities did not allow passengers to disembark, citing Continuous Journey regulation as the main reason.
- Of 376 passengers, only 20 who managed to prove their residential status were permitted to disembark. The ship was scheduled to sail back to India on July 23, 1914.
Komagata Maru Incident
Komagata Maru Incident of 1914 was a crucial event in both Canadian and Indian history, marked by a series of significant developments. Baba Gurdit Singh hired the ship to facilitate the entry of Indians into Canada. The ship carrying 376 passengers sailed from Hong Kong on April 3 and reached Vancouver Harbour on May 22, 1914.
- Canadian Immigration Policies: Canada enforced strict laws restricting Indian immigration, allowing only those who travelled directly from India to Canada on their ship.
- Supreme Court Ruling (1913): In November 1913, the Supreme Court of Canada allowed 35 Indians to enter Canada after making a continuous journey. This ruling motivated Gurdit Singh, an Indian contractor from Singapore, to act.
- Chartering Komagata Maru: Inspired by the court ruling, Gurdit Singh chartered the Japanese ship Komagata Maru to transport Indian passengers from East and Southeast Asia to Vancouver, Canada.
- Ghadar Party Involvement: At a stop in Yokohama, Japan, Ghadar Party members (Ghadarites) boarded the ship, delivering revolutionary speeches and distributing anti-colonial literature to the passengers.
- Denied Entry in Vancouver: Upon arrival in Vancouver, Canadian authorities denied the passengers entry. In response, a Shore Committee led by Hussain Rahim, Sohan Lal Pathak, and Balwant Singh was formed to advocate for the passengers' rights.
- Campaign in the U.S.: Indian activists such as Barkatullah, Bhagwan Singh, Ram Chandra, and Sohan Singh Bhakna launched a strong campaign in the U.S. in support of the Komagata Maru passengers, but despite these efforts, the ship was forced to leave Canadian waters.
- World War I and Return Journey: As the ship sailed back, World War I broke out, and the British government ordered that passengers could only disembark in Calcutta.
- Tragic Clash at Budge Budge: On September 27, 1914, the ship arrived at Budge Budge, near Calcutta. Following harassment and hostility from authorities, a violent clash occurred, resulting in the death of 18 passengers.
- The Budge Budge tragedy sparked unrest, especially in Punjab, leading to a series of political robberies in the districts of Jalandhar, Amritsar, and Ludhiana, in response to the perceived injustices suffered by the passengers.
Komagata Maru Incident Response of Ghadar Party
Ghadar Party, a revolutionary group, had a crucial role in reacting to the Komagata Maru incident and leveraging it to advance their cause. Below are the key aspects of the Ghadar Party's response:
- Exposing Human Rights Abuses: The Komagata Maru incident revealed the arbitrary detention and mistreatment of passengers by British authorities. This exposed the repressive nature of British rule in India, raising awareness about the urgency of Indian independence.
- Discriminatory Laws: The incident spotlighted Canada's discriminatory immigration laws, particularly the Asian Exclusion Act, which restricted Asian immigration. It challenged racial prejudices and the colonial mindset behind such policies.
- Ghadar Party's Mobilization: The Ghadar Party used the Komagata Maru incident as a rallying point to gather support for a large-scale uprising against British colonialism, intensifying the push for Indian independence.
- International Solidarity: As the ship stopped at various ports, Ghadar leaders, including Sohan Singh Bakhna and Bhai Bhagwan Singh, visited the passengers, providing arms and ammunition, and delivering speeches. These actions attracted international support and raised global awareness of the Indian independence movement.
Komagata Maru Incident Significance
Komagata Maru incident exposed the racial discrimination Indians faced abroad. It also shattered the belief that being British subjects would not guarantee equal treatment, as essential amenities, food, water, and medical care were not provided for two months.
- The incident played a significant role in Indian Nationalism. It aggravated the anti-colonial sentiments and galvanised the Ghadar Movement.
- The incident sparked significant uproar in Punjab, particularly in the Amritsar district, leading to broad engagement in the movement against colonial rule.
Komagata Maru Incident Legacy
The Komagata Maru incident left a lasting legacy in India’s independence movement. In 2016, Trudeau, then Prime Minister, formally apologized in the House of Commons for the incident. He also referred to it as a “dark chapter” in the country’s history.
