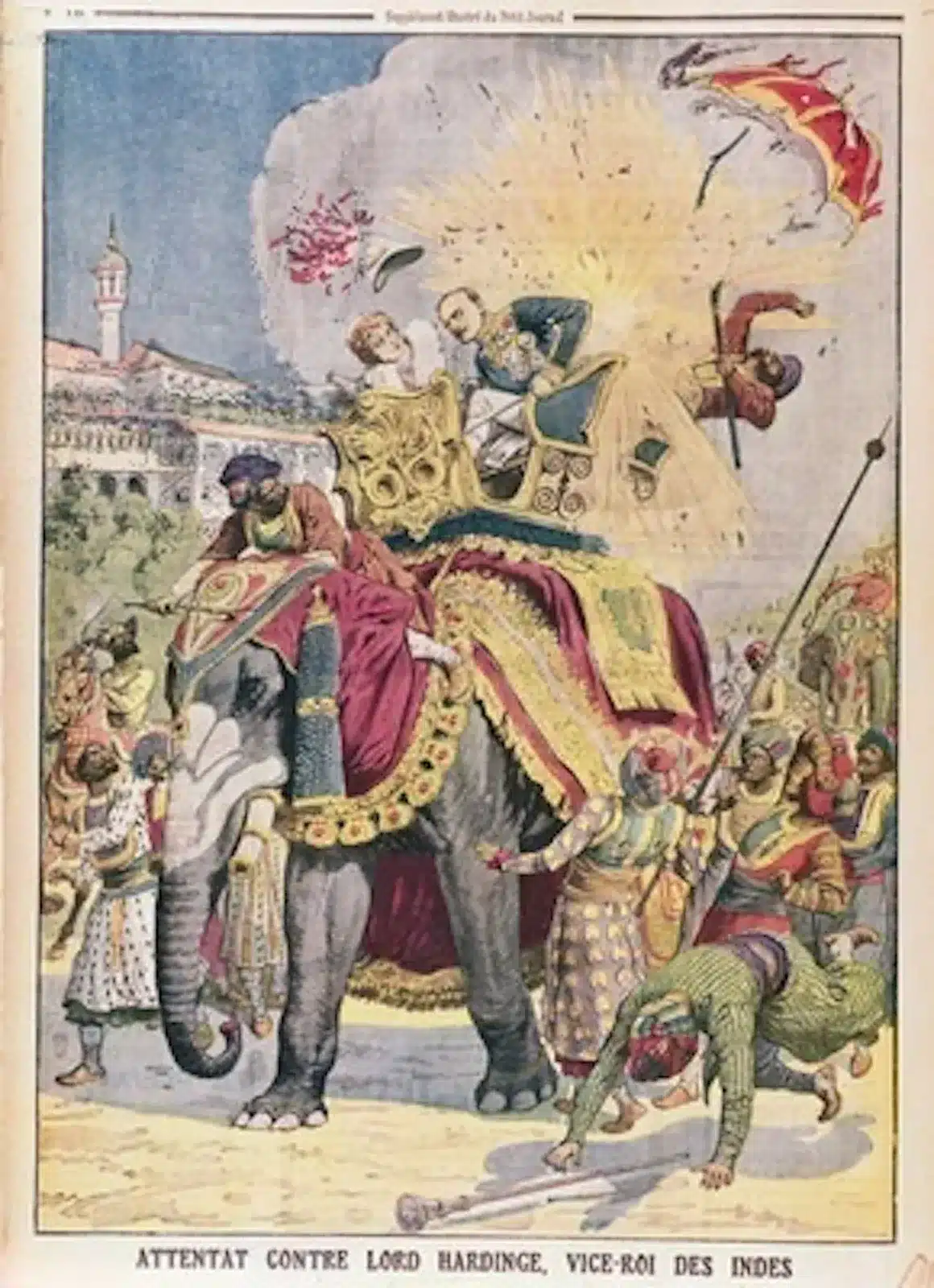
Delhi Conspiracy Case, also known as the Delhi-Lahore Conspiracy Case, was a key event in India's independence history. On December 23, 1912, revolutionary leaders, including Rash Behari Bose and Basant Kumar Biswas, attempted to assassinate Viceroy Lord Hardinge during a procession in Delhi by throwing a bomb. Though Lord Hardinge survived, the attack marked an important act of defiance against British rule.
Delhi Conspiracy Case intensified British repression, particularly in revolutionary hotspots like Punjab and Bengal. It fueled the revolutionary cause, leading to a shift from moderate to militant tactics. The British response involved stricter control, arrests, and executions of key revolutionaries, further fueling the fight for independence.
Delhi Conspiracy Case Overview
Delhi Conspiracy case, also known as the Delhi-Lahore Conspiracy case, involved a group of revolutionaries who intended to overthrow the British Government. This took place on December 23, 1912, when the revolutionaries planned to assassinate the then Viceroy of India, Lord Hardinge, during his procession on an elephant through Chandni Chowk, Delhi.
- Basant Kumar Biswas, one of the revolutionaries, threw a locally made bomb at Viceroy Lord Hardinge. The Viceroy was wounded in the attempt, but his Mahavat (driver and keeper of an elephant) was killed.
