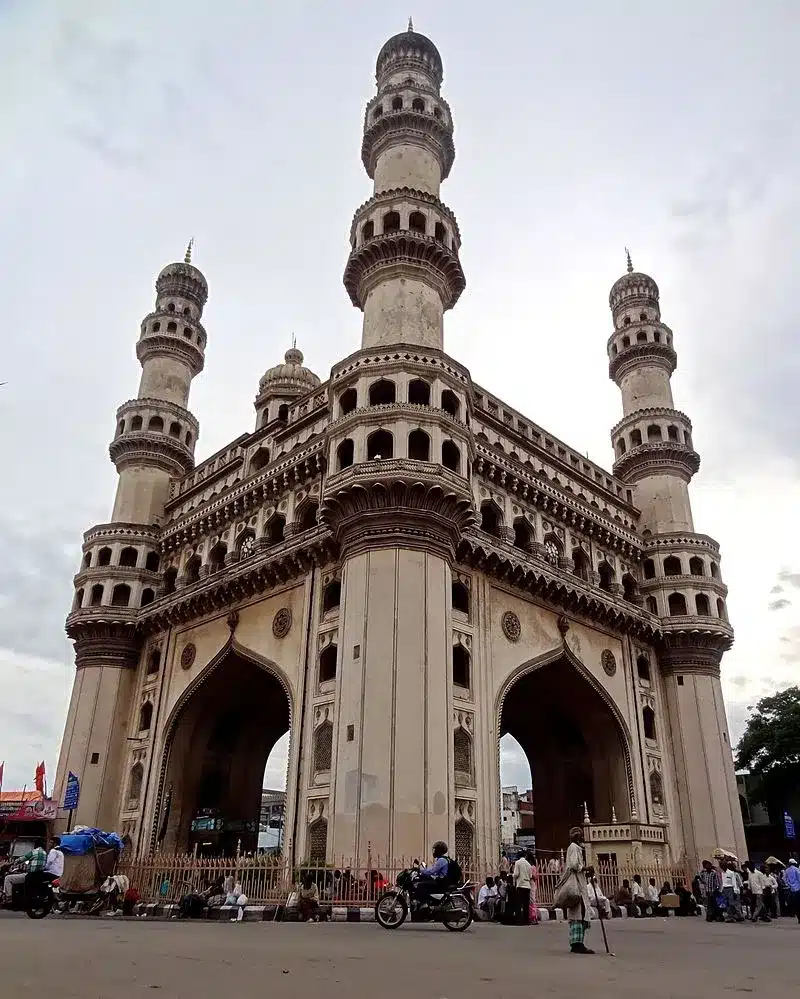
Deccan Sultanates emerged in the 15th century after the Bahmani Sultanate's decline, forming five states: Bijapur, Ahmednagar, Berar, Golconda, and Bidar. Despite their rivalries, they united to defeat the Vijayanagara Empire. These Sultanates significantly influenced architecture, art, and literature, with iconic monuments like Gol Gumbaz and Charminar and structures like Janjira and Ahmednagar forts.
However, internal discord, weak governance, and external pressures from the Mughal Empire, particularly under Akbar and Aurangzeb, accelerated their decline. Aurangzeb's military campaigns led to the annexation of Bijapur in 1686 and Golconda in 1687, marking the end of the Sultanates.
Deccan Sultanates Overview
Deccan Sultanate emerged as a powerful force in the Indian subcontinent after the disintegration of the Bahmani Sultanate in the 15th century. Initially, the Northern Deccan plateau was governed by the Bahmani Sultanate and the Sultanate of Khandesh, while the Southern region was under the Vijayanagar Empire.
- As the Bahmani Sultanate fragmented, it gave rise to five distinct Sultanates.
- The five states which were collectively called the Deccan Sultanates were: Adil Shahi of Bijapur (1490), Nizamshahi of Ahmednagar (1490), Imad Shahi of Berar (1490), Qutb Shahi of Golconda (1518), and Barid Shahi of Bidar (1528).
- NizamShahi, Adil Shahi, and Qutb Shahi rulers promoted coexistence.