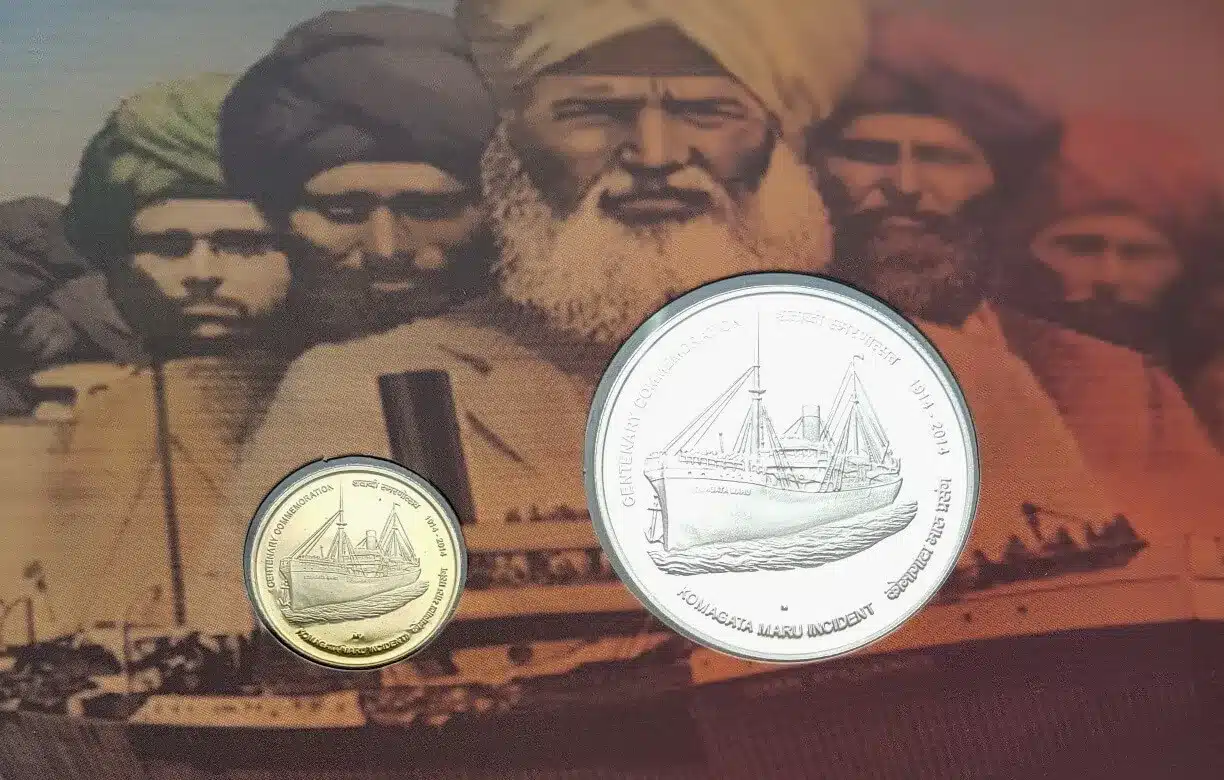
- To commemorate the centenary of the struggle of the Komagata Maru passengers, the Canadian postal department issued a stamp in 2014.
- Similarly, the Indian government issued commemorative coins in denominations of one hundred and five rupees in the same year.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC has released UPSC Toppers List 2025 with the Civil Services final result on its official website.
→ Anuj Agnihotri secured AIR 1 in the UPSC Civil Services Examination 2025.
→ UPSC Marksheet 2025 Will be out soon.
→ UPSC Notification 2026 & UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Shakti Dubey secures AIR 1 in UPSC CSE Exam 2024.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Komagata Maru FAQs
Q1. What was Komagata Maru incident?+
Q2. Who chartered the Komagata Maru?+
Q3. What happened to the passengers of Komagata Maru when they returned to India?+
Q4. How did the Ghadar Party respond to the Komagata Maru incident?+
Q5. What was the significance of the Komagata Maru incident?+
Tags: Komagata Maru Incident quest upsc modern history notes