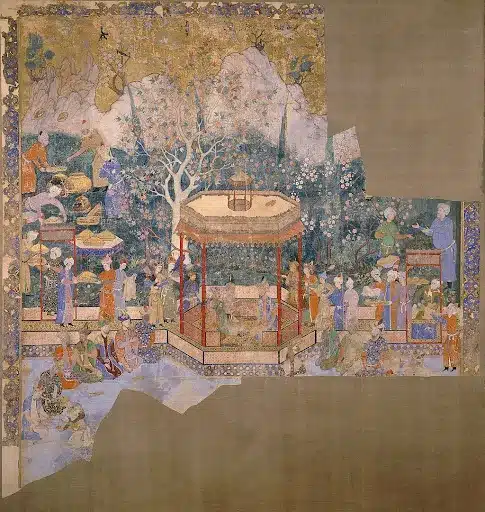
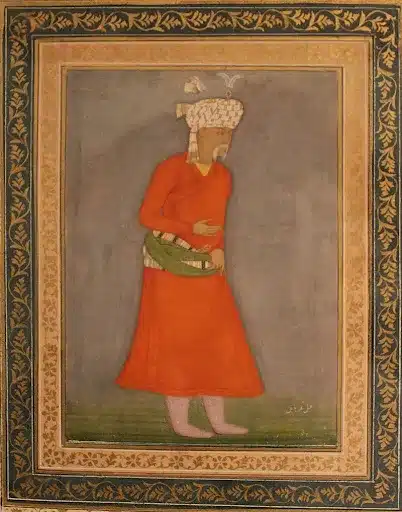
Mughal paintings are a distinguished Indian painting form that flourished during the Mughal Empire, particularly between the 16th and mid-19th centuries. Renowned for its intricate Persian miniature style, Mughal painting was primarily created on paper for book illustrations or as standalone pieces in albums known as muraqqa.
Mughal paintings emphasise realistic portraiture and detailed, lifelike depictions of animals and plants. Over time, Mughal paintings gave rise to regional styles often described as "post-Mughal" or "provincial Mughal," leaving a lasting impact on South Asia.
Mughal Paintings Origin
Mughal painting, a distinctive art form of the Indian subcontinent, emerged during the 16th century under the patronage of the Mughal Empire. Its origins trace back to the fusion of Persian miniature painting with indigenous Indian styles, influenced by the cultural exchanges facilitated by the Mughal court.
- The foundation for Mughal painting was laid by the early Mughal emperors, especially Humayun, who, during his exile in Persia, invited Persian artists Mir Sayyid Ali and Abd al-Samad to India.
- These Persian artists, following Humayun's guidance, produced several remarkable artworks, including the famed Khamsa of Nizami.
- Unlike conventional Persian art, these creations marked the beginning of a distinct style known as Mughal painting.
- Under Mughal Emperor Akbar's reign (1556–1605), these influences amalgamated, leading to the establishment of a royal atelier that produced richly illustrated manuscripts such as the Hamzanama.
- Emperor Jahangir (1605–1627) further refined this art form by emphasising naturalistic elements and incorporating European artistic techniques, resulting in lifelike portraits and studies of flora and fauna.
- Over time, the Mughal school incorporated elements from Indian, Persian, and European art, resulting in a rich, syncretic visual culture that influenced later regional painting traditions across India.
Mughal Paintings Features
Mughal paintings are a distinctive form of Indian miniature art that flourished under the Mughal Empire, known for their intricate details, vibrant colours, and a unique blend of Persian, Indian, and European artistic styles. Major Mughal Paintings features are:
- Miniature Paintings: Mughal paintings were characterised by their compact size, which is why they are commonly referred to as "miniature paintings."
- Emphasis on Realism and Naturalism: A hallmark of Mughal painting is its commitment to realism. Artists meticulously depicted flora, fauna, and human figures with lifelike precision, reflecting a keen observation of the natural world.
- Diverse Subject Matter: The thematic range of Mughal paintings is vast, encompassing royal portraits, court scenes, battles, hunting expeditions, and depictions of nature.
- Use of Rich Materials: Artists employed high-quality materials, including fine paper, gold, and vibrant pigments derived from minerals and plants.
- Method of Foreshortening: They introduced the method of foreshortening to Indian artists, a technique where objects are depicted in a manner that makes them appear nearer and smaller than their actual size.