- Although rivals, the Sultanates united in 1565 to defeat the Vijayanagar Empire, severely weakening it in the Battle of Talikota.
Deccan Sultanates Ahmednagar Sultanate
Ahmednagar Sultanate (Nizam Shahi dynasty) was part of the Deccan Sultanates, located between the sultanates of Gujarat and Bijapur. It was established in 1490 by Malik Ahmed Nizam Shah I, the Bahmani governor of Junnar, after defeating the Bahmani army. Initially, the capital was in Junnar, later renamed Shivneri, but in 1494, Malik Ahmed founded the new capital, Ahmednagar.
- After he died in 1510, his son Burhan Shah I succeeded him, followed by Hussain Shah I, and later Murtaza Shah.
- Murtaza Shah annexed Berar in 1574, and after his death, Ibrahim Shah briefly ruled before being succeeded by his infant son Bahadur Nizam Shah, with Chand Bibi as regent.
- In 1596, Chand Bibi successfully repelled a Mughal attack, but after she died in 1600, Murtaza Shah II was declared the sultan.
- The capital was initially moved to Junnar and later to a new city called Khadki, which eventually became Aurangabad.
- The Sultanate ultimately fell in 1636 when Aurangzeb, the Mughal viceroy of the Deccan, overthrew the Ahmednagar Sultanate.
Deccan Sultanates Bijapur Sultanate
Bijapur Sultanate, ruled by the Adil Shahi dynasty from 1490 to 1686, was located in southwestern India, between the Western Ghats of Maharashtra and Karnataka. Yusuf Adil Shah, who initially served as a Governor under the Bahmani Sultanate, established an independent Bijapur in 1490.
- The Adil Shahis fought the Vijayanagara Empire and other Deccan Sultanates, securing a key victory in the 1565 Battle of Talikota, which gave them control of the Raichur Doab and later Bidar in 1619.
- However, in the 17th century, the Marathas under Chhatrapati Shivaji captured much of their territory, and the weakened sultanate fell to Aurangzeb in 1686.
Deccan Sultantes Berar Sultanate
Berar Sultanate was founded by Fathullah Imad-ul-Mulk in 1490, a Kannadiga Hindu kidnapped by the Bahmani force. He initially served as a Governor of Berar under the Bahmani Sultanate. He declared independence and founded the Imad Shahi dynasty with Achalpur as the capital. Upon his death in 1504, his son Alauddin Imad Shah succeeded him.
- Alauddin Imad Shah, with help from Bahadur Shah of Gujarat, resisted Ahmednagar's aggression in 1528.
- Darya, the next ruler, initially allied with Bijapur but later supported Ahmednagar against Bijapur.
- After Darya died in 1562, his son Burhan was overthrown by the minister Tufal Khan.
- Ahmednagar consistently attacked Berar and finally annexed it in 1574.
Deccan Sultanates Golconda Sultanate
Golconda Sultanate, also called the Qutb Shahi dynasty, was founded by Sultan Quli Qutb-ul-Mulk, who migrated from Persia to Delhi in the early 16th century. He later served Bahmani Sultan Mohammed Shah I in the Deccan. Following the Bahmani Sultanate's decline, Qutb-ul-Mulk declared independence in 1518, establishing the Qutb Shahi dynasty. The dynasty ruled for 171 years until Mughal emperor Aurangzeb captured Golconda in 1687.
Deccan Sultanates Bidar Sultanate
Bidar Sultanate, the smallest of the five Deccan sultanates, was founded by Qasim Barid I in 1528. a Georgian slave who rose through the ranks of the Bahmani Sultanate. In 1492, he became the de facto ruler of Bahmani, although Sultan Mahmud Shah remained nominally in charge.
- After Mahmud died in 1504, Qasim's son Amir Barid took control, and by 1528, Amir became practically independent when the last Bahmani ruler fled.
- The Bidar Sultanate continued under his son Ali Barid, who participated in the Battle of Talikota until it was annexed by the Bijapur Sultanate in 1619 following the defeat of Amir Barid Shah III.