Delhi Conspiracy Case Revolutionaries
The Delhi Conspiracy case revolutionaries, including prominent figures such as Rash Behari Bose, Basant Kumar Biswas, Master Amir Chand, and Bhai Balmukund, centred their efforts around an assassination attempt on the then Viceroy of India, Lord Hardinge, in 1912. This event showcased the organized efforts of Indian revolutionaries to challenge colonial power.
- Rash Behari Bose: Bose was vital in the Delhi conspiracy case. He was responsible for planning and coordinating the assassination of Lord Hardinge. After the assassination attempt, Bose managed to escape arrest.
- He took shelter in the Madan Mohan temple and finally escaped to Japan in 1915.
- Basant Kumar Biswas: He had considerable expertise in bomb-making and had undergone training in firearms. In the unsuccessful attempt to assassinate Lord Hardinge, he was the main accused. He threw the bomb at Lord Hardinge.
- He was arrested in February 1914 and hanged in the Central Jail of Ambala in 1915.
- Master Amir Chand: He was a notable worker in the Swadeshi movement. He also became a member of the Ghadar party and came in close contact with Rash Behari Bose, and was active in revolutionary activities in north India.
- He was arrested in 1914 and was hanged in 1915 in the Central Jail of Delhi.
- Bhai Balmukund: He was a Punjabi revolutionary who was active in Delhi. He used print media to spread revolutionary ideas. He learned how to use firearms and make explosives. He was a convict in the Delhi Conspiracy Case and was accused of a bomb blast in Lahore's Lawrence Garden in 1913.
- He was arrested in 1914 and was executed in 1915.
- Avadh Behari: He collaborated with Rash Behari Bose in the Delhi Conspiracy Case. In 1914, he, along with Basant Kumar Vishwas, Amir Chand, and Bal Mukund, was arrested and later executed at Ambala Central Jail in 1915.
Delhi Conspiracy Case Causes
The bomb was thrown at the Viceroy Lord Hardinge at Chandni Chowk, Delhi, to assassinate him while he was making his grand entry into Delhi after transferring the capital of British India from Calcutta to Delhi.
- The shifting of capital was done to reduce the importance of Calcutta, as it was the heart of Indian Nationalism.
- Also, by attacking the highest representative of the British crown in India, the Viceroy would send a clear message that Indians could resist British rule even through violence.
Delhi Conspiracy Case Impact
Delhi Conspiracy Case was a pivotal event that intensified British repression and inspired further revolutionary resistance. It marked a shift towards more militant tactics and highlighted growing discontent with colonial rule, while the British response led to widespread suppression of revolutionaries.
- British repression: In response to the Delhi Conspiracy Case, the British authorities ramped up their efforts to suppress the Revolutionary movement in India, particularly in hotspots like Punjab and Bengal.
- This involved stricter control measures, arrests, and increased surveillance to prevent the spread of anti-colonial sentiment and uprising.
- Discontent with British rule: The conspiracy further highlighted the deepening discontent among Indians toward British rule. The lack of meaningful reforms, coupled with oppressive colonial policies, fueled a strong desire for self-rule and complete independence from British rule in India.
- Revolutionary inspiration: The execution of revolutionaries involved in the case, such as Basant Kumar Das and others, acted as a catalyst for future resistance.
- Their martyrdom became a powerful symbol for the independence movement, encouraging more people to take up the cause of Indian freedom and fight against British rule.
- Radical shift: The case represented a clear shift within the nationalist movement from moderate, constitutional methods to more aggressive and violent tactics.
- Revolutionaries like Rash Behari Bose demonstrated that some factions were ready to overthrow the British government through armed struggle, signalling a new phase in the freedom movement.
Last updated on March, 2026
→ UPSC Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC IFoS Notification 2026 is now out on the official website at upsconline.nic.in.
→ UPSC Calendar 2026 has been released.
→ UPSC Final Result 2025 is expected to be released soon.
→ Check out the latest UPSC Syllabus 2026 here.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Interview Guidance Programme for expert help to crack your final UPSC stage.
→ UPSC Mains Result 2025 is now out.
→ UPSC Prelims 2026 will be conducted on 24th May, 2026 & UPSC Mains 2026 will be conducted on 21st August 2026.
→ The UPSC Selection Process is of 3 stages-Prelims, Mains and Interview.
→ Prepare effectively with Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Prelims Test Series 2026 featuring full-length mock tests, detailed solutions, and performance analysis.
→ Enroll in Vajiram & Ravi’s UPSC Mains Test Series 2026 for structured answer writing practice, expert evaluation, and exam-oriented feedback.
→ Join Vajiram & Ravi’s Best UPSC Mentorship Program for personalized guidance, strategy planning, and one-to-one support from experienced mentors.
→ Check UPSC Marksheet 2024 Here.
→ UPSC Toppers List 2024 is released now. Shakti Dubey is UPSC AIR 1 2024 Topper.
→ Also check Best UPSC Coaching in India
Delhi Conspiracy Case FAQs
Q1. What was the Delhi conspiracy case?+
Q2. Who were the revolutionaries involved in the Delhi conspiracy case?+
Q3. Who was the target of the bomb thrown in Delhi in 1912?+
Q4. What was the cause of the Delhi conspiracy case?+
Q5. Which revolutionaries were convicted in the Delhi conspiracy case?+