Mughal Painting Process
Mughal painting process typically appeared as miniatures in manuscripts and royal albums, integrating visual art and text within a single format. The creation of book paintings started with preparing and cutting handmade paper to fit the manuscript size. This process allowed designated spaces for the artist’s compositions. After the text was added to the pages, the artist followed these steps:
- Initial Composition (Tarh): The artist created a rough sketch of the overall layout.
- Portraits (Chiharanama): The artist then focused on developing detailed portraits.
- Colouring Stage (Rangamizi): Finally, the artist added colours to bring the artwork to life.
Colours and Techniques Used in Mughal Paintings
Mughal paintings are celebrated for their vibrant colours and intricate details, achieved through natural pigments, fine brushes, and meticulous techniques. These masterpieces were often collaborative efforts, reflecting the artistic excellence of the Mughal era.
- Natural Pigments for Vibrant Colours: Mughal painters meticulously sourced their colours from natural materials.
- Bright red came from cinnabar (vermilion), blue from lapis lazuli (ultramarine), yellow from orpiment, while white was created by grinding shells.
- Lampblack, derived from charcoal, provided rich black tones, and precious metals like gold and silver were either mixed with colours or dusted for a shimmering effect.
- Handmade Paper Preparation: The paintings were created on specially prepared handmade paper. This surface was treated to achieve a smooth, durable texture suitable for detailed artwork, ensuring longevity and brilliance.
- Brushes of Animal Hair: Painters used brushes crafted from the fine hair of squirrels or kittens, providing precise control for intricate details, essential for the delicate and refined style of Mughal miniatures.
- Collaborative Workshop Model: Artwork creation was often a team effort. One artist sketched the initial outline, another prepared pigments, a third filled in colours, and a fourth added intricate details.
- Burnishing with Agate Stone: Once completed, the painting was polished using an agate stone, which not only set the colours but also enhanced their radiance, giving the artwork a luminous finish.
Mughal Paintings Under Mughal Emperors
Mughal paintings under Mughal emperors flourished between the 16th century AD and the 18th century AD, blending Persian, Indian, and Central Asian styles. Each emperor, from Akbar to Aurangzeb, influenced the evolution of this distinctive artistic tradition.
Mughal Paintings Under Babur
After a series of battles, Babur founded the Mughal dynasty. Although his reign was brief, limiting his ability to extensively commission artwork, he is believed to have supported the Persian artist Bihzad, who created illustrations depicting the Mughal family lineage.
Mughal Paintings Under Humayun
Mughal paintings under Humayun were influenced by his exposure to Persian miniature art while in exile at the Safavid court. Humayun commissioned a large painting titled Princes of the House of Timur, originally a group portrait featuring his sons. This work was later expanded by Jahangir to include deceased ancestors.
- Persian Artists: Upon returning to India, Humayun brought two accomplished Persian artists, Abd al-Samad and Mir Sayyid Ali, to establish a studio in his royal court.
- Khamsa of Nizami: His major commission, a Khamsa of Nizami, featured 36 illuminated pages showcasing diverse artistic styles.
Mughal Paintings Under Akbar
Mughal Paintings Under Akbar flourished as a distinctive art form, blending Persian, Indian, and Central Asian styles. Akbar's patronage transformed painting into a royal enterprise, with a vibrant atelier of skilled artists.
- Tasvir Khana: Mughal Emperor Akbar set up a specialised department focused on painting and manuscript preparation. Known as the Tasvir Khana, this formal art studio employed artists on a salary basis, allowing them to develop unique artistic styles under royal patronage.
- Characteristics of Akbar-Era Art: Paintings from Akbar’s reign are recognised for their use of three-dimensional figures and the technique of foreshortening, which added depth and perspective to the artwork.
- Integration of Calligraphy: Artists during Akbar’s period frequently incorporated calligraphy into their works, blending visual art with literary beauty, making the artworks more refined.
- Shift from Popular to Court Art: This era marked a transition from popular folk art to sophisticated court art, with a focus on depicting royal scenes, courtly life, and imperial grandeur rather than the lives of common people.
- Notable Artists: Prominent painters of Akbar’s time included Daswanth, Basawan, and Kesu, who gained recognition for their exceptional skills and contributions.
- Famous Illustrated Manuscripts: Some of the most celebrated illustrated manuscripts produced during Akbar's reign include Tutinama, Hamzanama, Anvar-i-Suhaili, and Gulistan of Sadi.
Mughal Paintings Under Jahangir
Mughal Paintings Under Jahangir saw a significant evolution, marked by intricate detail, vibrant colours, and a blend of Persian and Indian influences. Mughal paintings reached their peak during the reign of Jahangir.