Deccan Sultanates Architecture
The Deccan Sultanates contributed significantly to cultural development, including literature, art, architecture, and music. The Dakhani language, which developed under the Bahmani rulers, evolved into an independent literary language. It blended Arabic-Persian, Marathi, Kannada, and Telugu, becoming a distinct form of communication in the Deccan region. Over time, this evolved into Dakhani Urdu, setting it apart from North Indian Urdu.
- Deccani Miniature Painting flourished in the Ahmadnagar, Bijapur, and Golconda courts.
- Key Architecture: It includes Charminar, Gol Gumbaz, and other monuments that remain significant.
Ahmednagar Sultanate Architecture
Ahmednagar Sultanate architecture flourished under the Nizam Shahi dynasty. Ahmednagar saw cultural and architectural growth with a Persian influence. Ahmednagar was praised for its grandeur, being compared to cities like Cairo and Baghdad. The significant architectural sites in Ahmednagar include the Farah Bakhsh Bagh, Ahmednagar Fort, Hasht Bihisht Bagh, and Manjarsumbah.
- Malik Ambar built Janjira Fort in 1567 to defend against invasions.
- Farah Bagh, constructed by the Nizam Shahi rulers in 1583, was a royal retreat where Murtaza Nizam Shah spent time and built Lakad Mahal for a Delhi singer.
Bijapur Sultanate Architecture
Bijapur's sultanate architecture flourished under the Adil Shahi dynasty, blending Indo-Islamic and Middle Eastern styles. Yusuf Adil Shah initiated key developments, like dargahs at Gulbarga and the Jama Masjid under Ali I. Moreover, Mohammed Adil Shah's Gol Gumbaz stands as a monumental symbol of Bijapur.
Berar Sultanate Architecture
Berar Sultanate Architecture is attributed to the Imad Shahi dynasty. The Hauz Katora palace, located about 3 kilometres west of Achalpur, is a significant historical structure and the only surviving monument of this dynasty.
Golconda Sultanate Architecture
The Golconda Sultanate's architecture is exemplified by the fortified city of Golconda and the Charminar in Hyderabad, completed in 1591. Other notable structures include the Qutb Shahi tombs, Mecca Masjid, and Toli Masjid. Persian artists at the Golconda court influenced Deccan miniature paintings with works like Anwar-i-Suhayli and Sindbad Namah, which later evolved into the Hyderabad style.
- Literature: Literature in Persian, Telugu, and Dakhani flourished, with Dakhani blending Persian and local elements. Muhammad Quli Qutb Shah, a renowned poet, contributed significantly with works like the Kulliyat, exploring themes of love, nature, and society.
Bidar Sultanate Architecture
The Bidar Sultanate's architecture includes garden tombs, with Ali Barid Shah's tomb (1577) standing out as a domed chamber set in a Persian-style garden. Other notable structures are the Rangin Mahal, known for its intricate decoration, the tomb of Qasim II, and the Kali Masjid. Bidar also became the birthplace of Bidriware, a distinctive metalwork featuring a black zinc alloy inlaid with silver and brass designs.
Deccan Sultanates Decline
Deccan Sultanates decline was driven by internal discord and external pressures, especially after their 1565 victory over Vijayanagara at the Battle of Talikota. Despite initial unity, internal rivalries weakened them, paving the way for their eventual downfall. The rise of the Maratha Empire and the Mughal Empire, particularly under Akbar and Aurangzeb, accelerated this process. Aurangzeb's military campaigns led to the annexation of Bijapur in 1686 and Golconda in 1687.
- In addition to military pressure, the Sultanate's capacity to defend itself against outside challenges was undermined by internal deterioration, including bad governance, high taxes, and economic hardships.
- As the Mughals grew in power, their centralized and more efficient governance overshadowed the decentralized system of the Sultanates, hastening their decline.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Deccan Sultanate FAQs
Q1. When did the Deccan Sultanates emerge?+
Q2. What were the Deccan Sultanates?+
Q3. Who founded the Bijapur Sultanate?+
Q4. What architecture is associated with Golconda?+
Q5. Which Deccan Sultanate is famous for the Gol Gumbaz?+
Tags: quest UPSC Medieval History