- Shift to Albums: Jahangir had a strong affinity for nature, favouring paintings that depicted flora and fauna, such as birds, animals, trees, and flowers. His preference shifted from illustrated manuscripts to creating albums, with a focus on infusing naturalism into portraiture.
- Ornate Margins: A distinctive feature of this period was the development of ornate margins surrounding paintings, which often rivalled the intricacy of the artwork itself.
- Muraqqas: The practice of mounting individual paintings into albums, known as Muraqqas, gained popularity during his reign.
- Blending of European Themes: Jahangir's exposure to European artworks and decorative objects sparked his interest in European themes. This led to a vibrant blend of these influences with the Indo-Iranian style in the Jahangir school of art.
- Notable Paintings:
- Jahangir’s Dream was created by painter Abul Hasan.
- Further, the painting of Jahangir in Darbar from the Jahangirnama was attributed to Abul Hasan and Manohar.
Mughal Paintings Under Shah Jahan
Mughal paintings under Shah Jahan emphasised a blend of imagination and documentation, with artists encouraged to create magnificent works. Idealisation and stylisation were more important than realistic depiction, highlighting beauty with bright colours and detailed designs.
- Features: During this period, Mughal paintings featured multiple perspectives, a rich colour palette, and sophisticated compositions.
- They depicted royal, historical, and mystical themes.
- Shah Jahan's admiration for sparkling jewels and monumental architecture was evident in the paintings created during Shah Jahan’s reign.
- Moreover, during his period, the Mughal School of Painting inspired European artists, including Rembrandt, who studied Indian drawings to master delicate lines.
- The Padshahnama stands out as one of the most significant painting projects of his court, highlighting the peak of Indian miniature painting.
Mughal Paintings Under Aurangzeb
Mughal Paintings under Aurangzeb saw a decline in artistic patronage, as Aurangzeb himself did not support painting. Consequently, many Mughal court painters left for provincial courts in places like Rajasthan, leading to a significant decrease in painting activities during his reign.
Mughal Paintings Under Muhammad Shah
Mughal Paintings under Muhammad Shah witnessed a short-lived revival, thanks to the emperor's strong patronage of the arts. He brought in two of the era's finest artists, Nidha Mal and Chitarman. Their works frequently depicted royal court scenes, grand feasts, celebrations, the king's hunting adventures, and daring activities like hawking.
Famous Painters During Mughal Period
Mughal paintings were characterised by collaboration among skilled artists, blending Persian influences with Indian techniques. Renowned painters from the Mughal court, including early Persian artists and later Indian masters, significantly shaped the evolution of Indian Paintings.
- Persian Influence: Early Persian painters, such as Mir Sayyid Ali and Abd al-Samad, played a vital role in shaping the Mughal art style.
- Key Mughal Artists: Artists like Daswanth, Basawan, Miskin, and Lal were instrumental in sustaining Mughal painting in the 16th and 17th centuries.
- Govardhan’s Legacy: The renowned painter Govardhan worked under the reigns of Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan, contributing significantly to Mughal art.
- Other Notable Artists: Artists like Kamal, Mushfiq, and Fazl made significant contributions to the development of Mughal paintings.
- Artists in Rajput Courts: With the decline of the Mughal Empire, artists such as Bhawanidas and Dalchand found employment in Rajput courts, continuing their artistic endeavours.
Mughal Paintings Decline
The decline of Mughal paintings can be attributed to several factors, primarily the weakening of the Mughal empire in the 18th century. As imperial patronage diminished, so did the funding and support for artists.
- The later Mughal emperors, particularly after Aurangzeb, were less interested in the arts, leading to a reduced focus on courtly painting.
- Additionally, external pressures, such as invasions and the rise of regional powers, disrupted the traditional Mughal art workshops.
- The growing influence of British rule in India further marginalised Mughal painting, as Western styles and techniques began to dominate.
- While Mughal painting saw a brief revival during the reign of Emperor Muhammad Shah, it never fully regained its former prominence.
- Over time, the unique Mughal style blended with other regional and European influences, leading to a gradual transformation rather than a complete continuation of its original form.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Mughal Paintings FAQs
Q1. Which is the Mughal famous painting?+
Q2. What are the main features of Mughal painting?+
Q3. What was Mughal art called?+
Q4. Who is the father of Mughal art?+
Q5. Which Mughal painting is most expensive?+